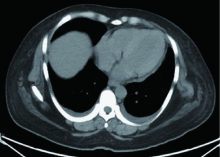
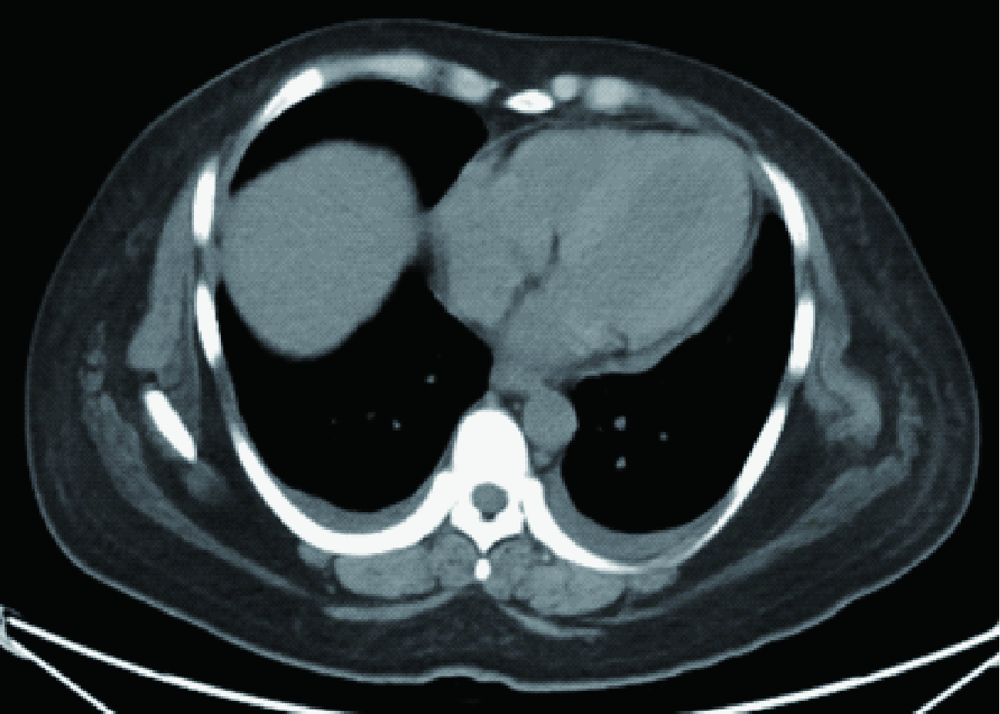
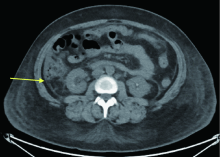
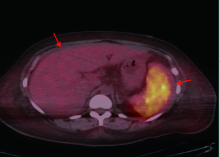
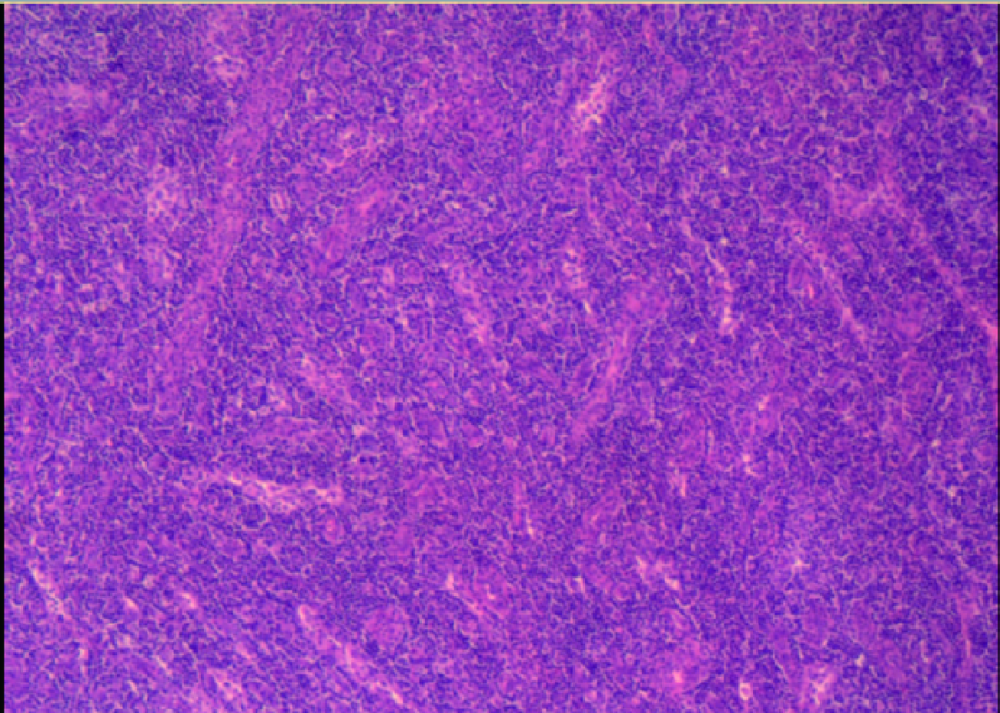
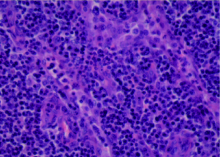
Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (4): 814-817. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.04.034
A case report of TAFRO syndrome
ZHOU Guang-ping1,ZHOU Qian-yun2,Δ( ),ZHU Ji-hong1
),ZHU Ji-hong1
- 1. Department of Emergency, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
2. Intensive Care Unit, Peking University Shougang Hospital, Beijing 100144, China
CLC Number:
- R692.5
| [1] |
Takai K, Nikkuni K, Momoi A, et al. Thrombocytopenia with reticulin fibrosis accompanied by fever, anasarca and hepatosplenomegaly: A clinical report of five cases [J]. J Clin Exp Hematop, 2013, 53(1):63-68.
doi: 10.3960/jslrt.53.63 |
| [2] |
Castleman B, Towne VW. Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital: Case No.40231 [J]. N Engl J Med, 1954, 250(23):1001-1005.
doi: 10.1056/NEJM195406102502308 |
| [3] |
Castleman B, Iverson L, Menendez VP. Localized mediastinal lymphnode hyperplasia resembling thymoma [J]. Cancer, 1956, 9(4):822-830.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1097-0142 |
| [4] |
Kojima M, Nakamura S, Nishikawa M, et al. Idiopathic multicentric Castleman’s disease. A clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of five cases [J]. Pathol Res Pract, 2005, 201(4):325-332.
doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2005.01.006 |
| [5] |
Kojima M, Nakamura N, Tsukamoto N, et al. Clinical implications of idiopathic multi centric castleman disease among Japanese: A report of 28 cases [J]. Int J Surg Pathol, 2008, 16(4):391-398.
doi: 10.1177/1066896908315812 |
| [6] |
Fajgenbaum DC, Uldrick TS, Bagg A, et al. International, evidence-based consensus diagnostic criteria for HHV-8-negative/idiopathic multicentric Castleman disease [J]. Blood, 2017, 129(12):1646-1657.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-10-746933 pmid: 28087540 |
| [7] |
Iwaki N, Fajgenbaum DC, Nabel CS, et al. Clinicopathologic analysis of TAFRO syndrome demonstrates a distinct subtype of HHV-8-negative multicentric Castleman disease [J]. Am J Hematol, 2016, 91(2):220-226.
doi: 10.1002/ajh.24242 |
| [8] |
Igawa T, Sato Y. TAFRO syndrome [J]. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am, 2018, 32(1):107-118.
doi: 10.1016/j.hoc.2017.09.009 |
| [9] |
Masaki Y, Kawabata H, Takai K, et al. Proposed diagnostic criteria, disease severity classification and treatment strategy for TAFRO syndrome [J]. Int J Hematol, 2016, 103(6):686-692.
doi: 10.1007/s12185-016-1979-1 |
| [10] |
Kikuchi T, Shimizu T, Toyama T, et al. Successful treatment of TAFRO syndrome with tocilizumab, prednisone, and cyclophosphamide [J]. Intern Med, 2017, 56(16):2205-2211.
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.8522-16 |
| [11] |
Yamaga Y, Tokuyama K, Kato T, et al. Successful treatment with cyclosporin A in tocilizumab-resistant TAFRO syndrome [J]. Intern Med, 2016, 55(2):185-190.
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.55.4710 |
| [12] |
Shirai T, Onishi A, Waki D, et al. Successful treatment with tacrolimus in TAFRO syndrome [J]. Medicine, 2018, 97(23):e11045.
doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000011045 |
| [13] | 王素霞, 邹古明, 章友康, 等. Castleman病肾损害的临床病理分析 [J]. 中华肾脏病杂志, 2009, 25(8):585-590. |
| [14] |
Kawashima M, Usui T, Okada H, et al. TAFRO syndrome: 2 cases and review of the literature [J]. Mod Rheumatol, 2017, 27(6):1093-1097.
doi: 10.3109/14397595.2015.1059982 pmid: 26052800 |
| [1] | Jia-xin PAN,Sai-nan ZHU,Shuang-ling LI,Dong-xin WANG. Factors associated with long-term survival in critically ill patients following surgery for solid tumors complicated with paraneoplastic pemphigus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(5): 981-990. |
| [2] | AN Wen-cheng,YAN Hui-xian,DENG Zheng-zhao,CHEN Fang,OU Xiao-hong,JIN Hong-xin,HUANG Wei. Chronic kidney disease after adrenalectomy in a patient with primary aldosteronism [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(6): 1201-1204. |
| [3] | ZHANG Lei,LI Guo-liang,DANG Zong-hui, ,A yong,WU Ling-jie,LIU Li-jun. Analysis of bleeding risk in percutaneous renal biopsy in Tibet [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(2): 298-301. |
| [4] | LI Xi-hui, XIAO Feng, ZHANG Si-yu. Investigation of risk factors of acute kidney injury after off-pump coronary artery bypass grafting and 3 years’ follow-up [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(1): 131-136. |
|
||