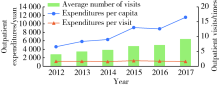
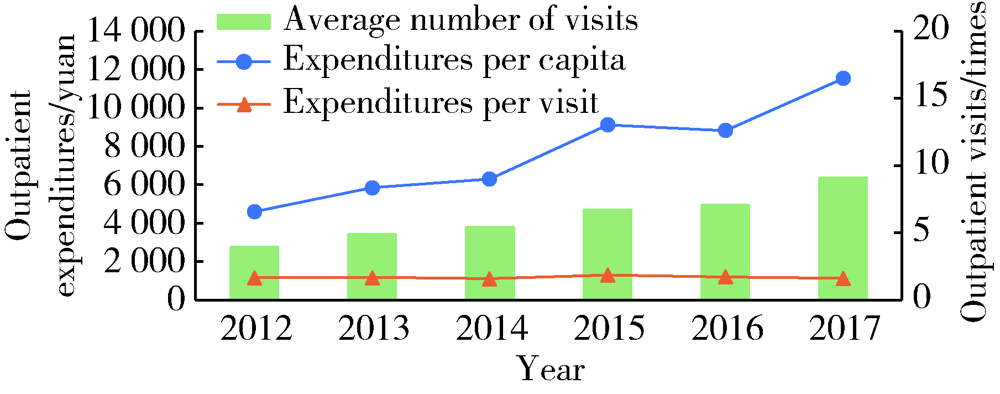
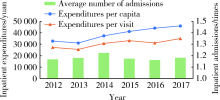
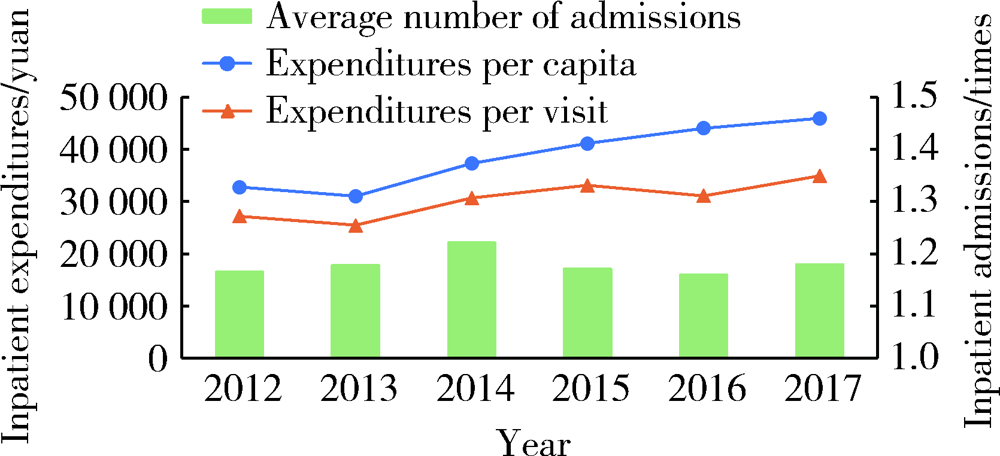
Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (1): 215-219. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.01.033
Previous Articles Next Articles
Trend in medical expenditures for patients with kidney diseases: An analysis from a tertiary hospital in Beijing
BI Shu-hong1,LI Zi-fan2,WANG Tao1,Δ( ),WANG Yue1,ZHANG Chen3,JI Hong3,SHI Ju2,Δ(
),WANG Yue1,ZHANG Chen3,JI Hong3,SHI Ju2,Δ( )
)
- 1. Division of Nephrology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
2. School of Economics, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
3. Data Center, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
CLC Number:
- R197.3
| [1] |
GBD 2017 DALYs and HALE Collaborators. Global, regional, and national disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) for 359 diseases and injuries and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017[J]. Lancet, 2018,392(10159):1859-1922.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32335-3 pmid: 30415748 |
| [2] |
Jha V, Garcia-Garcia G, Iseki K, et al. Chronic kidney disease: global dimension and perspectives[J]. Lancet, 2013,382(9888):260-272.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60687-X |
| [3] |
Wang V, Vilme H, Maciejewski ML, et al. The economic burden of chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease[J]. Semin Nephrol, 2016,36(4):319-330.
doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2016.05.008 pmid: 27475662 |
| [4] | 陈正祥, 程晓明, 李冀男, 等. 杭州市终末期肾病血液透析患者疾病经济负担研究[J]. 中国卫生经济, 2005,24(6):44-47. |
| [5] | 肖月, 隋宾艳, 赵琨. 我国终末期肾病现状及透析技术的应用、费用及支付情况分析[J]. 中国卫生政策研究, 2011,4(5):29-33. |
| [6] | 于洋, 王芝芳, 张希玉, 等. 威海市 2009 年终末期肾病疾病负担研究[J]. 中国卫生统计, 2013,30(2):272-274. |
| [7] | 祝菁菁, 范文君, 黄韻宇, 等. 我国2 型糖尿病及糖尿病肾病的经济负担现状[J]. 中国卫生经济, 2013,32(4):32-34. |
| [8] | 杜晔, 孟群. 我国慢性肾脏病防治政策及策略研究:基于卫生经济学视角[J]. 中国卫生政策研究, 2018,11(7):78-83. |
| [9] |
Eriksson JK, Neovius M, Jacobson SH, et al. Healthcare costs in chronic kidney disease and renal replacement therapy: a population-based cohort study in Sweden[J]. BMJ Open, 2016,6(10):e012062.
doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2016-012062 pmid: 27855091 |
| [10] |
Small C, Kramer HJ, Griffin KA, et al. Non-dialysis dependent chronic kidney disease is associated with high total and out-of-pocket healthcare expenditures[J]. BMC Nephrol, 2017,18(1):3.
doi: 10.1186/s12882-016-0432-2 pmid: 28056852 |
| [11] |
Kerr M, Bray B, Medcalf J, et al. Estimating the financial cost of chronic kidney disease to the NHS in England[J]. Nephrol Dial Transplant, 2012, 27(Suppl 3): iii73-iii80.
doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfs269 |
| [12] | Ahlawat R, Tiwari P, D’Cruz S. Direct cost for treating chronic kidney disease at an outpatient setting of a tertiary hospital: evidence from a cross-sectional study[J/OL]. Value Health Reg Issues, 2017(2017-05-12)[2019-06-01]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vhri.2016.10.003. |
| [13] |
Anutrakulchai S, Mairiang P, Pongskul C, et al. Mortality and treatment costs of hospitalized chronic kidney disease patients between the three major health insurance schemes in Thailand[J]. BMC Health Serv Res, 2016,16(1):528.
doi: 10.1186/s12913-016-1792-9 pmid: 27686066 |
| [1] | WANG Xiao-qi,CHEN Mei-jun,YUN Qing-ping,SUN Si-wei,WANG Xi-kai,SHI Yu-hui,JI Ying,GUAN Zhong-jun,CHANG Chun. Impact of health literacy on patient experience of outpatients in China and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(3): 560-565. |
| [2] | Wei-yu ZHANG,Qiu-xiang XIA,Hao HU,Jing-wen CHEN,Yi-ran SUN,Ke-xin XU,Xiao-peng ZHANG. Analysis of urodynamic study of female outpatients with lower urinary tract symptoms and follow-up of the patients with detrusor underactive [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(5): 856-862. |
| [3] | YANG Chao, WANG Jin-wei, YANG Yao-zheng, BAI Kun-hao, GAO Bi-xia, ZHAO Ming-hui, ZHANG Lu-xia, WU Shou-ling, WANG Fang. Impact of anemia and chronic kidney disease on the risk of cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality among diabetic patients [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(3): 495-500. |
| [4] | LIN Hong-bo, CHEN Yi, SHEN Peng, LI Xiao-yong,SI Ya-qin, ZHANG Du-dan, TANG Xun, GAO Pei. Incidence and risk factors of chronic kidney disease in community-based patients with diabetes [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(3): 416-421. |
| [5] | ZHANG Hu-yang, JIAN Wei-yan, FANG Hai. Analysis of substitutional effect of outpatient expenditure on inpatient expenditure in hypertensive patients with rural new cooperative medical scheme [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2016, 48(3): 472-477. |
| [6] | ZHAO Xin-ju, WEI Tao,DONG Bao, JIA Yuan, WANG Mei1. Renal damage caused by Rhupus syndrome associated with anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies vasculitis and cryoglobulinemia [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2015, 47(5): 870-874. |
| [7] | LI Jing-Zi, WANG Su-Xia, QIN Xiao-Qi, XU Yuan, PANG Wei, E Jie, ZHENG Xin. Correlation between urinary sediment spectra and pathological patterns of renal biopsies [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2014, 46(6): 920-925. |
| [8] | QIU Min, LU Jian, MA Lu-Lin, YAN Ye, ZHANG Shu-Dong. Retroperitoneal laparoscopic partial nephrectomy for treatment of cystic nephroma:one case report [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2014, 46(4): 650-652. |
| [9] | WANG Pin-Ze, LIU Min, DAI Xiao-Qiu, YANG Xue-Song, HAI Shan-·Ka-De-尔Bai, LI Xiao-Guang, SHEN Li, WANG Zheng-Hui, WU Hua, XU Jie, NING Yong-Zhong. Establishment of early warning control charts based on the syndromic surveillance data of outpatient diarrhea in Beijing [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2014, 46(3): 424-428. |