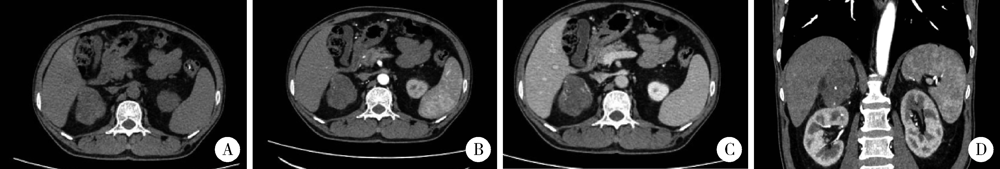
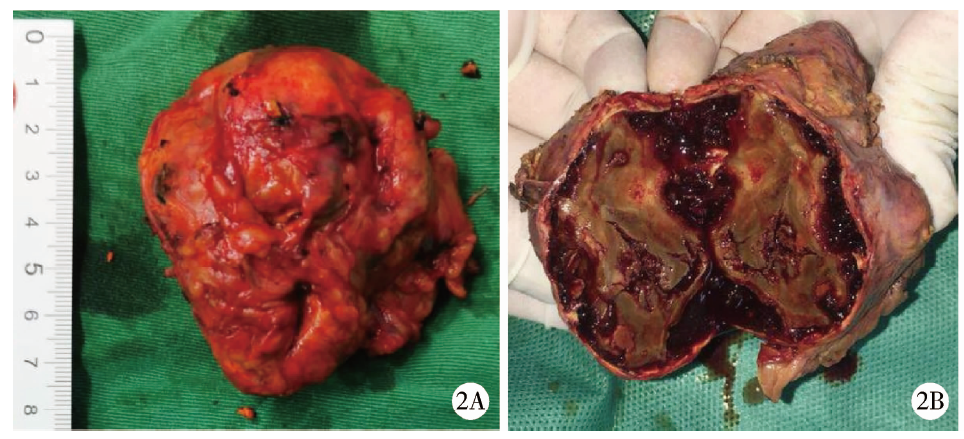
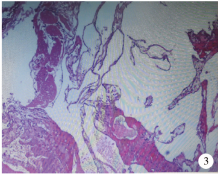
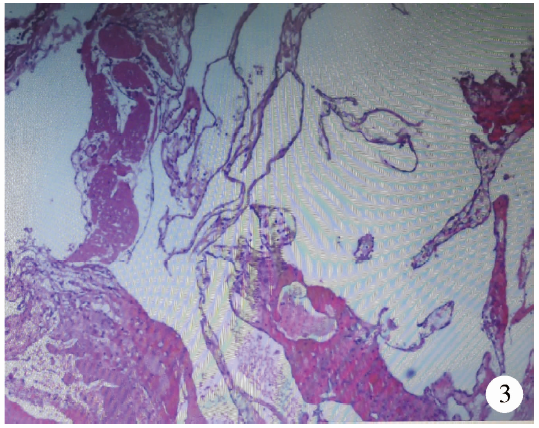
Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (4): 808-810. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.04.032
Previous Articles Next Articles
Adrenal cavernous hemangioma: A case report and literature review
KANG Wen-yu1,WANG Lu2,QIU Min2,Δ( ),ZHANG Fan2,GUO Wei1,Δ(
),ZHANG Fan2,GUO Wei1,Δ( ),QIANG Ya-yong1,TUO Peng-fei1,ZONG You-long1,LIU Lei-lei1,WANG Shuai-shuai1
),QIANG Ya-yong1,TUO Peng-fei1,ZONG You-long1,LIU Lei-lei1,WANG Shuai-shuai1
- 1. Department of Urology, Yan’an City Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Yan’an 716000, Shaanxi, China
2. Department of Urology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
CLC Number:
- R736.6
| [1] |
Feo CV, De Troia A, Pedriali M, et al. Adrenal cavernous hemangioma: a case report [J]. BMC Surg, 2018, 18(1):103-107.
doi: 10.1186/s12893-018-0429-9 |
| [2] |
Degheili JA, Abou HN, El-Moussawi M, et al. Adrenal cavernous hemangioma: A rarely perceived pathology-case illustration and review of literature [J]. Case Rep Pathol, 2019, 2019:8463890.
doi: 10.1155/2019/8463890 pmid: 31949968 |
| [3] | Noh JJ, Choi SH, Hwang HK, et al. Adrenal cavernous heman-gioma: a case report with review of the literature [J]. JOP, 2014, 15(3):254-257. |
| [4] |
Johnson CC, Jeppesen FB. Hemangioma of the adrenal [J]. J Urol, 1955, 74(5):573-577.
doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(17)67320-8 |
| [5] |
Hashimoto A, Yoshino H, Yoshikawa F, et al. Giant cavernous hemangioma of the adrenal gland in an elderly patient [J]. Intern Med, 2018, 57(9):1317-1319.
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.9711-17 |
| [6] |
Agrusa A, Romano G, Salamone G, et al. Large cavernous hemangioma of the adrenal gland: Laparoscopic treatment. Report of a case [J]. Int J Surg Case Rep, 2015, 16:150-153.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2015.09.040 |
| [1] | Bin CHEN,Chao WU,Bin LIU,Tao YU,Zhen-yu WANG. Prognosis of patients with spinal intramedullary cavernous hemangioma by different treatments [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 652-657. |
| [2] | Yu-chao HUANG-FU,Yi-qing DU,Lu-ping YU,Tao XU. Risk factors of persistent hypertension in primary aldosteronism patients after surgery [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(4): 686-691. |
| [3] | AN Wen-cheng,YAN Hui-xian,DENG Zheng-zhao,CHEN Fang,OU Xiao-hong,JIN Hong-xin,HUANG Wei. Chronic kidney disease after adrenalectomy in a patient with primary aldosteronism [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(6): 1201-1204. |
| [4] | Lei LIU,Guo-liang WANG,Lu-lin MA,Min LU,Cheng LIU,Xiao-fei HOU. Diagnosis and surgical treatment of massive adrenal area tumor with tumor thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(4): 684-688. |
| [5] | FAN Hua, LI Han-zhong, XU Wei-feng, JI Zhi-gang, ZHANG Yu-shi. Surgery treatment of ectopic adrenocorticotrophic hormone syndrome [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(4): 652-656. |
| [6] | QIU Min, ZONG Ya-nan, LU Jian, MA Lu-lin, ZHENG Qing, GUO Xiang-yang. Rocuronium anesthesia induced anaphylactic shock: a case report [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2015, 47(5): 885-887. |
| [7] | WU Chu-Jun, QIU Min, MA Lu-Lin. Progress in diagnosis and treatment of adrenal metastases tumor [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2015, 47(4): 728-731. |
|
||