Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (5): 870-874. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.05.012
Previous Articles Next Articles
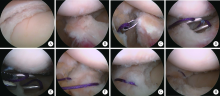
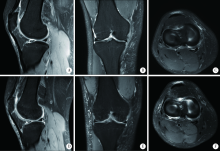
A mid-term clinical follow-up study on repair of the meniscus tears by a modified arthroscopic outside-in puncture suture technique
Zhong-di LIU,Ting-min XU,Yu DANG( ),Dian-ying ZHANG,Zhong-guo FU
),Dian-ying ZHANG,Zhong-guo FU
- Trauma Medicine Center, Department of Trauma and Orthopaedics, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
CLC Number:
- R684
| [1] |
Kurzweil PR, Cannon WD, DeHaven KE. Meniscus repair and replacement[J]. Sports Med Arthrosc Rev, 2018,26(4):160-164.
doi: 10.1097/JSA.0000000000000224 pmid: 30395058 |
| [2] |
Vaquero-Picado A, Rodríguez-Merchín EC. Arthroscopic repair of the meniscus: surgical management and clinical outcomes[J]. EFORT Open Rev, 2018,3(11):584-594.
doi: 10.1302/2058-5241.3.170059 pmid: 30595844 |
| [3] |
Karia M, Ghaly Y, Al-Hadithy N, et al. Current concepts in the techniques, indications and outcomes of meniscal repairs[J]. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol, 2019,29(3):509-520.
doi: 10.1007/s00590-018-2317-5 pmid: 30374643 |
| [4] |
Steiner S, Feeley SM, Ruland JR, et al. Outside-in repair technique for a complete radial tear of the lateral meniscus[J]. Arthrosc Tech, 2018,7(3):e285-e288.
doi: 10.1016/j.eats.2017.09.006 pmid: 29881702 |
| [5] |
Barrett GR, Treacy SH, Ruff CG. Preliminary results of the T-fix endoscopic meniscus repair technique in an anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction population[J]. Arthroscopy, 1997,13(2):218-223.
doi: 10.1016/s0749-8063(97)90157-2 pmid: 9127080 |
| [6] |
Lysholm J, Gillquist J. Evaluation of knee ligament surgery results with special emphasis on use of a scoring scale[J]. Am J Sports Med, 1982,10(3):150-154.
doi: 10.1177/036354658201000306 pmid: 6896798 |
| [7] |
Fox AJ, Wanivenhaus F, Burge AJ, et al. The human meniscus: a review of anatomy, function, injury, and advances in treatment[J]. Clin Anat, 2015,28(2):269-287.
doi: 10.1002/ca.22456 pmid: 25125315 |
| [8] |
Ouyang X, Wei B, Hong SD, et al. Arthroscopic characteristics of normal and discoid meniscus injury, and efficiency of recovery in each type of meniscus injury[J]. Cell Biochem Biophys, 2015,72(2):433-437.
doi: 10.1007/s12013-014-0483-6 pmid: 25572056 |
| [9] |
Badlani JT, Borrero C, Golla S, et al. The effects of meniscus injury on the development of knee osteoarthritis: data from the osteoarthritis initiative[J]. Am J Sports Med, 2013,41(6):1238-1244.
pmid: 23733830 |
| [10] |
Rai MF, Brophy RH, Sandell LJ. Osteoarthritis following meniscus and ligament injury: insights from translational studies and animal models[J]. Curr Opin Rheumatol, 2019,31(1):70-79.
doi: 10.1097/BOR.0000000000000566 pmid: 30394938 |
| [11] |
Rai MF, McNulty AL. Meniscus beyond mechanics: Using biology to advance our understanding of meniscus injury and treatment[J]. Connect Tissue Res, 2017,58(3/4):221-224.
doi: 10.1080/03008207.2017.1312921 |
| [12] |
Twomey-Kozak J, Jayasuriya CT. Meniscus repair and regeneration: a systematic review from a basic and translational science perspective[J]. Clin Sports Med, 2020,39(1):125-163.
doi: 10.1016/j.csm.2019.08.003 pmid: 31767102 |
| [13] | Muniandy M, Rajagopal S, Tahir SH. Arthroscopic all-inside repair of tear of the anterior horn of discoid lateral meniscus[J]. Surg J (NY), 2019,5(1):e35-e37. |
| [14] |
Muckenhirn KJ, Kruckeberg BM, Cinque ME, et al. Arthroscopic inside-out repair of a meniscus bucket-handle tear augmented with bone marrow aspirate concentrate[J]. Arthrosc Tech, 2017,6(4):e1221-e1227.
doi: 10.1016/j.eats.2017.04.014 pmid: 29354421 |
| [15] |
Marinescu R, Laptoiu D, Negrusoiu M. Outside-in meniscus suture technique: 5 years' follow-up[J]. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc, 2003,11(3):167-172.
doi: 10.1007/s00167-003-0347-x pmid: 12774154 |
| [1] | Jiangjing WANG,Shunyi WEI,Yingfang AO,Yuping YANG. Comparison of the early analgesic efficacy of three different drugs after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 293-298. |
| [2] | Zhen-xing SHAO,Qing-fa SONG,Yu-qing ZHAO,Guo-qing CUI. An arthroscopic “inlay” Bristow procedure with suture button fixation: Surgical technique and radiology evaluation [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(5): 896-901. |
| [3] | Jia-peng ZHENG,Qi XIAO,Hui-yun DENG,Qing-quan WU,Wen-liang ZHAI,Da-sheng LIN. Arthroscopic classification and management for the popliteal hiatus of the lateral meniscus tears [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(5): 891-895. |
| [4] | Hao WU,Li-ping PAN,Heng LIU,Hong-bin WANG,Tai-guo NING,Yong-ping CAO. Effect of posterior tibial slope on the short-term outcome in mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(5): 877-882. |
| [5] | Dong JIANG,Yue-lin HU,Chen JIAO,Qin-wei GUO,Xing XIE,Lin-xin CHEN,Feng ZHAO,Yan-bin PI. Mid-to-long term outcomes and influence factors of postoperative concurrent chronic ankle instability and posterior ankle impingement [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(3): 505-509. |
| [6] | Cui-ping ZHANG,Pei-pei LIU,Qiang FU,Guan-ying GAO,Li-gang CUI,Yan XU,Jian-quan WANG. Application of ultrasound-guided hip joint drug injection in the postoperative rehabilitation of arthroscopie repair of acetabular labral tears [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(2): 265-267. |
| [7] | ZHANG Hui, LIU Xin, HONG Lei, GENG Xiang-su, FENG Hua. Arthroscopic all-inside reconstruction for posterior cruciate ligament and popliteus tendon compared with popliteofibular ligament reconstruction: clinical outcome of minimum 2-year follow-up [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2016, 48(2): 237-243. |
| [8] | LIU Bo, CHEN Shan-lin, ZHU Jin, WANG Zhi-xin, YANG Chen, SHEN Jie, TIAN Guan-lei. Arthroscopic management of lesser arc perilunate injuries [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2016, 48(2): 234-236. |
| [9] | HUANG Hong-shi, JIANG Yan-fang, YANG Jie, YU Yuan-yuan, WANG Yi, XU Yan, AO Ying-fang. Effect of anterior cruciate ligament rupture on hamstring∶quadriceps ratio during isokinetic knee extension and flexion at 30 degrees of flexion [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2015, 47(5): 787-790. |
| [10] | WU Guan, JIANG Chun-Yan, LU Yi, ZHU Yi-Ming, LI Feng-Long, LI Xu. Modified arthroscopic Latarjet procedure for the treatment of anterior shoulder instability [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2015, 47(2): 321-325. |
| [11] | LI Feng-Long, JIANG Chun-Yan, LU Yi, ZHU Yi-Ming, LI Xu. Arthroscopic coracoclavicular ligament reconstruction versus open modified Weaver-Dunn procedure for acromioclavicular joint dislocations:comparison of curative effect [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2015, 47(2): 253-257. |
|
||