Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (3): 442-449. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.03.009
Previous Articles Next Articles
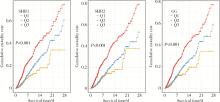
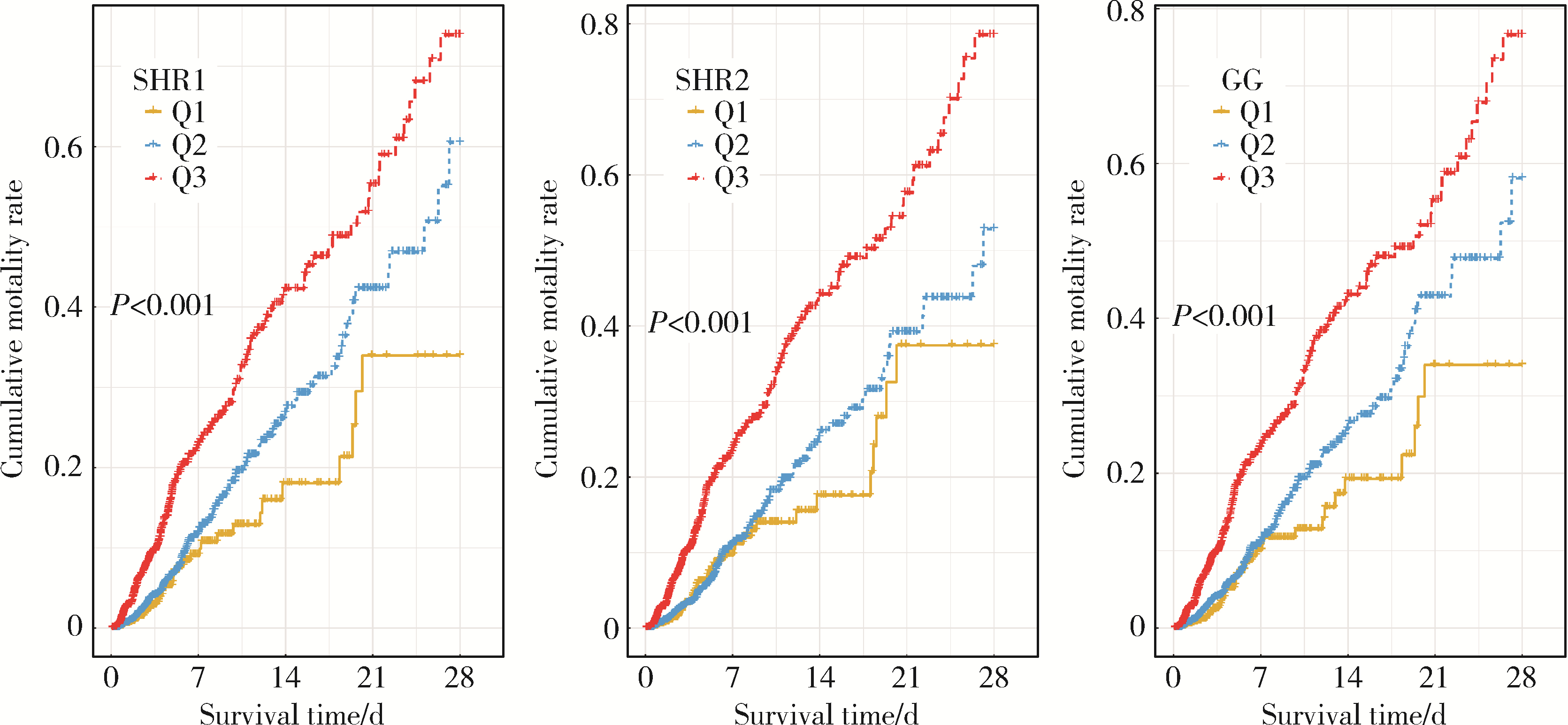
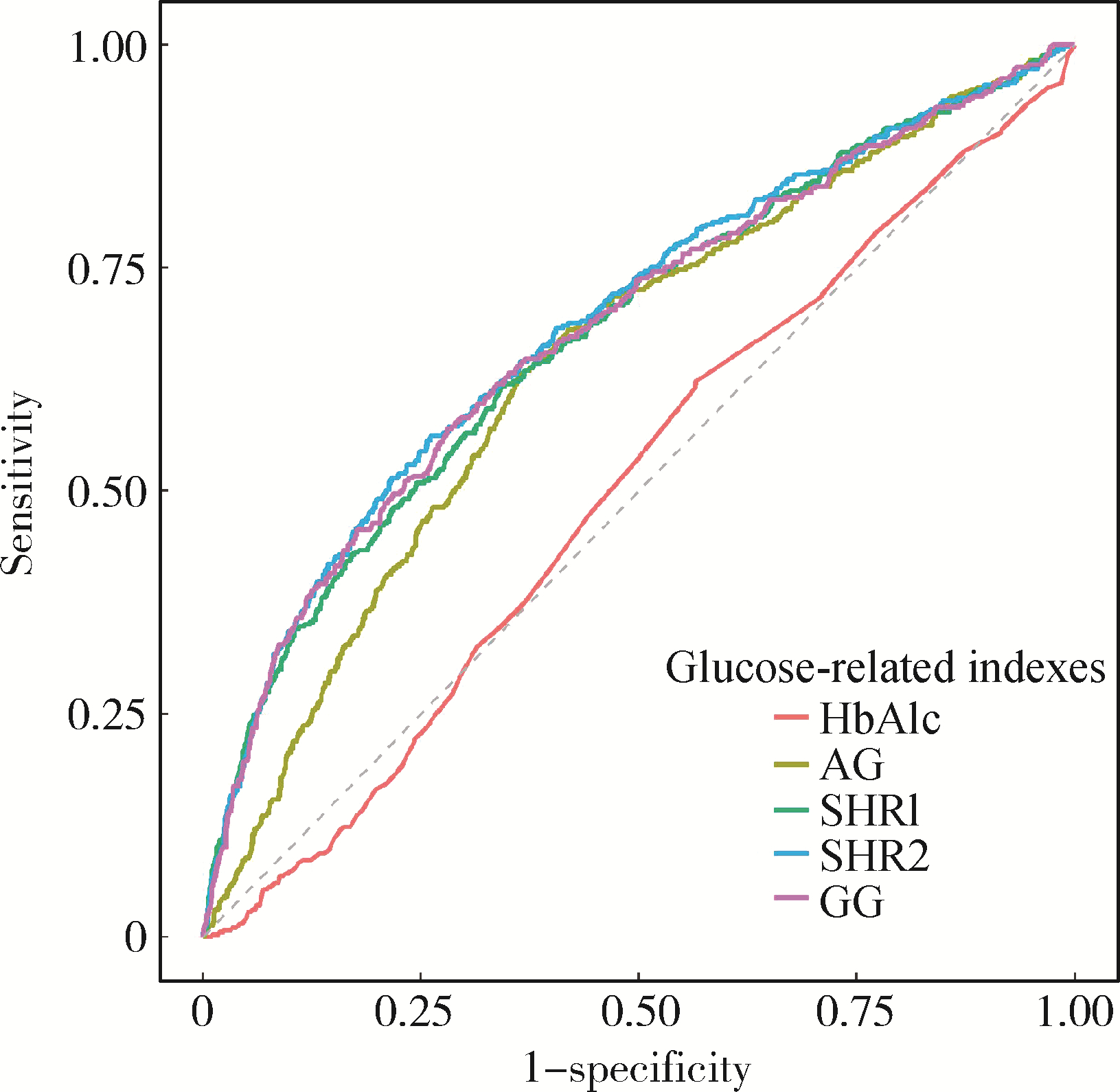
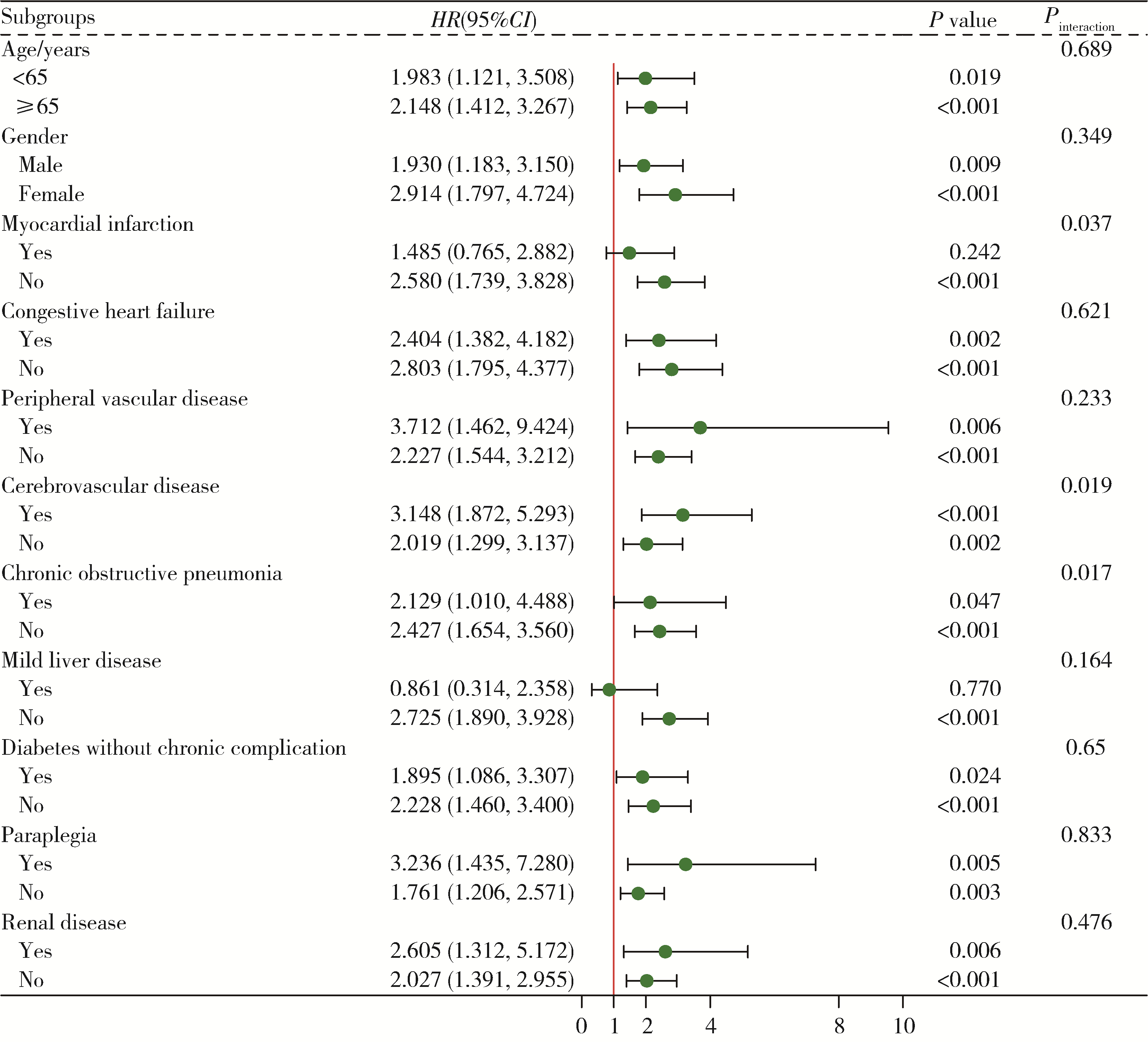
Predictive value of stress-induced hyperglycemia on 28 d risk of all-cause death in intensive care patients
Yu-xin WANG,Yu-han DENG,Yin-liang TAN,Bao-hua LIU*( )
)
- Department of Social Medicine and Health Education, Peking University School of Public Health, Beijing 100191, China
CLC Number:
- R193.3
| 1 |
Mousai O , Tafoureau L , Yovell T , et al.Clustering analysis of geriatric and acute characteristics in a cohort of very old patients on admission to ICU[J].Intensive Care Med,2022,48(12):1726-1735.
doi: 10.1007/s00134-022-06868-x |
| 2 |
Dungan KM , Braithwaite SS , Preiser JC .Stress hyperglycaemia[J].Lancet,2009,373(9677):1798-1807.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60553-5 |
| 3 |
Harp JB , Yancopoulos GD , Gromada J .Glucagon orchestrates stress-induced hyperglycaemia[J].Diabetes Obes Metab,2016,18(7):648-653.
doi: 10.1111/dom.12668 |
| 4 |
Roberts GW , Quinn SJ , Valentine N , et al.Relative hyperglycemia, a marker of critical illness: Introducing the stress hyperglycemia ratio[J].J Clin Endocrinol Metab,2015,100(12):4490-4497.
doi: 10.1210/jc.2015-2660 |
| 5 |
Liao WI , Wang JC , Chang WC , et al.Usefulness of glycemic gap to predict ICU mortality in critically ill patients with diabetes[J].Medicine (Baltimore),2015,94(36):e1525.
doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000001525 |
| 6 |
Lee TF , Drake SM , Roberts GW , et al.Relative hyperglycemia is an independent determinant of in-hospital mortality in patients with critical illness[J].Critical Care Medicine,2020,48(2):e115-e122.
doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000004133 |
| 7 |
Mcdonnell ME , Garg R , Gopalakrishnan G , et al.Glycemic gap predicts mortality in a large multicenter cohort hospitalized with covid-19[J].J Clin Endocrinol Metab,2023,108(3):718-725.
doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgac587 |
| 8 |
Xia Z , Gu T , Zhao Z , et al.The stress hyperglycemia ratio, a novel index of relative hyperglycemia, predicts short-term mortality in critically ill patients after esophagectomy[J].J Gastrointest Oncol,2022,13(1):56-66.
doi: 10.21037/jgo-22-11 |
| 9 |
Chen G , Li M , Wen X , et al.Association between stress hyperglycemia ratio and in-hospital outcomes in elderly patients with acute myocardial infarction[J].Front Cardiovasc Med,2021,8,698725.
doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.698725 |
| 10 |
Zhu B , Pan Y , Jing J , et al.Stress hyperglycemia and outcome of non-diabetic patients after acute ischemic stroke[J].Front Neurol,2019,10,1003.
doi: 10.3389/fneur.2019.01003 |
| 11 | Guo Y , Wang G , Jing J , et al.Stress hyperglycemia may have higher risk of stroke recurrence than previously diagnosed diabetes mellitus[J].Aging (Albany NY),2021,13(6):9108-9118. |
| 12 | Johnson A, Bulgarelli L, Pollard T, et al. Mimic-Ⅳ documentation (version 1.0)[EB/OL]. (2021-01-01)[2022-10-01]. https://mimic.mit.edu/docs/iv/ |
| 13 |
Koyfman L , Brotfain E , Erblat A , et al.The impact of the blood glucose levels of non-diabetic critically ill patients on their clinical outcome[J].Anaesthesiol Intensive Ther,2018,50(1):20-26.
doi: 10.5603/AIT.2018.0004 |
| 14 |
Olariu E , Pooley N , Danel A , et al.A systematic scoping review on the consequences of stress-related hyperglycaemia[J].PLoS One,2018,13(4):e0194952.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0194952 |
| 15 |
Johnson AE , Kramer AA , Clifford GD .A new severity of illness scale using a subset of acute physiology and chronic health evaluation data elements shows comparable predictive accuracy[J].Cri-tical Care Medicine,2013,41(7):1711-1718.
doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31828a24fe |
| 16 |
Su YW , Hsu CY , Guo YW , et al.Usefulness of the plasma glucose concentration-to-HbA1c ratio in predicting clinical outcomes during acute illness with extreme hyperglycaemia[J].Diabetes Metab,2017,43(1):40-47.
doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2016.07.036 |
| 17 |
Allison PD .Multiple imputation for missing data: A cautionary tale[J].Sociol Methods Res,2000,28(3):301-309.
doi: 10.1177/0049124100028003003 |
| 18 |
Murphy AH .A new decomposition of the brier score: Formulation and interpretation[J].Mon Weather Rev,1986,114(12):2671-2673.
doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1986)114<2671:ANDOTB>2.0.CO;2 |
| 19 |
Nicolau JC , Serrano CV Jr , Giraldez RR , et al.In patients with acute myocardial infarction, the impact of hyperglycemia as a risk factor for mortality is not homogeneous across age-groups[J].Diabetes Care,2012,35(1):150-152.
doi: 10.2337/dc11-1170 |
| 20 |
Merlino G , Pez S , Gigli GL , et al.Stress hyperglycemia in patients with acute ischemic stroke due to large vessel occlusion undergoing mechanical thrombectomy[J].Front Neurol,2021,12,725002.
doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.725002 |
| 21 |
Li W , Ning Y , Ma Y , et al.Association of lung function and blood glucose level: A 10-year study in China[J].BMC Pulm Med,2022,22(1):444.
doi: 10.1186/s12890-022-02208-3 |
| 22 |
Zonneveld TP , Nederkoorn PJ , Westendorp WF , et al.Hyperglycemia predicts poststroke infections in acute ischemic stroke[J].Neurology,2017,88(15):1415-1421.
doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000003811 |
| 23 |
Ergul A , Abdelsaid M , Fouda AY , et al.Cerebral neovascularization in diabetes: Implications for stroke recovery and beyond[J].J Cereb Blood Flow Metab,2014,34(4):553-563.
doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2014.18 |
| 24 |
Cai ZM , Zhang MM , Feng RQ , et al.Fasting blood glucose-to-glycated hemoglobin ratio and all-cause mortality among chinese in-hospital patients with acute stroke: A 12-month follow-up study[J].BMC Geriatr,2022,22(1):508.
doi: 10.1186/s12877-022-03203-3 |
| [1] | Ya-nan ZHAO,Hui-yun FAN,Xiang-yu WANG,Ya-nan LUO,Rong ZHANG,Xiao-ying ZHENG. Early death and causes of death of patients with autism spectrum disorders: A systematic review [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 375-383. |
| [2] | WU Jing-yi,LIN Yu,LIN Ke,HU Yong-hua,KONG Gui-lan. Predicting prolonged length of intensive care unit stay via machine learning [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(6): 1163-1170. |
| [3] | LIN Yu,WU Jing-yi,LIN Ke,HU Yong-hua,KONG Gui-lan. Prediction of intensive care unit readmission for critically ill patients based on ensemble learning [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(3): 566-572. |
| [4] | LIN Ke, XIE Jun-qing, HU Yong-hua, KONG Gui-lan. Application of support vector machine in predicting in-hospital mortality risk of patients with acute kidney injury in ICU [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(2): 239-244. |