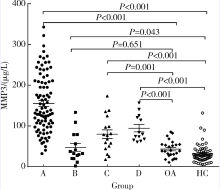
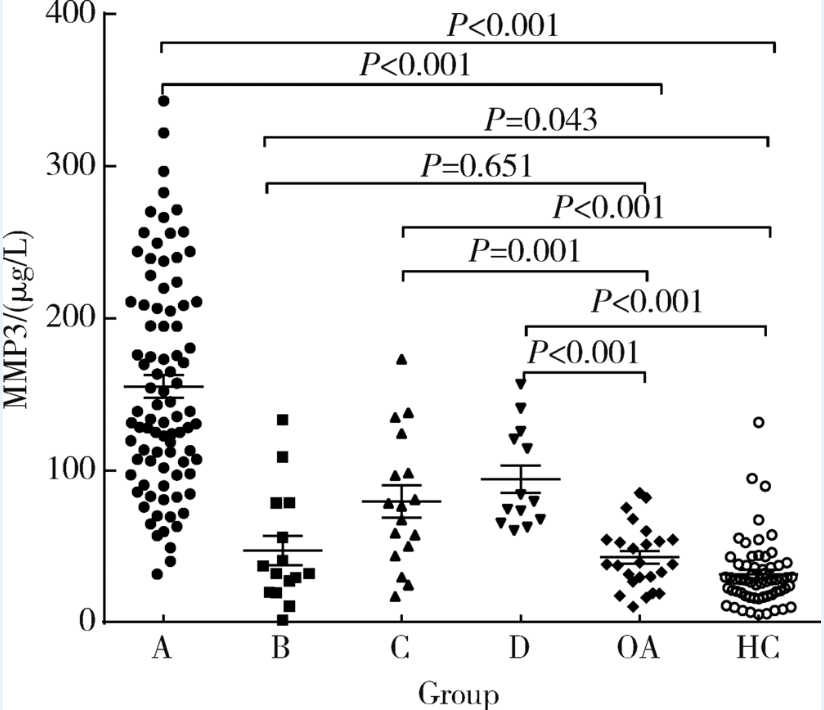
Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences) ›› 2018, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (6): 981-985. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2018.06.007
• Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Value of serum matrix metalloproteinase 3 in the assessment of early rheumatoid arthritis
Meng-ke LIU1,2,3,Lu-chen WANG1,2,3,Fan-lei HU1,2,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Peking University People’s Hospital & Beijing Key Laboratory for Rheumatism Mechanism and Immune Diagnosis (BZ0135) Beijing 100044, China
2. State Key Laboratory of Natural and Biomimetic Drugs,Peking University School of Pharmaceutical Sciences,Beijing 100191, China
3. Nanchang University Queen Mary School, Nanchang 330000, China
CLC Number:
- R593.22
| [1] |
Smolen JS, Aletaha D , McInnes IB. Rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Lancet, 2016,388(10055):2023-2038.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30173-8 |
| [2] | 葛均波, 徐永健 . 内科学[M]. 8版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2014: 808-814. |
| [3] |
Mittal R, Patel AP, Debs LH , et al. Intricate functions of matrix metalloproteinases in physiological and pathological conditions[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2016,231(12):2599-2621.
doi: 10.1002/jcp.25430 pmid: 27187048 |
| [4] | 耿学丽, 武英伟, 孙常铭 , 等. 类风湿关节炎患者基质金属蛋白酶-3的检测[J]. 广东医学, 2016,37(4):555-557. |
| [5] |
Hiura K, Iwaki-Egawa S, Kawashima T , et al. The diagnostic utility of matrix metalloproteinase-3 and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein for predicting rheumatoid arthritis in anti-cyclic citrullina-ted peptide antibody-negative patients with recent-onset undifferentiated arthritis[J]. Rheumatol Int, 2013,33(9):2309-2314.
doi: 10.1007/s00296-013-2716-1 pmid: 23503938 |
| [6] |
马剑达, 王晓莹, 莫颖倩 , 等. 血清基质金属蛋白酶3评价类风湿关节炎患者病情活动的价值[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2015,95(47):3823-3828.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2015.47.006 |
| [7] |
Lee YC, Hackett J, Frits M , et al. Multibiomarker disease activity score and C-reactive protein in a cross-sectional observational study of patients with rheumatoid arthritis with and without concomitant fibromyalgia[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2016,55(4):640-648.
doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kev388 pmid: 4795537 |
| [8] | Ma JD, Wei XN, Zheng DH , et al. Continuously elevated serum matrix metalloproteinase-3 for 3-6 months predict one-year radiographic progression inrheumatoid arthritis: a prospective cohort study[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2015,14(17):289-302. |
| [9] | Ainola MM, Mandelin JA, Liljestrom MP , et al. Pannus invasionand cartilage degradation in rheumatoid arthritis: involvement of MMP-3 and interleukin-1β[J]. Clin Exp Rheumatol, 2005,23(5):644-650. |
| [10] |
Takeshita M, Kuno A, Suzuki K , et al. Alteration of matrix metalloproteinase-3O-glycan structure as a biomarker fordisease activity of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2016,18(1):112-121.
doi: 10.1186/s13075-016-1013-2 pmid: 4875599 |
| [11] |
Houseman M, Potter C, Marshall N , et al. Baseline serum MMP-3 levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis are still independently predictive of radiographic progression in a longitudinal observational cohort at 8 years follow up[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2012,14(1):30-36.
doi: 10.1186/ar3734 pmid: 3392825 |
| [12] |
Shiozawa K, Yamane T, Murata M , et al. MMP-3 as a predictor for structural remission in RA patients treated with MTX mono-therapy[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2016,18(1):55-64.
doi: 10.1186/s13075-016-0948-7 pmid: 4769545 |
| [13] |
Urata Y, Uesato R, Tanaka D , et al. Treating to target matrix metalloproteinase 3 normalisation together with disease activity score below 2.6 yields better effects than each alone in rheumatoid arthritis patients: T-4 study[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2012,71(4):534-540.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-200108 pmid: 22021897 |
| [14] |
孔卓, 吴俊, 张海文 , 等. 血清基质金属蛋白酶3与类风湿关节炎的相关性研究[J]. 标记免疫分析与临床, 2014,21(6):636-639.
doi: 10.11748/bjmy.issn.1006-1703.2014.06.004 |
| [15] | 李立新, 蔡蓓, 廖竞宇 , 等. 血清基质金属蛋白酶3对类风湿性关节炎患者骨关节损伤和疗效评估的价值[J]. 细胞与分子免疫学杂志, 2013,29(9):966-969 |
| [16] | 史睿, 韩玲, 陈慕芝 , 等. MMP-3、TIMP-1及HCgp-39在早期RA患者血清中的变化及意义[J]. 检验医学与临床, 2017,14(3):325-327. |
| [1] | Jia jia XU,Yan WANG,He SUN,Ru lin JIA,Xue wu ZHANG,Yang MENG,Li li REN,Xiao lin SUN. Clinical significance of detection of soluble interleukin 2 receptor alpha chain in the assessment of rheumatoid arthritis disease activity [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(6): 975-980. |
|
||