北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (5): 990-994. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.05.030
牙周健康的上颌前牙唇侧嵴顶上牙龈的三维形态分析
- 北京大学口腔医学院·口腔医院, 1.牙周科,北京 100081
2.放射科 国家口腔医学中心 国家口腔疾病临床医学研究中心 口腔数字化医疗技术和材料国家工程实验室,北京 100081
Three-dimensional morphology analysis of the supraosseous gingival profile of periodontally healthy maxillary anterior teeth
YANG Gang1,HU Wen-jie1,△( ),CAO Jie1,LIU Deng-gao2
),CAO Jie1,LIU Deng-gao2
- 1. Department of Periodontology, Beijing 100081, China
2. Department of Radiology, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
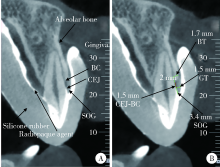
目的: 利用锥形束体层摄影术(cone-beam computed tomography,CBCT)分析牙周健康的汉族青年上颌前牙唇侧中央嵴顶上牙龈(supraosseous gingiva,SOG)的三维形态及相关解剖结构。方法: 选取25名牙周健康的汉族青年共计150颗上颌前牙纳入研究,受试者男性11名,女性14名,平均年龄(24.5±1.6)岁,佩戴含有显影剂的硅橡胶印模拍摄软组织间接显影CBCT。对影像资料进行三维重建并测量分析唇侧中央嵴顶上牙龈的形态,包括SOG高度、釉牙骨质界(cemento-enamel junction,CEJ)到骨嵴顶的距离、CEJ处牙龈厚度、骨嵴顶下2 mm牙槽骨厚度等。数据用SPSS 22.0软件进行统计分析,比较各牙位参数之间的差异,分析其相互之间的相关关系。结果: 上颌前牙唇侧中央SOG高度测量结果,中切牙为(3.54±0.67) mm、侧切牙为(3.48±0.81) mm、尖牙为(3.49±0.70) mm,各牙位SOG高度差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。上颌前牙唇侧中央CEJ水平牙龈平均厚度测量结果,中切牙为(1.45±0.23) mm,侧切牙为(1.13±0.24) mm,尖牙为(1.14±0.22) mm,中切牙牙龈最厚,与侧切牙和尖牙相比差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。唇侧中央SOG与CEJ处牙龈厚度在所有牙位上均无明显相关性(P>0.05)。结论: 牙周健康的上颌前牙唇侧嵴顶上牙龈中,中切牙牙龈最厚,未发现上颌前牙区唇侧中央SOG高度与厚度存在相关性。
中图分类号:
- R783
| [1] |
Arora R, Narula S, Sharma R, et al. Supracrestal gingival tissue: Assessing relation with periodontal biotypes in a healthy periodon-tium [J]. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent, 2013, 33(6):763-771.
doi: 10.11607/prd.1501 |
| [2] |
Perez JR, Smukler H, Nunn M E. Clinical evaluation of the supraosseous gingivae before and after crown lengthening [J]. J Periodontol, 2007, 78(6):1023-1030.
pmid: 17539715 |
| [3] |
Gargiulo AW, Wentz FM, Orban B. Dimensions and relations of the dentogingival junction in humans [J]. J Periodontol, 1961, 32(3):261-267.
doi: 10.1902/jop.1961.32.3.261 |
| [4] |
Kois JC. Altering gingival levels: The restorative connection part I: Biologic variables [J]. J Esthet Restor Dent, 1994, 6(1):3-7.
doi: 10.1111/j.1708-8240.1994.tb00825.x |
| [5] | Vacek JS, Gher ME, Assad DA, et al. The dimensions of the human dentogingival junction [J]. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent, 1994, 14(2):154-165. |
| [6] |
Fischer KR, Grill E, Jockel-Schneider Y, et al. On the relationship between gingival biotypes and supracrestal gingival height, crown form and papilla height [J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2014, 25(8):894-898.
doi: 10.1111/clr.2014.25.issue-8 |
| [7] | 乐迪, 张豪, 胡文杰, 等. 牙周探诊法判断牙龈生物型的初步研究 [J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2012, 47(2):81-84. |
| [8] | 曹洁, 胡文杰, 张豪, 等. 基于锥形束计算机体层摄影术测量牙龈厚度 [J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2013, 45(1):135-139. |
| [9] | 张艳玲, 张豪, 胡文杰, 等. 120名汉族青年前段牙弓唇侧角化龈宽度的测量 [J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2010, 45(8):477-481. |
| [10] |
Zhang YL, Le D, Hu WJ, et al. Assessment of dynamic smile and gingival contour in young Chinese people [J]. Int Dent J, 2015, 65(4):182-187.
doi: 10.1111/idj.12174 |
| [11] |
Perez JR, Smukler H, Nunn ME. Clinical dimensions of the supraosseous gingivae in healthy periodontium [J]. J Periodontol, 2008, 79(12):2267-2272.
doi: 10.1902/jop.2008.080101 pmid: 19053916 |
| [12] |
Cao J, Hu WJ, Zhang H, et al. A novel technique for measurement of dentogingival tissue by cone beam computed tomography [J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol, 2015, 119(2):e82-e87.
doi: 10.1016/j.oooo.2014.10.022 |
| [13] |
Alves PHM, Alves TCLP, Pegoraro TA, et al. Measurement pro-perties of gingival biotype evaluation methods [J]. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res, 2018, 20(3):280-284.
doi: 10.1111/cid.2018.20.issue-3 |
| [14] |
Hausmann E, Allen K, Clerehugh V. What alveolar crest level on a bite-wing radiograph represents bone loss? [J]. J Periodontol, 1991, 62(9):570-572.
pmid: 1941497 |
| [15] |
Ghassemian M, Nowzari H, Lajolo C, et al. The thickness of facial alveolar bone overlying healthy maxillary anterior teeth [J]. J Periodontol, 2012, 83(2):187-197.
doi: 10.1902/jop.2011.110172 pmid: 21692627 |
| [16] |
Nowzari H, Molayem S, Chiu CH, et al. Cone beam computed tomographic measurement of maxillary central incisors to determine prevalence of facial alveolar bone width ≥2 mm [J]. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res, 2012, 14(4):595-601.
doi: 10.1111/cid.2012.14.issue-4 |
| [17] |
Taylor R. Interpretation of the correlation coefficient: A basic review [J]. J Diagn Med Sonogr, 1990, 6(1):35-39.
doi: 10.1177/875647939000600106 |
| [18] | Kao RT, Fagan MC, Conte GJ. Thick vs thin gingival biotypes: A key determinant in treatment planning for dental implants [J]. J Calif Dent Assoc, 2008, 36(3):193-198. |
| [19] |
Müller HP, Könönen E. Variance components of gingival thickness [J]. J Periodontal Res, 2005, 40(3):239-244
pmid: 15853970 |
| [20] |
Fu JH, Yeh CY, Chan HL, et al. Tissue biotype and its relation to the underlying bone morphology [J]. J Periodontol, 2010, 81(4):569-574.
doi: 10.1902/jop.2009.090591 |
| [21] |
La Rocca AP, Alemany AS, Levi P Jr. Anterior maxillary and mandibular biotype: Relationship between gingival thickness and width with respect to underlying bone thickness [J]. Implant Dent, 2012, 21(6):507-515.
doi: 10.1097/ID.0b013e318271d487 |
| [22] | Frumkin N, Via S, Klinger A. Evaluation of the width of the alveolar bone in subjects with different gingival biotypes: A prospective cohort study using cone beam computed tomography [J]. Quintessence Int, 2017, 48(3):209-216. |
| [23] | Cook DR, Mealey BL, Verrett RG, et al. Relationship between clinical periodontal biotype and labial plate thickness: An in vivo study [J]. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent, 2011, 31(4):345-354. |
| [24] |
Batista EL, Moreira CC, Batista FC, et al. Altered passive eruption diagnosis and treatment: A cone beam computed tomography-based reappraisal of the condition [J]. J Clin Periodontol, 2012, 39(11):1089-1096.
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2012.01940.x pmid: 22966787 |
| [1] | 刘思民,赵一姣,王晓燕,王祖华. 动态导航下不同深度环钻定位精确度的体外评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 146-152. |
| [2] | 邱淑婷,朱玉佳,王时敏,王飞龙,叶红强,赵一姣,刘云松,王勇,周永胜. 姿势微笑位口唇对称参考平面的数字化构建及初步应用验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 193-199. |
| [3] | 袁临天,马利沙,刘润园,齐伟,张栌丹,王贵燕,王宇光. 计算机模拟亚甲基蓝与牙龈卟啉单胞菌部分蛋白的分子对接[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(1): 23-30. |
| [4] | 任国勇,吴雪梅,李颖,李婕妤,孙伟平,黄一宁. 大血管闭塞性脑卒中亚急性期磁敏感血管征的表现[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(6): 1133-1138. |
| [5] | 李媛,林红,张铁军. 对比传统成像与数字成像对牙科复合树脂X射线阻射性的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(5): 995-1001. |
| [6] | 邵振兴,宋庆法,赵宇晴,崔国庆. 一种结合线袢固定的关节镜下“嵌入式”喙突移位术:手术技术及术后影像学分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(5): 896-901. |
| [7] | 吴一凡,张晓圆,任爽,玉应香,常翠青. 基于磁共振的青年男性股四头肌的测量和评估[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(5): 843-849. |
| [8] | 郜洪宇,孟焕新,侯建霞,黄宝鑫,李玮. 钙结合蛋白在健康牙周组织和实验性牙周炎组织的表达分布[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(4): 744-749. |
| [9] | 李新飞, 彭意吉, 余霄腾, 熊盛炜, 程嗣达, 丁光璞, 杨昆霖, 唐琦, 米悦, 吴静云, 张鹏, 谢家馨, 郝瀚, 王鹤, 邱建星, 杨建, 李学松, 周利群. 肾部分切除术前CT三维可视化评估标准的初步探究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(3): 613-622. |
| [10] | 胡迪,张苗,康惠颖,彭芸. 0~2岁婴幼儿磁共振脑白质模板的建立及验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(2): 341-347. |
| [11] | 陈迪,徐翔宇,汪明睿,李芮,臧根奥,张悦,钱浩楠,闫光荣,范田园. 熔融沉积成型3D打印盐酸维拉帕米胃漂浮制剂的制备与体外评价[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(2): 348-354. |
| [12] | 黄新瑞,李莎,高嵩. 冷冻电镜成像中噪声的滤波方法进展[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(2): 425-433. |
| [13] | 穆海丽,田福聪,王晓燕,高学军. 玻璃体和通用型复合树脂耐磨性的临床对照研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(1): 120-125. |
| [14] | 高璐,谷岩. 中国人群腭中缝形态特点分期与Demirjian牙龄的相关性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(1): 133-138. |
| [15] | 岳兆国,张海东,杨静文,侯建霞. 数字化评估CAD/CAM个性化基台与成品基台影响粘接剂残留的体外研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(1): 69-75. |
|