Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (1): 43-48. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.01.008
Previous Articles Next Articles
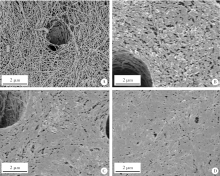
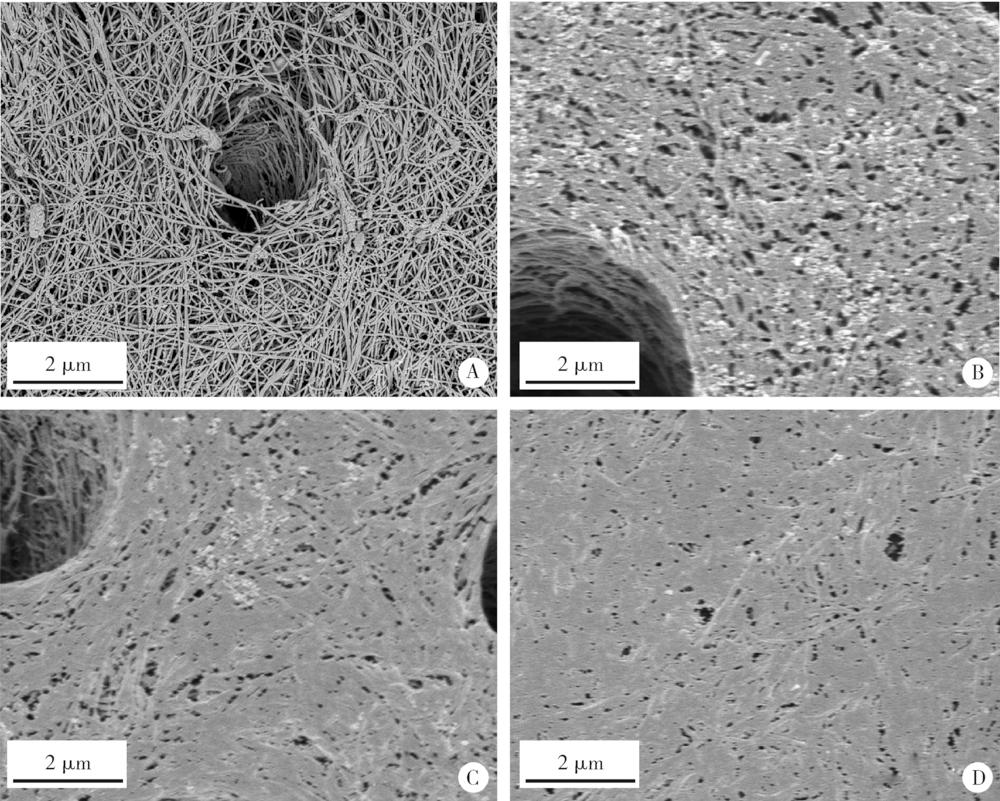
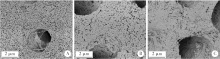
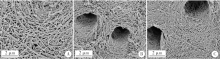
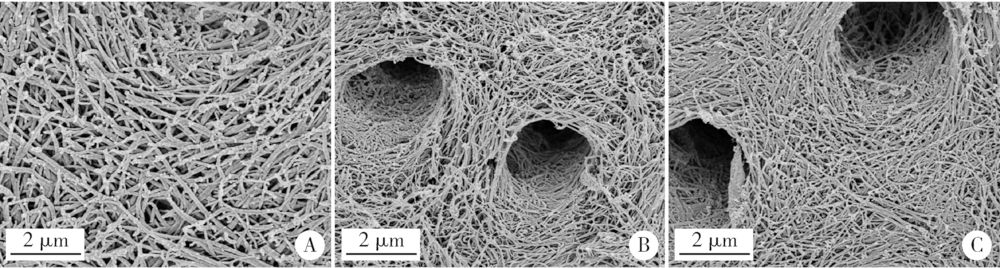
Effect of a novel cold atmospheric plasma jet treatment with different temperatures on resin-dentin bonding
Xiao-ming ZHU1,Xuan QI2,De-li LI1,Yu-wei ZHANG3,He-ping LI4,Jian-guo TAN2,△( )
)
- 1. Second Clinical Division, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100101, China
2. Department of Prosthodontics, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
3. Department of Stomatology, Aerospace Center Hospital, Beijing 100049, China
4. Department of Engineering Physics, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
CLC Number:
- R783.4
| [1] |
Liu Y, Liu Q, Yu QS , et al. Nonthermalatmospheric plasmas in dental restoration[J]. J Dent Res, 2016,95(5):496-505.
doi: 10.1177/0022034516629425 pmid: 26848068 |
| [2] | 熊青 . 大气压低温等离子体射流的研究[D]. 湖北: 华中科技大学, 2013. |
| [3] |
Lehmann A, Rueppell André, Schindler A , et al. Modification ofenamel and dentin surfaces by non-thermal atmospheric plasma[J]. Plasma Processe Polymer, 2013,10(3):262-270.
doi: 10.1002/ppap.201200088 |
| [4] |
Zhu XM, Zhou JF, Guo H , et al. Effects of a modified cold atmospheric plasma jet treatment on resin-dentin bonding[J]. Dent Mater J, 2018,37(5):798-804.
doi: 10.4012/dmj.2017-314 pmid: 29962414 |
| [5] |
Eick JD, Robinson SJ, Chappell RP , et al. The dentinal surface: its influence on dentinal adhesion. Part Ⅲ[J]. Quintessence Int, 1993,24(8):571.
pmid: 1813914 |
| [6] |
Pashley DH, Tay FR, Breschi L , et al. State of the art etch-and-rinse adhesives[J]. Dent Mater, 2011,27(1):1-16.
doi: 10.1016/j.dental.2010.10.016 pmid: 21112620 |
| [7] |
Hwang YJ, Lyubovitsky JG . The structural analysis of three-dimensional fibrous collagen hydrogels by raman microspectroscopy[J]. Biopolymers, 2013,99(6):349-356.
doi: 10.1002/bip.22183 pmid: 23529687 |
| [8] |
Steven R, Armstrong JL, Erik W , et al. Effects of polar solvents and adhesive resin on the denaturation temperatures of demine-ralised dentine matrices[J]. J Dent, 2008,36(1):8-14.
doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2007.10.003 pmid: 2909542 |
| [9] |
Chen M, Zhang Y, Dusevich V , et al. Non-thermal atmospheric plasma brush induces HEMA grafting onto dentin collagen[J]. Dent Mater, 2014,30(12):1369-1377.
doi: 10.1016/j.dental.2014.10.004 pmid: 25458523 |
| [10] |
Choi JH, Lee ES, Hong KB , et al. Surface modification of natural leather using low-pressure parallel plate plasma[J]. Surf Coat Tech, 2003,171(1/2/3):257-263.
doi: 10.1016/S0257-8972(03)00282-2 |
| [11] |
Zhu XM, Guo H, Zhou JF , et al. Influences of the cold atmospheric plasma jet treatment on the properties of the demineralized dentin surfaces[J]. Plasma Sci Technol, 2018,20(4):044010.
doi: 10.1088/2058-6272/aaa6be |
| [12] | Gwinnett AJ . Quantitative contribution of resin infiltration/hybri-dization to dentin bonding[J]. Am J Dent, 1993,6(1):7-9. |
| [13] |
Pashley DH, Carvalho RM . Dentine permeability and dentine adhesion[J]. J Dent, 1997,25(5):355.
doi: 10.1016/S0300-5712(96)00057-7 pmid: 9241954 |
| [1] | MA Xin-rong,ZHU Xiao-ming,LI Jing,LI De-li,LI He-ping,TAN Jian-guo. Effect of a novel radio-frequency atmospheric-pressure glow discharge plasma jet treatment on crosslinking of dentin collagen [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(1): 83-88. |
| [2] | DU Qiang,HONG Kai,PAN Bo-chen. Comparison of two methods for detection of Chlamydia trachomatis and Ureaplasma urealyticum in male reproductive tract [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(4): 785-788. |
| [3] | SHI Mao-jing,GAO Wei-bo,HUANG Wen-feng,ZHU Ji-hong. Clinical analysis of 61 patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(1): 210-214. |
| [4] | Mei-qing ZHU,Rong CUI. Determination of UV-327 and UV-328 in mouse plasma by high performance liquid chromatography [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(3): 591-596. |
| [5] | Zhao-nian WANG,Wen-jing GAO,Bi-qi WANG,Wei-hua CAO,Jun LV,Can-qing YU,Zeng-chang PANG,Li-ming CONG,Hua WANG,Xian-ping WU,Yu LIU,Li-ming LI. Correlation between fasting plasma glucose, HbA1c and DNA methylation in adult twins [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(3): 425-431. |
| [6] | Miao ZHENG,Ling-lu ZHAN,Zhi-qiang LIU,He-ping LI,Jian-guo TAN. Effect of different plasma treated zirconia on the adhensive behaviour of human gingival fibroblasts [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(2): 315-320. |
| [7] | WU Tian-wei, CUI Rong, ZHANG Bao-xu. Determination of 8-methoxypsoralen in mouse plasma by high performance liquid chromatography and its application to pharmacokinetic study [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(5): 792-796. |
| [8] | ZHANG Si, LI Wen-hai, ZHAO Yan, CAI Lin. A case report of cutaneous plasmacytosis [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(4): 752-754. |
| [9] | LIAO Yu, LIU Xiao-qiang, CHEN Li, ZHOU Jian-feng, TAN Jian-guo. Effects of different surface treatments on the zirconia-resin cement bond strength [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(1): 53-57. |
| [10] | FENG Yong-liang, FAN Jing-hui, LIN Xian-juan, YANG Ji-chun, CUI Qing-hua, TANG Xin-jing, XU Guo-heng, GENG Bin. Facilitating the measurement of circulatory hydrogen sulfide with fluorescence probe-coated microplates [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(6): 1060-1065. |
| [11] | ZHU Meng-meng, WANG Guo-min, SUN Ke, LI Ying-long, PAN Jie. Bonding strength of resin and tooth enamel after teeth bleaching with cold plasma [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2016, 48(1): 116-120. |
| [12] | ZHANG Jing, REN Jing-yi, CHEN Hong, HAN Guan-ping. Statins decreases expression of five inflammation-associated microRNAs in the plasma of patients with unstable angina [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2015, 47(5): 761-768. |
| [13] | PENG Rong, WEI Xiao-Ping, LIANG Xiao-Hua, CHEN Jie, LIU You-Xue, ZHANG Ting, LI Ting-Yu- . Effect of dietary vitamin A intake on plasma vitamin A concentration in preschool children of Banan district, Chongqing, China [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2014, 46(3): 366-372. |
| [14] | CHEN Zhi-bin , LIN Qin , MA Chang-hua , LIU Kai-ning, MENG Huan-xin. Characteristic of sample banks isolated from EDTA-blood by sedimentation method [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2014, 46(1): 111-114. |
|