Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (4): 726-729. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.04.025
Previous Articles Next Articles
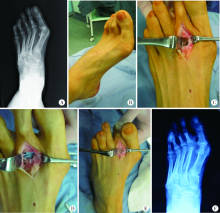
Evaluation of therapeutic efficacy of arthroplasty with Swanson prosthesis in the surgical treatment of 2-5 metatarsophalangeal joint diseases
Zhong-di LIU,Hao LU,Yu-song YUAN,Hai-lin XU( )
)
- Department of Trauma and Orthopedics, Trauma Medical Center, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
CLC Number:
- R649.9
| [1] |
Nery C, Baumfeld D. Lesser metatarsophalangeal joint instability: Treatment with tendon transfers[J]. Foot Ankle Clin, 2018,23(1):103-126.
pmid: 29362027 |
| [2] | Swanson AB, de Groot Swanson G. Use of grommets for flexible hinge implant arthroplasty of the great toe[J]. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1997(340):87-94. |
| [3] |
Phisitkul P. Managing complications of lesser toe and metatarsophalangeal joint surgery[J]. Foot Ankle Clin, 2018,23(1):145-156.
pmid: 29362029 |
| [4] | Davies MS, Saxby TS. Metatarsal neck osteotomy with rigid internal fixation for the treatment of lesser toe metatarsophalangeal joint pathology[J]. Foot Ankle Int, 1999,20(10):630-635. |
| [5] |
Stevens J, de Bot R, Hermus J, et al. Clinical outcome following total joint replacement and arthrodesis for hallux rigidus: A systematic review[J]. JBJS Rev, 2017,5(11):e2.
pmid: 29135720 |
| [6] |
Erdil M, Elmadaǧ NM, Polat G, et al. Comparison of arthrodesis, resurfacing hemiarthroplasty, and total joint replacement in the treatment of advanced hallux rigidus[J]. J Foot Ankle Surg, 2013,52(5):588-593.
doi: 10.1053/j.jfas.2013.03.014 pmid: 23659913 |
| [7] | O'Malley MJ, Basran HS, Gu Y, et al. Treatment of advanced stages of hallux rigidus with cheilectomy and phalangeal osteotomy[J]. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2013,95(7):606-610. |
| [8] |
Swanson AB, Lumsden RM, Swanson GD. Silicone implant arthroplasty of the great toe. A review of single stem and flexible hinge implants[J]. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1979, (142):30-43.
pmid: 387324 |
| [9] |
Moeckel BH, Sculco TP, Alexiades MM, et al. The double-stemmed silicone-rubber implant for rheumatoid arthritis of the first metatarsophalangeal joint. Long-term results[J]. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1992,74(4):564-570.
pmid: 1583051 |
| [10] |
Peace RA, Hamilton GA. End-stage hallux rigidus: cheilectomy, implant, or arthrodesis?[J]. Clin Podiatr Med Surg, 2012,29(3):341-353.
pmid: 22727376 |
| [11] | Valentini R, de Fabrizio G, Piovan G. First metatarsophalangeal joint replacement with total arthroplasty in the surgical treatment of the hallux rigidus[J]. Acta Biomed, 2014,85(Suppl 2):113-117. |
| [12] |
Stone OD, Ray R, Thomson CE, et al. Long-term follow-up of arthrodesis vs total joint arthroplasty for hallux rigidus[J]. Foot Ankle Int, 2017,38(4):375-380.
doi: 10.1177/1071100716682994 pmid: 28367694 |
| [13] |
Brewster M. Does total joint replacement or arthrodesis of the first metatarsophalangeal joint yield better functional results? A syste-matic review of the literature[J]. J Foot Ankle Surg, 2010,49(6):546-552.
doi: 10.1053/j.jfas.2010.07.003 pmid: 20833566 |
| [14] |
Shereff MJ, Jahss MH. Complications of silastic implant arthroplasty in the hallux[J]. Foot Ankle, 1980,1(2):95-101.
pmid: 7274905 |
| [15] |
Erkocak OF, Senaran H, Altan E, et al. Short-term functional outcomes of first metatarsophalangeal total joint replacement for hallux rigidus[J]. Foot Ankle Int, 2013,34(11):1569-1579.
doi: 10.1177/1071100713496770 pmid: 23877170 |
| [1] | Silan AN,Qunyi ZHENG,Kai WANG,Shan GAO. Characteristics and influencing factors of early pain in patients after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 167-173. |
| [2] | Ran ZHAO,Yan-qing LIU,Hua TIAN. Cumulative sum control chart analysis of soft tissue balance in total knee replacement assisted by electronic pressure sensor [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 658-664. |
| [3] | Yi-lin YE,Heng LIU,Li-ping PAN,Wei-bing CHAI. Periprosthetic gout flare after total knee arthroplasty: A misdiagnostic case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 362-365. |
| [4] | LI Zhi-chang,HOU Yun-fei,ZHOU Zhi-wei,JIANG Long,ZHANG Shu,LIN Jian-hao. Patient factors influencing preoperative expectations of patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(1): 170-176. |
| [5] | Hao WU,Li-ping PAN,Heng LIU,Hong-bin WANG,Tai-guo NING,Yong-ping CAO. Effect of posterior tibial slope on the short-term outcome in mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(5): 877-882. |
| [6] | WANG Xin-guang,GENG Xiao,LI Yang,WU Tian-chen,LI Zi-jian,TIAN Hua. Comparison of alignment and operative time between portable accelerometer-based navigation device and computer assisted surgery in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(4): 728-733. |
| [7] | JI Song-jie,HUANG Ye,WANG Xing-shan,LIU Jian,DOU Yong,JIANG Xu,ZHOU Yi-xin. Multivariate analysis of varus after Oxford unicompartmental knee arthroplasty [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(2): 293-297. |
| [8] | KE Yan,ZHANG Qiang,MA Yun-qing,LI Ru-jun,TAO Ke,GUI Xian-ge,LI Ke-peng,ZHANG Hong,LIN Jian-hao. Short-term outcomes of total hip arthroplasty in the treatment of Tönnis grade 3 hip osteoarthritis in patients with spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(1): 175-182. |
| [9] | Sen-lei LI,Xian-teng YANG,Xiao-bin TIAN,Li SUN. Early functional recovery of direct anterior approach versus anterolateral approach for total hip arthroplasty [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(2): 268-272. |
| [10] | LIU Heng, LI Zhuo-yang, CAO Yong-ping, CUI Yun-peng, WU Hao. Measurement of the tibial alignment after total knee replacement without the extramedullary cutting guide [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(5): 850-854. |
| [11] | LI Yang, LI Bang-guo, ZHAO Ran, TIAN Hua, ZHANG Ke. Effect of autologous blood transfusion device on preventing blood loss in primary total knee arthroplasty using comprehensive hemostatic methods [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(4): 651-656. |
| [12] | WANG Jun-feng, LI Zhao, ZHANG Ke-shi, YUAN Feng, LI Ru-jun, ZHONG Qun-jie, GUAN Zhen-peng. Unilateral patellar resurfacing in bilateral total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled study [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(5): 861-866. |
| [13] | LI Yang, LI Zi-jian, ZHANG Ke, TIAN Hua, LIU Yan-qing, CAI Hong, LI Feng, ZHAO Min-wei. Analysis on the causes of unscheduled suspensions of knee and hip arthroplasty [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(2): 231-235. |
| [14] | TANG Jing, LV Ming, ZHOU Yi-xin, ZHANG Ji. Application of bilateral direct anterior approach total hip arthroplasty: a report of 22 cases [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(2): 221-225. |
| [15] | XU Jie, ZHUANG Wei-da, LI Xin-wei, YU Guo-yu, LIN Yuan, LUO Fen-qi, XIAO Yu-hua. Comparison of the effects of total hip arthroplasty via direct anterior approach and posterolateral piriformis-sparing approach [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(2): 214-220. |
|
||