目的 探讨人肾小球系膜细胞(human mesangial cells,HMCs)中是否表达免疫球蛋白A(immunoglobulin A,IgA)。方法 培养人HMCs细胞系,以免疫荧光染色检测Ig α、Ig κ、Ig λ在系膜细胞中的表达;以反转录聚合酶链式反应(reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, RT-PCR)和DNA测序检测HMCs中Ig α、Ig κ、Ig λ恒定区转录本表达;以Western blot方法检测细胞裂解液及培养上清液中Ig α、Ig κ、Ig λ蛋白水平表达;以jacalin为配体的亲和层析纯化上清液蛋白质,以蛋白质谱检测纯化的蛋白氨基酸序列。结果 免疫荧光染色检测到HMCs细胞浆Ig α、 Ig κ、 Ig λ的阳性表达;RT-PCR检测到细胞内Ig α1、Ig α2重链、Ig κ轻链、Ig λ轻链恒定区转录本表达,且其核苷酸序列与美国国立生物技术信息中心(National Center of Biotechnology Information, NCBI)数据库相应的mRNA序列比对,同源性分别达到99%、97%、98%和97%;Western blot检测到细胞内Ig α1、Ig α2和Ig λ蛋白水平的表达,Ig κ目前检测为阴性;细胞上清液中可见完整IgA分子表达;以jacallin为配体亲和层析纯化的培养上清液中的IgA,蛋白质谱测序所得的氨基酸片段序列与NCBI数据库比对,显示HMCs分泌的蛋白质与B细胞表达的Ig α1恒定区52~104之间53个氨基酸、154~221之间68个氨基酸、以及276~327之间52个氨基酸的序列完全相同,与Ig α2重链恒定区52~113之间62个氨基酸、151~204之间54个氨基酸、以及251~314之间64个氨基酸的序列完全相同,提示系膜细胞可以将合成的IgA分泌到胞外。结论 HMCs可能合成并分泌IgA。
Objective: To investigate the expression of immunoglobulin A (IgA) in human mesangial cells (HMCs).Methods: The HMCs were cultured. The subcellular location of IgA was detected by immunofluorescence staining; the transcripts of Ig α,Ig κ and Ig λ constant region were detected by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and further analyzed by DNA sequencing. The expressions of Ig α and Ig λ were detected at transcription level by Western blot after the cytoplasmic protein extraction. The culture supernatant was collected to explore whether IgA could be secreted out of the cell and the protein was further analyzed by mass spectrometry after being purified by affinity chromato-graphy with jacalin-sepharose. The results of DNA sequencing and mass spectrometry were aligned with the mRNA and amino acid sequences in the National Center of Biotechnology Information (NCBI) database.Results: By immunofluorescence staining, we detected the presence of IgA heavy chain Ig α, light chain, both Ig κ and Ig λ in expressions of transcripts of Ig α1, Ig α2, Ig κ and Ig λ in the HMCs and the alignment of the sequences of the RT-PCR products with those of the Ig Cα1, Ig Cα2, Ig κ and Ig λ mRNA in the NCBI database exhibited that the similarities were 99%, 97%, 98% and 97%, respectively. Western blot showed Ig α and Ig λ expressions in the cell lysate and secretion of Ig α1 and Ig α2 heavy chains in cell culture supernatant. To further explore the protein that secreted into the supernatant, after supernatant affinity chromatography with jacalin-sepharose, the proteins were separated by sodium dodecyl sulfonate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and the band approximating to 65 000 was cut and sent to mass spectrometry. The results were aligned with the amino acid sequences of Ig α1 and Ig α2 constant region in NCBI database, showing that amino acids between No.52 and No.104, amino acids between No.154 and No.221, amino acids between No.276 and No.327 from Ig Cα1 and amino acids between No.52 and No.113, amino acids between No.151 and No.204, amino acids between No.251 and No.314 from Ig Cα2 were the same with those derived from B cells.Conclusion: Our fin-dings suggested that HMCs could synthesize and secret IgA.
近20年越来越多的证据表明肿瘤细胞、正常细胞具有包括免疫球蛋白A(immunoglobulin A, IgA)在内的免疫球蛋白(immunoglobulin, Ig)基因V(D)J重排和转录以及蛋白质表达[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]。肿瘤来源的Ig与肿瘤细胞的生长、增殖、转化、迁移等密切相关[8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15], 正常细胞表达的Ig参与细胞正常生长、增殖甚至细胞骨架结构, 受到致病原或者炎症因子的调控[16]。本研究通过一系列实验方法从蛋白质和核酸水平在体外培养的人肾小球系膜细胞(human mesangial cells, HMCs)中探讨IgA的表达。
实验所用细胞系为T-SV40病毒永生化的HMCs。用含10%(体积分数)胎牛血清(fetal bovine serum, FBS)、1%(体积分数)青霉素、1%(体积分数)链霉素、1%(体积分数)胰岛素-转铁蛋白-硒添加剂(insulin-transferrin-selenium-A supplement, ITS-A)的洛斯维· 帕克纪念研究所(Roswell Park Memorial Institute, RPMI)-1640完全培养基培养, 于37 ℃恒温、5%(体积分数)CO2细胞培养箱中培养。HMCs每两天传代一次, 传代时放入细胞爬片, 待细胞长至50%~60%, 更换为含2%(体积分数)FBS的完全培养基, 待细胞长至80%~90%收集细胞爬片、细胞、细胞上清液进行实验。
RPMI-1640培养基、ITS-A添加剂、10 000 IU/mL青霉素、10 g/L链霉素、0.25%(体积分数)胰酶细胞消化液、Trizol购自美国Gibico公司, 胎牛血清购自澳大利亚Bioind公司, DAPI(C0060-1)和抗荧光衰减封片剂购自北京索莱宝公司, 逆转录试剂盒(K1622)购自美国Thermo公司, PCR试剂盒(MT201-1)购自北京博迈德公司, jacalin凝胶(6561-5)购自美国Biovision公司, 琼脂糖(91622)购自西班牙Biowest公司。用于免疫荧光染色的抗体:抗人Ig α -异硫氰酸荧光素(fluorescein isothiocyanate, FITC)抗体(ZA-0446)和山羊抗鼠-FITC二抗(ZF-0312)购自北京中杉金桥公司, 鼠抗人Ig κ 抗体(GK-1105)和鼠抗人Ig λ 抗体(GL-1207)购自北京西雅金桥公司; 用于Western blot的抗体:兔抗人Ig α 抗体(ab124716)、鼠抗人Ig α 1抗体(ab128791)、鼠抗人Ig α 2抗体(ab88250)、兔抗人Ig κ 抗体(ab124727)和兔抗人Ig λ 抗体(ab124719)购自美国Abcam公司。细胞爬片购自美国Nest公司, 相对分子质量50 000超滤离心管购自美国Millipore公司。
细胞爬片用预冷的丙酮固定5 min, 磷酸盐缓冲液(phosphate buffered saline, PBS)清洗3次, 用PBS配制的5%(质量分数)牛血清白蛋白(bovine serum albumin, BSA)室温封闭30 min; 倾去封闭液, 分别滴加抗人Ig α -FITC抗体(1 ∶ 50体积比稀释), 鼠抗人Ig κ 抗体(1 ∶ 25体积比稀释)、鼠抗人Ig λ 抗体(1 ∶ 25体积比稀释), 以PBS代替一抗作为阴性对照; 爬片放于湿盒, 4 ℃避光孵育过夜; 次日用PBS清洗爬片3次, 去除残余抗体, 抗人Ig α 组直接滴加10 mg/L 的4’ , 6-二脒基-2-苯基吲哚(4’ , 6-diamidino-2-phenylindole, DAPI), 常温避光染色2 min, 用抗荧光淬灭封片剂封片后以荧光显微镜观察结果; 而抗Ig κ 和抗Ig λ 组则滴加 FITC标记的山羊抗鼠二抗(1 ∶ 80体积比稀释)室温避光孵育1 h, 之后PBS清洗3次, 滴加DAPI, 观察荧光。
在1× 105个细胞中加入1 mL Trizol, 提取全细胞RNA, 测定浓度后取1.5 μ g进行逆转录, cDNA用无RNA酶水按1 ∶ 5稀释后, 取2 μ L作为模板进行PCR反应, 反应体系按试剂盒要求配制。分离人外周血单个核细胞(peripheral blood mononuclear cells, PBMC)进行RNA提取及后续RT-PCR作为阳性对照, 以水代替模板作为阴性对照。Ig α 恒定区(Ig α constant region, Ig Cα )上游引物序列为5'-ACCATGCAGGAGAAGGTGTC-3', 下游引物序列为5'-TCACTTGCACTGCTGCCTAC-3'(340 bp); Ig κ 恒定区(Ig Cκ )上游引物序列为5'-TGAGCAAAGCAGACTACGAGA-3', 下游引物序列为5'-GGGGTGAGGTGAAAGATGAG-3'(231 bp); Ig λ 恒定区(Ig Cλ )上游引物为5'-GGGACCAAGCTCACCGTCCTAG-3', 下游引物为5'-TCTTCTCCACGGTGCTCCCTTC-3'(316 bp), 退火温度分别为62 ℃、50 ℃、56 ℃ 30 s, 进行35个循环。
按每1× 106个HMCs加入80 μ L 细胞裂解液[1%(质量分数)的十二烷基硫酸钠, 5 mmol/L 二硫苏糖醇, 50 mmol/L Tris-HCl (pH 7.5)], 提取细胞胞浆蛋白, 加入5× 蛋白上样缓冲液后, 100 ℃煮沸 5 min, 备用。收集的细胞培养上清液用硫酸铵(313 g/L)沉淀, 4 ℃过夜, 经12 000 r/min, 4 ℃离心15 min, 弃去上清液; 沉淀蛋白加入500 μ L PBS溶解, 经超滤离心管脱盐后, 加入5× 蛋白上样缓冲液, 100 ℃煮沸5 min, 备用。进行十二烷基硫酸钠-聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳(sodium dodecyl sulfonate- polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, SDS-PAGE)时, 配制10%(质量分数)的分离胶。样品以正常人血清蛋白作为阳性对照。上样后以80 V电泳2.5 h, 以100 V恒压转膜1.5 h后经5%(质量分数)脱脂奶粉室温封闭2.5 h, 分别加入兔抗人Ig α (1 ∶ 1 000)、鼠抗人Ig α 1(1 ∶ 750)、鼠抗人Ig α 2(1 ∶ 800)、兔抗人Ig κ (1 ∶ 7 500)、兔抗人Ig λ (1 ∶ 50 000), 4 ℃孵育过夜。TBST洗膜3次, 每次10 min; 室温避光孵育相应的荧光二抗1 h, TBST洗膜3次后, 用Odyssey红外荧光扫描成像系统成像。
细胞培养上清液的处理同第1.5小节方法所述, 用硫酸铵(313 g/L)沉淀并进行脱盐之后, 用PBS稀释到500 μ L, 留取50 μ L为柱前液, 亲和层析操作按照jacalin-凝胶(6565-5, Biovison)说明书进行, 经亲和层析纯化细胞上清液后收集洗脱液, 洗脱液经超滤离心管脱盐浓缩后, 柱前液和洗脱液加入5× 蛋白质上样缓冲液和二硫苏糖醇, 100 ℃煮沸5 min, 进行SDS-PAGE。凝胶经固定液固定3 h, 考马斯亮蓝染液染色40 min, 脱色液脱色后, 切取与Western blot显色位置相同的条带送与北京华大蛋白质研发中心进行蛋白质谱检测。
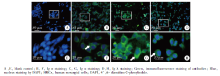
首先对细胞爬片进行IgA检测, 使用抗人Ig α 、Ig κ 、Ig λ 抗体进行免疫荧光染色, 结果显示HMCs细胞胞浆呈现Ig α 、Ig κ 、Ig λ 阳性表达(图1)。
为了探究HMCs中IgA基因转录, 本研究采用能够识别Ig α 、Ig κ 、Ig λ mRNA恒定区的引物进行RT-PCR, 以PBMC mRNA作为阳性对照, 得到Ig α 、Ig κ 、Ig λ 恒定区片段(图2A)。对目的片段进行核苷酸测序, 并将测序结果与NCBI数据库中Ig Cα 1 mRNA序列(GenBank:BC016369.1)、Ig Cα 2 mRNA序列(GenBank:BC073765.1), Ig Cκ mRNA序列(GenBank:Y14736.1)和Ig Cλ mRNA序列(GenBank:X57823.1)进行比对, 显示同源性分别为99%, 97%, 99%和97%(图2B~E), 提示IgA的转录本在HMCs与B细胞中高度同源。
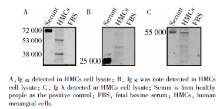
采用还原性Western blot检测HMCs细胞内IgA的表达, 用正常人血清作为阳性对照, 细胞裂解液为实验组, 为了排除HMCs吞噬或者结合FBS中可能存在的IgA的可能性, 同时检测FBS, 结果发现兔抗人Ig α 、兔抗人Ig κ 、兔抗人Ig λ 3种单克隆抗体分别在人血清中检测出与Ig α 、Ig κ 、Ig λ 相对分子质量大致相同的阳性条带, 在FBS均未检测出相对应的蛋白质条带。在HMCs裂解液, Ig α 显示2个阳性蛋白条带, 相对分子质量分别为53 000与38 000, 与抗体说明书参考条带位置一致; 兔抗人Ig λ 阳性条带出现于55 000处, 与说明书25 000不同, 根据相对分子质量及轻链的特点推测可能为Ig λ 的二聚体形式。兔抗人Ig κ 抗体检测到的阳性条带不明显, 结果如图3。
为了检测HMCs合成的IgA是否可以分泌到细胞上清液, 我们收集细胞上清液进行硫酸铵沉淀和超滤浓缩, 进行非还原性Western blot检测, 结果显示上清液在位于160 000处出现阳性条带, 与完整IgA分子大致相同, 如图4A。 Jacalin亲和层析所得洗脱液进行还原性Western blot, 结果显示在65 000处出现阳性Ig α 条带, 如图4B。将免疫印迹对应的SDS-PAGE目的条带(图4C)切下, 送至北京华大蛋白质研究中心进行蛋白质谱检测, 所得氨基酸片段序列与NBCI数据库比对, 显示与B细胞表达的Ig α 1恒定区52~104之间53个氨基酸、154~221之间68个氨基酸、以及276~327之间52个氨基酸的序列完全相同, 与Ig α 2重链恒定区52~113之间62个氨基酸、151~204之间57个氨基酸、以及251~314之间64个氨基酸的序列完全相同, 如图5。
IgA肾病( immunoglobulin A nephropathy, IgAN)病理特征是肾小球系膜区IgA沉积, 系膜细胞增生, 系膜基质增加。目前普遍认为发病的中心环节是患者B细胞产生的半乳糖缺乏的IgA1和IgG形成循环免疫复合物沉积于肾小球系膜区[17, 18], 激发免疫炎症反应, 导致系膜细胞增生并分泌炎症硬化因子[19, 20, 21]。然而, 这个学说难以回答许多基础和临床问题, 如为何多数IgAN患者血液中IgA水平不高?为何检测不到免疫复合物?皮肤黏膜感染诱发的IgAN仅仅只有2~3 d潜伏期, 如此短时间内、如此大分子的免疫复合物如何从血液中进入系膜区?
经典的免疫学理论认为成熟的B淋巴细胞或者浆细胞是合成和分泌免疫球蛋白的唯一来源, 近20年来, 一系列研究报道[22, 23, 24, 25, 26]显示多种肿瘤组织, 特别是上皮来源的肿瘤细胞以及正常组织细胞存在免疫球蛋白的表达[2, 3, 4, 5, 16, 27, 28], 且其表达与细胞生长、增殖、黏附功能甚至细胞骨架等结构密切相关, 为研究肿瘤及免疫相关疾病发生机制、创新诊疗手段提供新的思路。本实验通过一系列细胞分子生物学实验证实人肾小球系膜细胞存在IgA基因的转录和蛋白质表达, 为探究包括IgA肾病在内的肾小球疾病的发病机制提供新的思路。
本研究首先通过免疫荧光染色, 观察到了IgA的重链 Ig α 和轻链Ig κ 、Ig λ 在系膜细胞胞浆、胞膜和细胞周围的表达; 其次通过RT-PCR, 检测到IgA的重链Ig α 和轻链Ig κ 、Ig λ 恒定区mRNA转录, 经进一步的测序证实, 其碱基序列与B细胞相应片段mRNA序列高度同源; 再次, Western blot检测到IgA的重链Ig α 和轻链Ig λ 蛋白在细胞内表达, 这些结果分别从亚细胞定位、蛋白质和核酸水平提示HMCs可以表达IgA。
此外, 非还原Western blot检测到细胞上清液中IgA完整分子的表达, 还原性Western blot检测到细胞上清液中Ig α 链, 蛋白质谱检测进一步证实上清液中存在IgA1和IgA2重链恒定区的肽链片段, 由此可以推断HMCs不仅合成IgA, 还可以将合成的IgA分泌到细胞外。
肾小球系膜细胞具有吞噬功能, 对肾小球系膜区沉积的大分子物质具有一定的清除作用[29, 30], 可以通过细胞表面的Fc受体等吞噬免疫球蛋白[31]。血液循环中的IgA1可以与系膜细胞膜转铁蛋白受体结合[32]。为了排除系膜细胞吞噬、结合胎牛血清中可能存在的IgA, 本实验中对细胞培养所用胎牛血清进行Western blot检测, 各种抗人IgA轻、重链抗体在胎牛血清中均未检测到阳性条带, 表明胎牛血清中可能无IgA, 或者存在的IgA与人IgA无交叉反应。有报道提示FBS中可以检测到少量IgG1和IgM, 未检测到IgA[33], 这进一步提示系膜细胞裂解液及培养上清液中检测出的IgA为系膜细胞合成和分泌的, 但是用于构建实验所用系膜细胞系的原代细胞是否在人体内已经通过转铁蛋白受体结合了循环系统中的IgA, 通过目前的实验方法无法进行排除。虽然通过RT-PCR检测到了Ig α 、 Ig κ 、Ig λ 恒定区碱基序列与B细胞来源相应的mRNA序列高度同源, 但是并不能完全排除系膜细胞系原代细胞时期受人体内结合IgA的可能性。
本研究中细胞内Ig α 可检测到两种相对分子质量的蛋白条带, Ig λ 链也未出现在经典的25 000位置, 可能缘于免疫球蛋白在合成和加工过程中存在不同程度的剪切、修饰或者二聚体形成, 这种免疫球蛋白剪切或聚合的现象在其他的研究中也有类似的报道[34]; Western blot 检测到细胞裂解液Ig κ 链阳性条带并不明显, 与免疫荧光观察到细胞浆Ig κ 的阳性表达相矛盾, 可能与两种实验方法所用抗体不同有关。在细胞免疫荧光检测中, 抗人Ig κ 抗体识别Ig κ 的空间结构抗原决定簇, 而在Western blot 检测中, 抗人Ig κ 抗体识别Ig κ 蛋白的某一肽段氨基酸即一级结构。正常人血清中可以看到明显的Ig κ 条带, 这也提示我们系膜细胞表达的Ig κ 可能与B细胞来源的Ig κ 有一定的差异, 这与非B细胞表达特定的免疫球蛋白的特点是符合的[4, 35]。结合免疫荧光观察到Ig κ 和Ig λ 的阳性表达, 基因水平也检测到了Ig κ 和Ig λ 恒定区mRNA转录, 裂解液中检测到Ig λ 表达, 高度提示系膜细胞可以合成Ig κ 。
另外, 本研究中使用的亲和层析凝胶配体为jacalin, 是凝集素的一种, 通过结合IgA1铰链区的糖基链而亲和溶液中的IgA1分子, 因为IgA2缺少铰链区, 所以jacalin理论上只结合IgA1[36, 37]。本研究中, 在细胞上清液中检测到了IgA1和IgA2的重链, 有研究表明jacalin对IgA2也具有微弱的亲和力[32], 所以不能排除HMCs表达IgA2的可能性。
综上所述, 本研究结果证明HMCs细胞系可能合成并分泌IgA。本研究仅仅在系膜细胞系检测到了IgA基因转录、蛋白表达、亚细胞定位及分泌, 需要进一步证实在人原代培养系膜细胞甚至肾组织系膜细胞中明确IgA表达。此外, 阐明系膜细胞来源的IgA结构、功能及其有别于浆细胞来源的IgA的特点, 将更加有助于系膜细胞合成并分泌IgA的认同。
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|