Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (5): 884-889. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.05.020
Previous Articles Next Articles
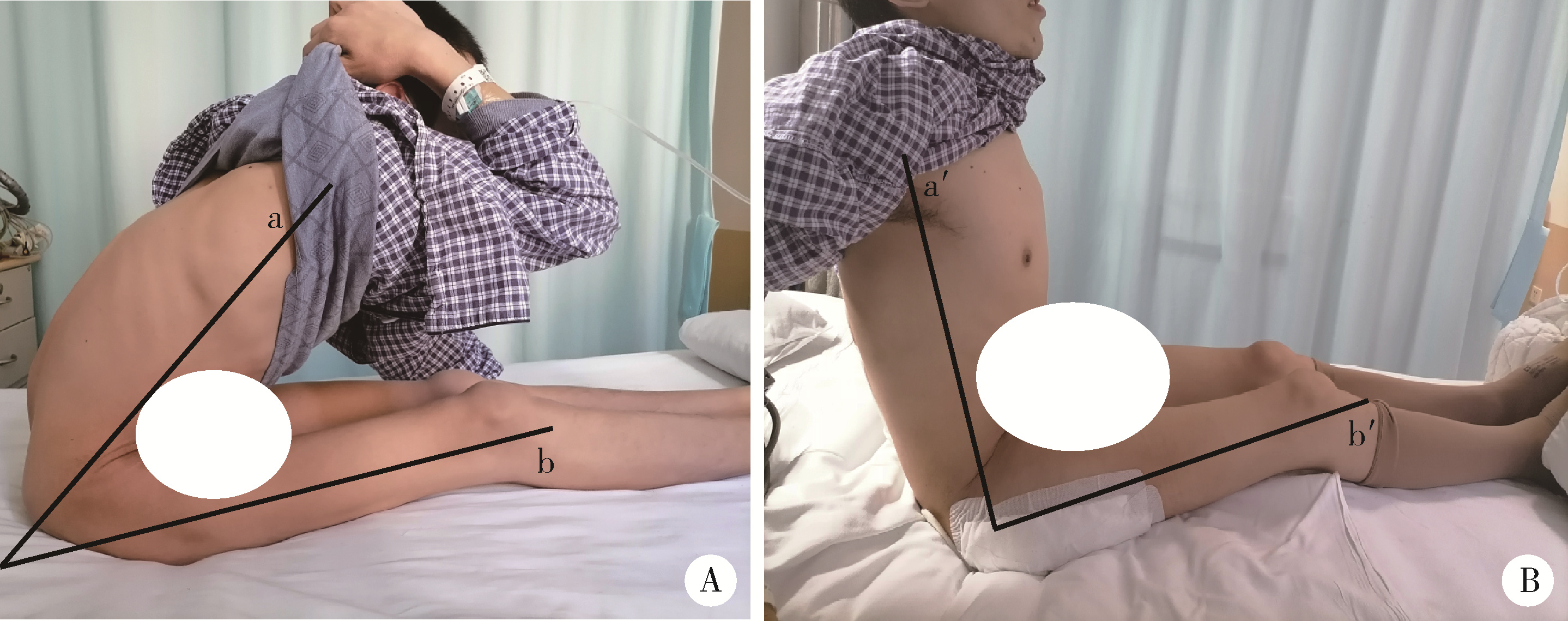
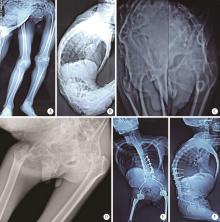
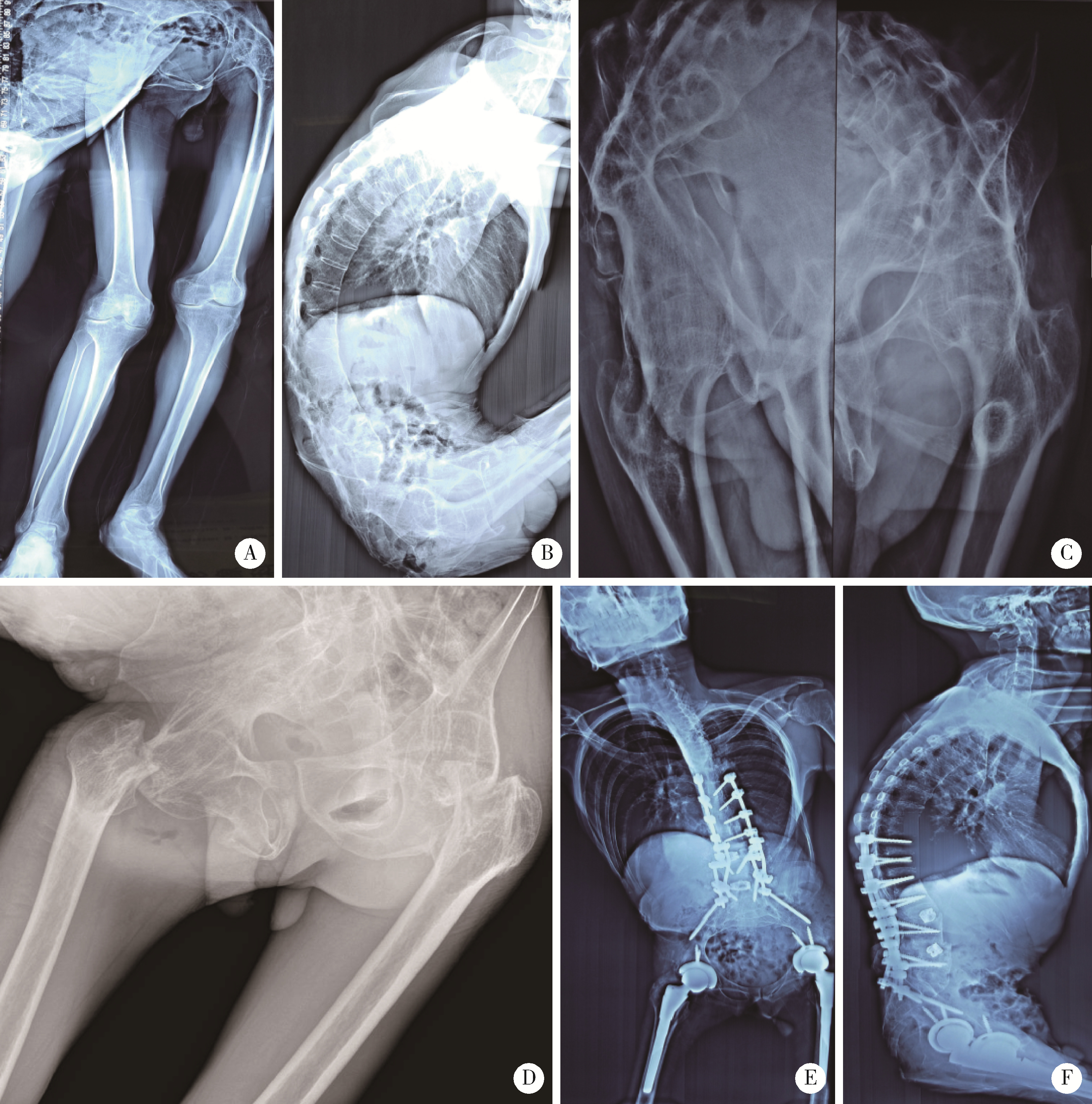
Therapeutic effect of modified femoral neck osteotomy on the surgical treatment of ankylosing spondylitis with severe flexion deformity
Qiwei WANG, Pengyu BAO, Shihao HONG, Xin YANG*( ), Yu WANG, Yongping CAO*(
), Yu WANG, Yongping CAO*( )
)
- Department of Orthopedics, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
CLC Number:
- R687.3
| 1 |
Luan H , Liu K , Kahaer A , et al. Pedicle subtraction osteotomy for the corrective surgery of ankylosing spondylitis with thoracolumbar kyphosis: Experience with 38 patients[J]. BMC Musculoskelet Disord, 2022, 23 (1): 731.
doi: 10.1186/s12891-022-05693-z |
| 2 |
Oommen AT , Hariharan TD , Chandy VJ , et al. Total hip arthroplasty in fused hips with spine stiffness in ankylosing spondylitis[J]. World J Orthop, 2021, 12 (12): 970- 982.
doi: 10.5312/wjo.v12.i12.970 |
| 3 |
Guo HZ , Yang CX , Tang ZP , et al. The effects of total hip arthroplasty in treating hip bony fusion in young and middle-aged patients with ankylosing spondylitis[J]. J Orthop Surg Res, 2019, 14 (1): 253.
doi: 10.1186/s13018-019-1288-5 |
| 4 |
Blizzard DJ , Penrose CT , Sheets CZ , et al. Ankylosing spondylitis increases perioperative and postoperative complications after total hip arthroplasty[J]. J Arthroplasty, 2017, 32 (8): 2474- 2479.
doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2017.03.041 |
| 5 |
Chung BC , Stefl M , Kang HP , et al. Increased dislocation rates following total hip arthroplasty in patients with ankylosing spondylitis[J]. Hip Int, 2023, 33 (6): 1026- 1034.
doi: 10.1177/11207000221126968 |
| 6 | Li Y , Qian BP , Qiu Y , et al. Influence of lumbar sagittal profile on pelvic orientation and pelvic motion during postural changes in patients with ankylosing spondylitis-related thoracolumbar kyphosis following pedicle subtraction osteotomy[J]. J Neurosurg Spine, 2021, 36 (4): 624- 631. |
| 7 |
Suwal SK , Songming P , Gang L , et al. Clinical evaluation of fused/ankylosed hip with severe flexion deformity after conversion to total hip arthroplasty[J]. J Nepal Med Assoc, 2016, 54 (202): 63- 66.
doi: 10.31729/jnma.2820 |
| 8 | Idulhaq M , Park KS , Diwanji SR , et al. Total hip arthroplasty for treatment of fused hip with 90 degrees flexion deformity[J]. J Arthroplasty, 2010, 25 (3): 498.e5- 498.e9. |
| 9 | Zeng Y , Huang Q , Ma H , et al. Two-stage treatment for ankylosing spondylitis with severe hip contracture[J]. Orthopedics, 2019, 42 (6): e502- e506. |
| 10 |
Yang X , Wang Q , Meng Z , et al. A femoral neck osteotomy for the patients with ankylosing spondylitis and thoracolumbar kyphosis combined with hip flexion contracture[J]. Orthop Surg, 2024, 16, 245- 253.
doi: 10.1111/os.13906 |
| 11 | 曾勇, 何睿, 李庆, 等. 脊柱楔形截骨并人工全髋关节置换术治疗强直性脊柱炎后凸畸形并髋关节重度屈曲挛缩畸形[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2014, 28 (8): 942- 946. |
| 12 | Gupta MC , Gupta S , Kelly MP , et al. Pedicle subtraction osteotomy[J]. JBJS Essent Surg Tech, 2020, 10 (1): e0028.1- e0028.11. |
| 13 |
Song DY , Zhang ZF , Wang TH , et al. Pedicle subtraction osteo-tomy in lateral position: A new strategy for correcting severe thoracolumbar kyphosis combined with hip flexion contracture in ankylosing spondylitis[J]. Orthop Surg, 2021, 13 (8): 2396- 2404.
doi: 10.1111/os.13169 |
| 14 | Rego P , Mascarenhas V , Mafra I , et al. Femoral neck osteotomy in skeletally mature patients: surgical technique and midterm results[J]. Int Orthop, 2021, 45 (1): 83- 94. |
| 15 | Faure PA , Zaltz I , Côté K , et al. Morscher osteotomy through surgical dislocation approach for true femoral neck lengthening with greater trochanter transposition[J]. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2020, 102 (Suppl 2): 66- 72. |
| [1] | LIU Rui, SUN Lin, LI Chang-hong, ZHAI Jia-yu, LIU Xiang-yuan. Cause analysis of spinal surgery in ankylosing spondylitis [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(5): 835-839. |
|
||