Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (3): 586-590. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.03.029
Previous Articles Next Articles
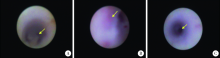
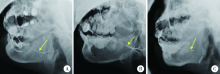
Inflammation grading and sialoendoscopic treatment of131I radioiodine-induced sialadenitis
Xiao LI1,Jia-zeng SU1,Yan-yan ZHANG1,Li-qi ZHANG2,Ya-qiong ZHANG2,Deng-gao LIU2,△( ),Guang-yan YU1,△(
),Guang-yan YU1,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
2. Department of Oral Radiology, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
CLC Number:
- R781.7
| [1] | van Nostrand D. The benefits and risks of I-131 therapy in patients with well-differentiated thyroid cancer[J]. Thyroid, 2009,19(12):1381-1391. |
| [2] | Lu L, Shan F, Li W, et al. Short-term side effects after radioiodine treatment in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2016,2016(9):1-5. |
| [3] | De Luca R, Vicidomini A, Trodella M, et al. Sialoendoscopy: A viable treatment for I131 induced sialoadenitis [J]. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2014,52(7):641-646. |
| [4] | 柳登高, 郭玉娇, 姜岚, 等. 43例慢性阻塞性腮腺炎内镜治疗疗效观察[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2012,47(9):81-84. |
| [5] | Ish-Shalom S, Durleshter L, Segal E, et al. Sialochemical and oxidative analyses in radioactive131I-treated patients with thyroid carcinoma [J]. Eur J Endocrinol, 2008,158(5):677-681. |
| [6] | Badam RK, Suram J, Babu DB, et al. Assessment of salivary gland function using salivary scintigraphy in pre and post radioactive iodine therapy in diagnosed thyroid carcinoma patients[J]. J Clin Diagn Res, 2016,10(1):60-62. |
| [7] | Ali MJ. Iodine-131 therapy and nasolacrimal duct obstructions: What we know and what we need to know[J]. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg, 2016,32(4):243-248. |
| [8] | Maruoka Y, Baba S, Isoda T, et al. A functional scoring system based on salivary gland scintigraphy for evaluating salivary gland dysfunction secondary to 131I therapy in patients with differentiated thyroid carcinoma [J]. J Clin Diagn Res, 2017, 11(8): TC23-TC28. |
| [9] |
Jarzab B, Handkiewicz-Junak D, Wloch J. Juvenile differentiated thyroid carcinoma and the role of radioiodine in its treatment: a qualitative review[J]. Endocr Relat Cancer, 2005,12(4):773-803.
pmid: 16322322 |
| [10] | Wu CB, Xi H, Zhou Q, et al. Sialendoscopy-assisted treatment for radioiodine-induced sialadenitis[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2015,73(3):475-481. |
| [11] |
Allweiss P, Braunstein GD, Katz A, et al. Sialadenitis following131I therapy for thyroid carcinoma: Concise communication [J]. J Nucl Med, 1984,25(7):755-758.
pmid: 6737074 |
| [12] |
Silberstein EB. Reducing the incidence of131I-induced sialadenitis: the role of pilocarpine [J]. J Nucl Med, 2008,49(4):546-549.
doi: 10.2967/jnumed.107.049411 pmid: 18344428 |
| [13] | Ko KY, Kao CH, Lin CL, et al. 131I treatment for thyroid cancer and the risk of developing salivary and lacrimal gland dysfunction and a second primary malignancy: A nationwide population-based cohort study [J]. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imag, 2015,42(8):1172-1178. |
| [14] | Chow S. Side effects of high-dose radioactive iodine for ablation or treatment of differentiated thyroid carcinoma[J]. J HK Coll Radiol, 2005(8):127-135. |
| [15] |
Malpani BL, Samuel AM, Ray S. Quantification of salivary gland function in thyroid cancer patients treated with radioiodine[J]. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 1996,35(3):535-540.
pmid: 8655377 |
| [16] |
Geres AE, Mereshian PS, Fernández S, et al. Sialadenitis after radioiodine therapy: Analysis of factors that influence the response to medical treatment[J]. Endocrinol Nutr, 2015,62(10):493-498.
pmid: 26459118 |
| [17] |
Wu JQ, Feng HJ, Ouyang W, et al. Systematic evaluation of salivary gland damage following I-131 therapy in differentiated thyroid cancer patients by quantitative scintigraphy and clinical follow-up[J]. Nucl Med Commun, 2015,36(8):819.
doi: 10.1097/MNM.0000000000000325 pmid: 25932534 |
| [18] | Nahlieli O, Nazarian Y. Sialadenitis following radioiodine therapy a new diagnostic and treatment modality[J]. Oral Disease, 2006,12(5):476-479. |
| [19] |
Gonzalez ME, Muttikkal TJ, Rehm PK. Sialadenitis following low dose I-131 diagnostic thyroid scan with Thyrogen® (recombinant human thyroid stimulating hormone-thyrotropin alfa) [J]. J Radiol Case Rep, 2015,9(6):44-49.
pmid: 26622936 |
| [20] | Prendes BL, Orloff LA, Eisele DW. Therapeutic sialendoscopy for the management of radioiodine sialadenitis[J]. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2012,138(1):15-19. |
| [1] | Xinxin CHEN, Zhe TANG, Yanchun QIAO, Wensheng RONG. Caries experience and its correlation with caries activity of 4-year-old children in Miyun District of Beijing [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 833-838. |
| [2] | Hua ZHONG, Yuan LI, Liling XU, Mingxin BAI, Yin SU. Application of 18F-FDG PET/CT in rheumatic diseases [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 853-859. |
| [3] | Zhengfang LI,Cainan LUO,Lijun WU,Xue WU,Xinyan MENG,Xiaomei CHEN,Yamei SHI,Yan ZHONG. Application value of anti-carbamylated protein antibody in the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 729-734. |
| [4] | Wenjing LI,Baozhou ZHANG,Heng LI,Liangpeng LAI,Hui DU,Ning SUN,Xiaofeng GONG,Ying LI,Yan WANG,Yong WU. Tibiotalocalcaneal arthrodesis for end-stage ankle and hindfoot arthropathy: Short- and mid-term clinical outcomes [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 299-306. |
| [5] | Xue ZOU,Xiao-juan BAI,Li-qing ZHANG. Effectiveness of tofacitinib combined with iguratimod in the treatment of difficult-to-treat moderate-to-severe rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1013-1021. |
| [6] | Hai-hong YAO,Fan YANG,Su-mei TANG,Xia ZHANG,Jing HE,Yuan JIA. Clinical characteristics and diagnostic indicators of macrophage activation syndrome in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and adult-onset Still's disease [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 966-974. |
| [7] | Min QIU,You-long ZONG,Bin-shuai WANG,Bin YANG,Chu-xiao XU,Zheng-hui SUN,Min LU,Lei ZHAO,Jian LU,Cheng LIU,Xiao-jun TIAN,Lu-lin MA. Treatment outcome of laparoscopic partial nephrectomy in patients with renal tumors of moderate to high complexity [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 833-837. |
| [8] | Lei WANG,Tian-dong HAN,Wei-xing JIANG,Jun LI,Dao-xin ZHANG,Ye TIAN. Comparison of safety and effectiveness of active migration technique and in situ lithotripsy technique in the treatment of 1-2 cm upper ureteral calculi by flexible ure-teroscopy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(3): 553-557. |
| [9] | Yan XIONG,Xin LI,Li LIANG,Dong LI,Li-min YAN,Xue-ying LI,Ji-ting DI,Ting LI. Evaluation of accuracy of pathological diagnosis based on thyroid core needle biopsy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 234-242. |
| [10] | Xue-mei HA,Yong-zheng YAO,Li-hua SUN,Chun-yang XIN,Yan XIONG. Solid placental transmogrification of the lung: A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 357-361. |
| [11] | Bo-han NING,Qing-xia ZHANG,Hui YANG,Ying DONG. Endometrioid adenocarcinoma with proliferated stromal cells, hyalinization and cord-like formations: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 366-369. |
| [12] | Rui-jie CAO,Zhong-qiang YAO,Peng-qing JIAO,Li-gang CUI. Comparison of diagnostic efficacy of different classification criteria for Takayasu arteritis in Chinese patients [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1128-1133. |
| [13] | Guang-yan YU,Jia-zeng SU,Deng-gao LIU,Li-ling WU,Xin CONG. Establishment and application of new techniques for submandibular gland preservation [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(5): 842-845. |
| [14] | Zhe HAO,Shu-hua YUE,Li-qun ZHOU. Application of Raman-based technologies in the detection of urological tumors [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(4): 779-784. |
| [15] | Bo YU,Yang-yu ZHAO,Zhe ZHANG,Yong-qing WANG. Infective endocarditis in pregnancy: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(3): 578-580. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 328
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 1296
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cited |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shared | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discussed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||