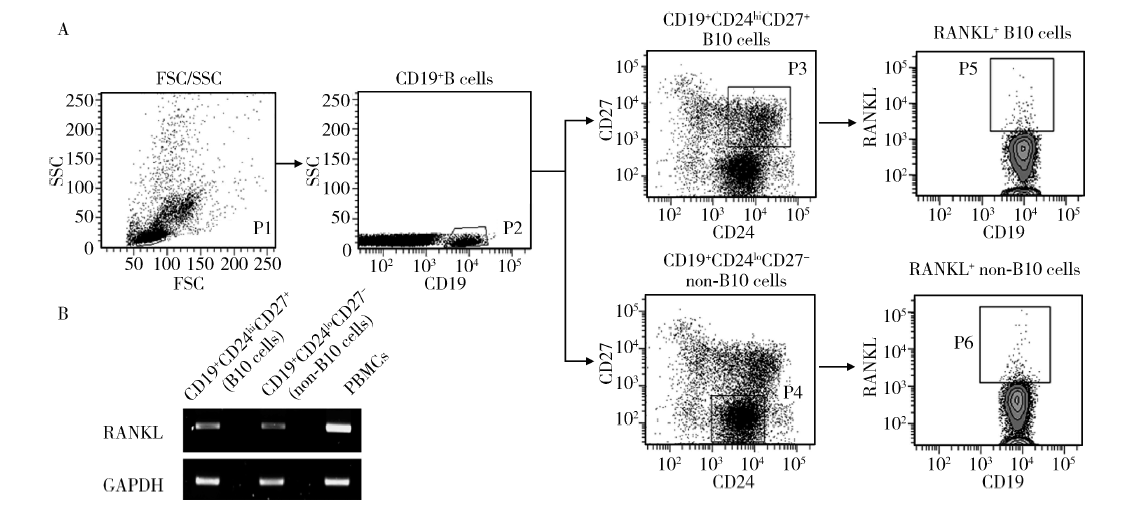
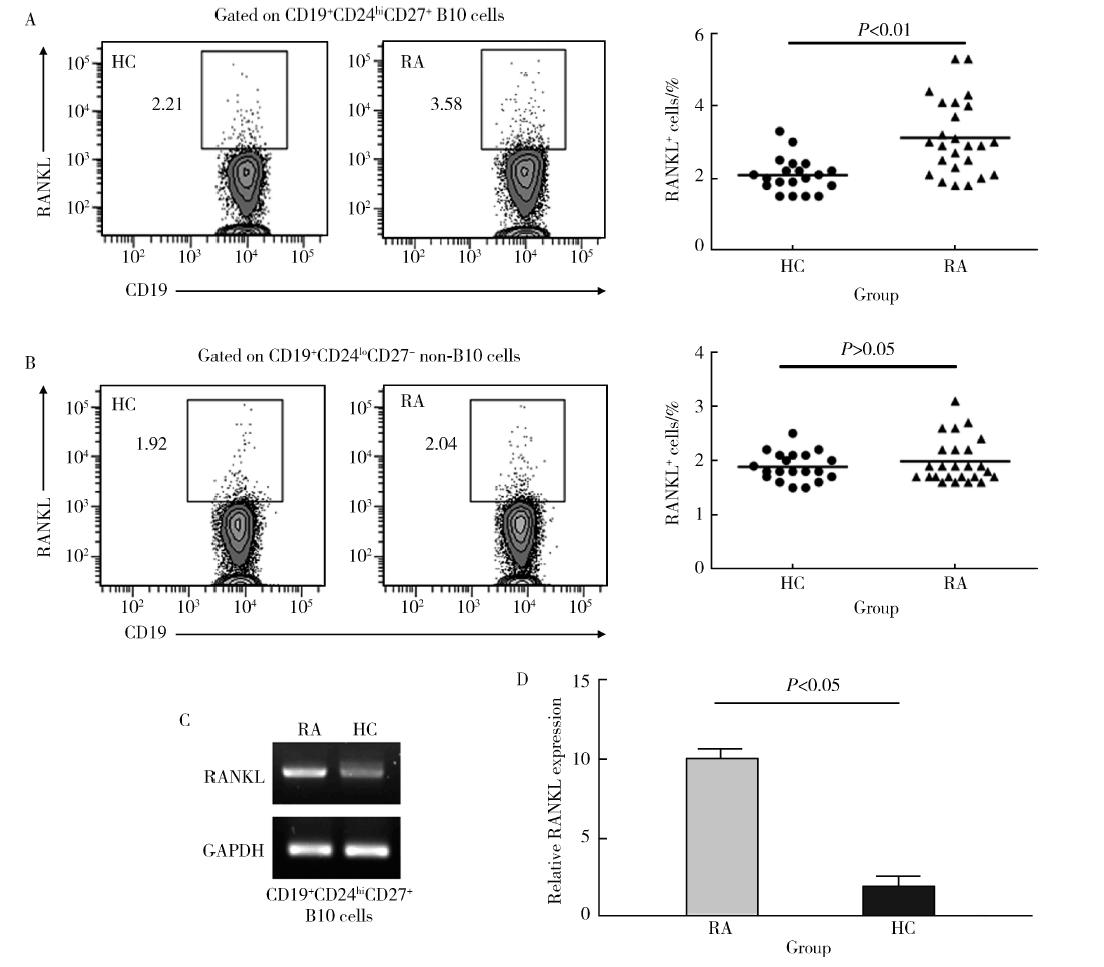
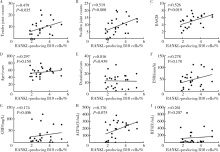
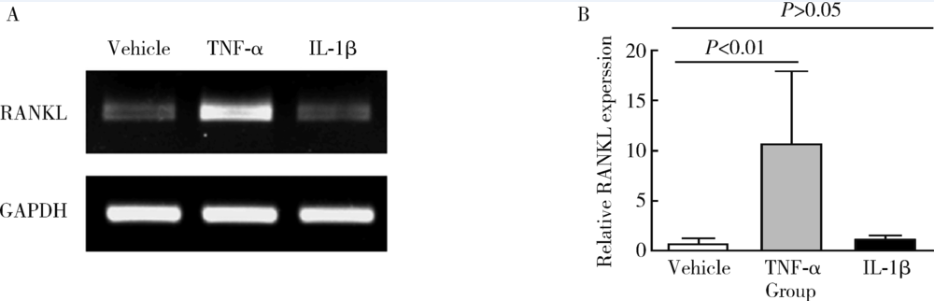
Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences) ›› 2018, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (6): 968-974. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2018.06.005
• Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Increased receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand expressed on B10 cells in rheumatoid arthritis
Hong jiang LIU1,Xiao feng GUO1,Fan lei HU2,Cui ping YAN1,Xiang jun CUI1,Xue liang YAN1,Zhan guo LI2,Yuan JIA2,△( ),Shu lin ONG1,△(
),Shu lin ONG1,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology,the People’s Hospital of China Three Gorges University,Yichang 443000, Hubei, China
2. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
CLC Number:
- R593.22
| [1] |
Mauri C, Bosma A . Immune regulatory function of B cells[J]. Annu Rev Immunol, 2012,30:221-241.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-020711-074934 pmid: 22224776 |
| [2] |
Kalampokis I, Yoshizaki A, Tedder TF . IL-10-producing regulatory B cells (B10 cells) in autoimmune disease[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2013,15(Suppl. 1):S1.
doi: 10.1186/ar3907 pmid: 3624502 |
| [3] |
Iwata Y, Matsushita T, Horikawa M , et al. Characterization of a rare IL-10-competent B-cell subset in humans that parallels mouse regulatory B10 cells[J]. Blood, 2011,117(2):530-541.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-07-294249 |
| [4] |
Rosser EC, Mauri C . Regulatory B cells: origin, phenotype, and function[J]. Immunity, 2015,42(4):607-612.
doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.04.005 pmid: 25902480 |
| [5] |
Daien CI, Gailhac S, Mura T , et al. Regulatory B10 cells are decreased in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and are inversely correlated with disease activity[J]. Arthritis Rheumatol, 2014,66(8):2037-2046.
doi: 10.1002/art.38666 pmid: 24729478 |
| [6] |
Ma L, Liu B, Jiang Z , et al. Reduced numbers of regulatory B cells are negatively correlated with disease activity in patients with new-onset rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Clin Rheumatol, 2014,33(2):187-195.
doi: 10.1007/s10067-013-2359-3 pmid: 23949637 |
| [7] |
Cui D, Zhang L, Chen J , et al. Changes in regulatory B cells and their relationship with rheumatoid arthritis disease activity[J]. Clin Exp Med, 2015,15(3):285-292.
doi: 10.1007/s10238-014-0310-9 pmid: 25245953 |
| [8] |
Hirayama T, Danks L, Sabokbar A , et al. Osteoclast formation and activity in the pathogenesis of osteoporosis in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2002,41(11):1232-1239.
doi: 10.1097/00003072-199902000-00015 pmid: 12421995 |
| [9] | Gravallese EM, Harada Y, Wang JT , et al. Identification of cell types responsible for bone resorption in rheumatoid arthritis and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Am J Pathol, 1998,152(4):943-951. |
| [10] |
Kong YY, Yoshida H, Sarosi I , et al. OPGL is a key regulator of osteoclastogenesis, lymphocyte development and lymph-node organogenesis[J]. Nature, 1999,397(6717):315-323.
doi: 10.1038/16852 |
| [11] |
Schett G, Gravallese E . Bone erosion in rheumatoid arthritis: mechanisms, diagnosis and treatment[J]. Nat Rev Rheumatol, 2012,8(11):656-664.
doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2012.153 pmid: 23007741 |
| [12] |
Gravallese EM, Manning C, Tsay A , et al. Synovial tissue in rheumatoid arthritis is a source of osteoclast differentiation factor[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2000,43(2):250-258.
doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200002)43:2<250::AID-ANR3>3.0.CO;2-P |
| [13] |
Yeo L, Toellner KM, Salmon M , et al. Cytokine mRNA profiling identifies B cells as a major source of RANKL in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2011,70(11):2022-2028.
doi: 10.1136/ard.2011.153312 pmid: 21742639 |
| [14] |
Yeo L, Lom H, Juarez M , et al. Expression of FcRL4 defines a pro-inflammatory, RANKL-producing B cell subset in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2015,74(5):928-935.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204116 pmid: 24431391 |
| [15] |
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA , et al. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 1988,31(3):315-324.
doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302 pmid: 3358796 |
| [16] |
Keystone E, Emery P, Peterfy CG , et al. Rituximab inhibits structural joint damage in patients with rheumatoid arthritis with an inadequate response to tumour necrosis factor inhibitor therapies[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2009,68(2):216-221.
doi: 10.1136/ard.2007.085787 pmid: 18388156 |
| [17] |
Wheater G, Hogan VE, Teng YK , et al. Suppression of bone turnover by B-cell depletion in patients with rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Osteoporos Int, 2011,22(12):3067-3072.
doi: 10.1007/s00198-011-1607-0 pmid: 21625887 |
| [18] |
Boumans MJ, Thurlings RM, Yeo L , et al. Rituximab abrogates joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis by inhibiting osteoclastogenesis[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2012,71(1):108-113.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-200198 pmid: 22072013 |
| [19] |
Harre U, Georgess D, Bang H , et al. Induction of osteoclasto-genesis and bone loss by human autoantibodies against citrullinated vimentin[J]. J Clin Invest, 2012,122(5):1791-1802.
doi: 10.1172/JCI60975 pmid: 3336988 |
| [20] |
Bugatti S, Caporali R, Manzo A , et al. Involvement of subchondral bone marrow in rheumatoid arthritis: lymphoid neogenesis and in situ relationship to subchondral bone marrow osteoclast recruitment[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2005,52(11):3448-3459.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1529-0131 |
| [21] |
Meednu N, Zhang H, Owen T , et al. Production of RANKL by memory B cells: a link between B cells and bone erosion in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Arthritis Rheumatol, 2016,68(4):805-816.
doi: 10.1002/art.39489 pmid: 26554541 |
| [22] |
Kobayashi K, Takahashi N, Jimi E , et al. Tumor necrosis factor alpha stimulates osteoclast differentiation by a mechanism independent of the ODF/RANKL-RANK interaction[J]. J Exp Med, 2000,191(2):275-286.
doi: 10.1084/jem.191.2.275 |
| [23] | Kitaura H, Kimura K, Ishida M , et al. Immunological reaction in TNF-alpha-mediated osteoclast formation and bone resorption in vitro and in vivo[J]. Clin Dev Immunol, 2013,2013:181849. |
| [24] | Heider U, Langelotz C, Jakob C , et al. Expression of receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand on bone marrow plasma cells correlates with osteolytic bone disease in patients with multiple myeloma[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2003,9(4):1436-1440. |
| [25] |
Han X, Kawai T, Eastcott JW , et al. Bacterial-responsive B lymphocytes induce periodontal bone resorption[J]. J Immunol, 2006,176(1):625-631.
doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.1.625 |
| [26] |
Onal M, Xiong J, Chen X , et al. Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand (RANKL) protein expression by B lymphocytes contributes to ovariectomy-induced bone loss[J]. J Biol Chem, 2012,287(35):29851-29860.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.377945 pmid: 3436192 |
| [27] |
Titanji K, Vunnava A, Sheth AN , et al. Dysregulated B cell expression of RANKL and OPG correlates with loss of bone mineral density in HIV infection[J]. PLoS Pathog, 2014,10(11):e1004497.
doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004497 pmid: 4231117 |
| [28] |
Manabe N, Kawaguchi H, Chikuda H , et al. Connection between B lymphocyte and osteoclast differentiation pathways[J]. J Immunol, 2001,167(5):2625-2631.
doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.167.5.2625 |
| [29] |
Pugliese LS, Goncalves TO, Popi AF , et al. B-1 lymphocytes differentiate into functional osteoclast-like cells[J]. Immunobiology, 2012,217(3):336-344.
doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2011.07.014 pmid: 21855167 |
| [30] |
Carter NA, Rosser EC, Mauri C . Interleukin-10 produced by B cells is crucial for the suppression of Th17/Th1 responses, induction of T regulatory type 1 cells and reduction of collagen-induced arthritis[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2012,14(1):R32.
doi: 10.1186/ar3736 pmid: 3392827 |
| [31] |
Yang M, Deng J, Liu Y , et al. IL-10-producing regulatory B10 cells ameliorate collagen-induced arthritis via suppressing Th17 cell generation[J]. Am J Pathol, 2012,180(6):2375-2385.
doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.03.010 |
| [1] | HAN Jie, CHEN Zhi-Bin, LI Wei, MENG Huan-Xin. Determination of bone metabolic marker levels in perio-implant crevicular fluid and analysis of dental implants stability by resonance frequency in the early stage of healing [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2015, 47(1): 37-41. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 393
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 1182
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cited |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shared | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discussed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||