Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (4): 678-683. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.04.015
Previous Articles Next Articles
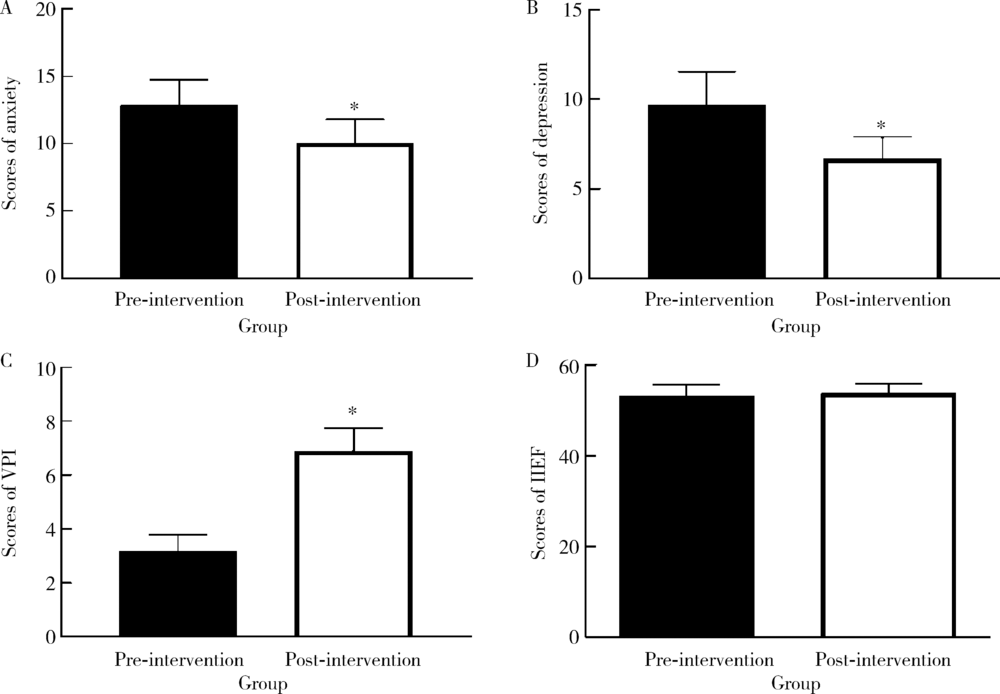
Decision regret analysis among Chinese patients receiving penile girth enhancement with acellular dermal matrix
Chun-long ZHANG,He LI,Qing LI,Wen-jun BAI,Tao XU,Xiao-wei ZHANG( )
)
- Department of Urology, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
CLC Number:
- R699.8
| [1] |
Tiggemann M, Martins Y, Churchett L. Beyond muscles: unexplored parts of men's body image[J]. J Health Psychol, 2008,13(8):1163-1172.
pmid: 18987089 |
| [2] | Lever J, Frederick DA, Peplau LA. Does size matter? Men’s and women’s views on penis size across the lifespan[J]. Psychol Men Masc, 2006,7(3):129. |
| [3] | Hehemann MC, Towe M, Huynh LM, et al. Penile girth enlargement strategies: What’s the evidence[J]. Sex Med Rev, 2019,7(3):535-547. |
| [4] | Svenson O. Differentiation and consolidation theory of human decision making: a frame of reference for the study of pre- and post-decision Processes[J]. Acta Psychol (Amst), 1992,80(1):143-168. |
| [5] | Zeelenberg M, Pieters R. A Theory of regret regulation 1.0[J]. J Consum Psychol, 2007,17(1):3-18. |
| [6] |
Wilson A, Ronnekleiv-Kelly SM, Pawlik TM. Regret in surgical decision making: a systematic review of patient and physician perspectives[J]. World J Surg, 2017,41(6):1454-1465.
pmid: 28243695 |
| [7] |
Yamauchi K, Nakao M, Nakashima M. Correlates of regret with treatment decision-making among Japanese women with breast cancer: results of an internet-based cross-sectional survey[J]. BMC Womens Health, 2019,19(1):86.
doi: 10.1186/s12905-019-0783-5 pmid: 31266493 |
| [8] |
Wang AW, Chang SM, Chang CS, et al. Regret about surgical decisions among early-stage breast cancer patients: Effects of the congruence between patients’ preferred and actual decision-making roles[J]. Psychooncology, 2018,27(2):508-514.
doi: 10.1002/pon.4522 pmid: 28792651 |
| [9] | Spyropoulos E, Christoforidis C, Borousas D, et al. Augmentation phalloplasty surgery for penile dysmorphophobia in young adults: considerations regarding patient selection, outcome evaluation and techniques applied[J]. Eur Urol, 2005,48(1):121-128 |
| [10] |
Xu T, Zhang G, Bai W, et al. Complications and management of penile girth enhancement with acellular dermal matrix[J]. J Sex Med, 2019,16(12):2011-2017.
doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2019.09.010 pmid: 31668731 |
| [11] |
Brehaut JC, O'Connor AM, Wood TJ, et al. Validation of a decision regret scale[J]. Med Decis Making, 2003,23(4):281-292.
doi: 10.1177/0272989X03256005 pmid: 12926578 |
| [12] |
Zhong T, Bagher S, Jindal K, et al. The influence of dispositional optimism on decision regret to undergo major breast reconstructive surgery[J]. J Surg Oncol, 2013,108(8):526-530.
doi: 10.1002/jso.23437 pmid: 24105811 |
| [13] |
Zigmond AS, Snaith RP. The hospital anxiety and depression scale[J]. Acta Psychiatr Scand, 1983,67(6):361-370.
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1983.tb09716.x pmid: 6880820 |
| [14] |
Bjelland I, Dahl AA, Haug TT, et al. The validity of the hospital anxiety and distress scale[J]. J Psychosom Res, 2002,52(2):69-77.
pmid: 11832252 |
| [15] | Leung CM, Ho S, Kan CS, et al. Evaluation of the Chinese version of the hospital anxiety and depression scale. A cross-cultural perspective[J]. Int J Psychosom, 1993,40(1/2/3/4):29-34. |
| [16] |
Yafi FA, Huynh LM, Ahlering T, et al. What is a “Validated Questionnaire”? A critical review of erectile function assessment[J]. J Sex Med, 2020,17(5):849-860.
doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2020.02.005 pmid: 32146130 |
| [17] |
Chen XB, Li RX, Yang HN, et al. A comprehensive, prospective study of penile dimensions in Chinese men of multiple ethnicities[J]. Int J Impot Res, 2014,26(5):172-176.
doi: 10.1038/ijir.2014.9 |
| [18] |
Vardi Y, Har-Shai Y, Gil T, et al. A critical analysis of penile enhancement procedures for patients with normal penile size: surgical techniques, success, and complications[J]. Eur Urol, 2008,54(5):1042-1050.
pmid: 18760874 |
| [19] |
Sheehan J, Sherman KA, Lam T, et al. Association of information satisfaction, psychological distress and monitoring coping style with post-decision regret following breast reconstruction[J]. Psychooncology, 2007,16(4):342-351.
doi: 10.1002/pon.1067 pmid: 16874745 |
| [20] |
Calderon C, Ferrando PJ, Lorenzo-Seva U, et al. Validity and reliability of the decision regret scale in cancer patients receiving adjuvant chemotherapy[J]. J Pain Symptom Manage, 2019,57(4):828-834.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2018.11.017 pmid: 30639730 |
| [21] |
Shaverdian N, Kishan AU, Veruttipong D, et al. Impact of the primary information source used for decision making on treatment perceptions and regret in prostate cancer[J]. Am J Clin Oncol, 2018,41(9):898-904.
doi: 10.1097/COC.0000000000000387 pmid: 28537990 |
| [22] |
Schumacher JR, Taylor LJ, Tucholka JL, et al. Socioeconomic factors associated with post-mastectomy immediate reconstruction in a contemporary cohort of breast cancer survivors[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2017,24(10):3017-3023.
doi: 10.1245/s10434-017-5933-0 pmid: 28766209 |
| [23] | 谌绍林, 丁敏, 朱健华, 等. 护士评判性思维能力的调查及其相关因素分析[J]. 中华现代护理杂志, 2011,17(11):1241-1244. |
| [24] | 石霞, 刘玉玲, 封锡玲. 护理人员获取网络资源信息的能力调查[J]. 护理学杂志, 2008,23(2):14-15. |
| [1] | Zhong-cheng XIN,Bi-cheng YANG,Meng LI,Yi-ming YUAN,Wan-shou CUI,Yuan TANG,Dong FANG,Wei-dong SONG. Appllication of human acellular dermal matrix in surgical treatment of genitourinary disease [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(4): 778-782. |
| [2] | Ting-min XU,Xiao-wei ZHANG,Guo-xi ZHANG,Wen-jun BAI,Qing LI,Tao XU. Complications and management for penile augmentation with acellular dermal matrix [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(4): 636-640. |
|
||