Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (6): 1001-1008. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.06.003
Previous Articles Next Articles
Comparison of clinical and immunological features between clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis and typical dermatomyositis
Yu-zhou GAN1,Yu-hui LI1,Li-hua ZHANG2,Lin MA3,Wen-wen HE4,Yue-bo JIN1,Yuan AN1,Zhan-guo LI1,Hua YE1,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Rheumatology & Immunology, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
2. Department of Rheumatology, Hulunbeier People’s Hospital, Hulunbeier 021008, Inner Mongolia, China
3. Department of Rheumatology, Hebei Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shijiazhuang 050200, China
4. Department of Endocrinology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing 400016, China
CLC Number:
- R593.26
| [1] |
Mariampillai K, Granger B, Amelin D, et al. Development of a new classification system for idiopathic inflammatory myopathies based on clinical manifestations and myositis-specific autoanti-bodies[J]. JAMA Neurol, 2018,75(12):1528-1537.
doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2018.2598 pmid: 30208379 |
| [2] |
Lundberg IE, Tjärnlund A, Bottai M, et al. 2017 European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for adult and juvenile idiopathic inflammatory myopathies and their major subgroups[J]. Arthritis Rheumatol, 2017,69(12):2271-2282.
pmid: 29106061 |
| [3] |
Sontheimer RD. Would a new name hasten the acceptance of amyopathic dermatomyositis (dermatomyositis siné myositis) as a distinctive subset within the idiopathic inflammatory dermato-myopathies spectrum of clinical illness[J]. J Am Acad Dermatol, 2002,46(4):626-636.
doi: 10.1067/mjd.2002.120621 pmid: 11907524 |
| [4] |
Sato S, Kuwana M. Clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis[J]. Curr Opin Rheumatol, 2010,22(6):639-643.
doi: 10.1097/BOR.0b013e32833f1987 pmid: 20827200 |
| [5] |
Muro Y, Sugiura K, Hoshino K, et al. Epidemiologic study of clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis and anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 antibodies in central Japan[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2011,13(6):R214.
doi: 10.1186/ar3547 pmid: 22192091 |
| [6] | McHugh NJ, Tansley SL. Autoantibodies in myositis[J]. Nat Rev Rheumatol, 2018,14(6):290-302. |
| [7] | Gerami P, Schope JM, McDonald L, et al. A systematic review of adult-onset clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis (dermatomyositis siné myositis): a missing link within the spectrum of the idiopathic inflammatory myopathies[J]. J Am Acad Dermatol, 2006,54(5):597-613. |
| [8] |
Travis WD, Costabel U, Hansell DM, et al. An official American thoracic society/European respiratory society statement: update of the international multidisciplinary classification of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2013,188(6):733-748.
pmid: 24032382 |
| [9] |
Mukae H, Ishimoto H, Sakamoto N, et al. Clinical differences between interstitial lung disease associated with clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis and classic dermatomyositis[J]. Chest, 2009,136(4):1341-1347.
doi: 10.1378/chest.08-2740 |
| [10] |
Ikeda S, Arita M, Misaki K, et al. Incidence and impact of interstitial lung disease and malignancy in patients with polymyositis, dermatomyositis, and clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis: a retrospective cohort study[J]. Springerplus, 2015,4:240.
doi: 10.1186/s40064-015-1013-8 pmid: 26101728 |
| [11] |
Chen Z, Hu W, Wang Y, et al. Distinct profiles of myositis-specific autoantibodies in Chinese and Japanese patients with poly-myositis/dermatomyositis[J]. Clin Rheumatol, 2015,34(9):1627-1631.
doi: 10.1007/s10067-015-2935-9 pmid: 25903820 |
| [12] |
Hoshino K, Muro Y, Sugiura K, et al. Anti-MDA5 and anti-TIF1-gamma antibodies have clinical significance for patients with dermatomyositis[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2010,49(9):1726-1733.
doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keq153 |
| [13] | Jablonski R, Bhorade S, Strek ME, et al. Recognition and management of myositis-associated rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease[J]. Chest, 2020,58(1):252-263. |
| [14] |
Long K, Danoff SK. Interstitial lung disease in polymyositis and dermatomyositis[J]. Clin Chest Med, 2019,40(3):561-572.
doi: 10.1016/j.ccm.2019.05.004 pmid: 31376891 |
| [15] | Liang J, Cao H, Ke Y, et al. Acute Exacerbation of interstitial lung disease in adult patients with idiopathic inflammatory myo-pathies: a retrospective case-control study[J]. Front Med (Lausanne), 2020,7:12. |
| [16] | Ning Y, Yang G, Sun Y, et al. Efficiency of therapeutic plasma-exchange in acute interstitial lung disease, associated with polymyositis/dermatomyositis resistant to glucocorticoids and immunosuppressive drugs: a retrospective study[J]. Front Med (Lausanne), 2019,6:239. |
| [17] |
Temmoku J, Sato S, Fujita Y, et al. Clinical significance of myositis-specific autoantibody profiles in Japanese patients with polymyositis/dermatomyositis[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2019,98(20):e15578.
doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000015578 |
| [18] |
Ghirardello A, Doria A. New insights in myositis-specific autoantibodies[J]. Curr Opin Rheumatol, 2018,30(6):614-622.
pmid: 30234722 |
| [19] |
Huang W, Ren F, Wang Q, et al. Clinical features of thirty-two patients with anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 antibodies[J]. Clin Exp Rheumatol, 2019,37(5):803-807.
pmid: 30767866 |
| [20] |
Li L, Wang H, Wang Q, et al. Myositis-specific autoantibodies in dermatomyositis/polymyositis with interstitial lung disease[J]. J Neurol Sci, 2019,397:123-128.
doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2018.12.040 |
| [21] |
Xu Y, Yang CS, Li YJ, et al. Predictive factors of rapidly progressive-interstitial lung disease in patients with clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis[J]. Clin Rheumatol, 2016,35(1):113-116.
doi: 10.1007/s10067-015-3139-z pmid: 26660480 |
| [22] |
Trallero-Araguás E, Rodrigo-Pendás J, Selva-O’Callaghan A, et al. Usefulness of anti-p155 autoantibody for diagnosing cancer-associated dermatomyositis: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2012,64(2):523-532.
doi: 10.1002/art.33379 pmid: 21953614 |
| [23] |
Fujimoto M, Murakami A, Kurei S, et al. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for detection of anti-transcriptional intermediary factor-1 gamma and anti-Mi-2 autoantibodies in dermatomyositis[J]. J Dermatol Sci, 2016,84(3):272-281.
doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2016.09.013 pmid: 27693019 |
| [24] |
Cruellas MG, Viana Vdos S, Levy-Neto M, et al. Myositis-specific and myositis-associated autoantibody profiles and their clinical associations in a large series of patients with polymyositis and dermatomyositis[J]. Clinics (Sao Paulo), 2013,68(7):909-914.
doi: 10.6061/clinics |
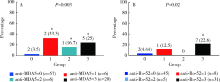
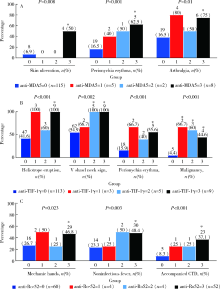
| [25] | Gan YZ, Zhang LH, Ma L, et al. Risk factors of interstitial lung diseases in clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis[J]. Chin Med J (Engl), 2020,133(6):644-649. |
| [26] |
Lee A. A review of the role and clinical utility of anti-Ro52/TRIM21 in systemic autoimmunity[J]. Rheumatol Int, 2017,37:1323-1333.
doi: 10.1007/s00296-017-3718-1 pmid: 28417151 |
| [27] |
van Dooren SH, van Venrooij WJ, Pruijn GJ. Myositis-specific autoantibodies: detection and clinical associations[J]. Auto Immun Highlights, 2011,2:5-20.
doi: 10.1007/s13317-011-0018-8 pmid: 26000115 |
| [28] |
Tansley SL, Snowball J, Pauling JD, et al. The promise, perceptions, and pitfalls of immunoassays for autoantibody testing in myositis[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2020,22(1):117.
pmid: 32414409 |
| [29] |
Mecoli CA, Albayda J, Tiniakou E, et al. Myositis autoanti-bodies: a comparison of results from the oklahoma medical research foundation myositis panel to the euroimmun research line blot[J]. Arthritis Rheumatol, 2020,72(1):192-194.
doi: 10.1002/art.41088 pmid: 31430029 |
| [30] |
Ikeda N, Yamaguchi Y, Kanaoka M, et al. Clinical significance of serum levels of anti-transcriptional intermediary factor 1-γ antibody in patients with dermatomyositis[J]. J Dermatol, 2020,47(5):490-496.
doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.15284 pmid: 32103537 |
| [31] | Wang T, Zheng XJ, Ji YL, et al. Tumour markers in rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease[J]. Clin Exp Rheu-matol, 2016,34(4):587-591. |
| [32] |
Jin Q, Zheng J, Xu X, et al. Value of serum carbohydrate antigen 19-9 and carcinoembryonic antigen in evaluating severity and prognosis of connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease[J]. Arch Rheumatol, 2018,33(2):190-197.
doi: 10.5606/ArchRheumatol.2018.6419 pmid: 30207560 |
| [33] |
Dai H, Liu J, Liang L, et al. Increased lung cancer risk in patients with interstitial lung disease and elevated CEA and CA125 serum tumour markers[J]. Respirology, 2014,19(5):707-713.
doi: 10.1111/resp.12317 pmid: 24903079 |
| [1] | Xiao-yan XING,Jun-xiao ZHANG,Feng-yun-zhi ZHU,Yi-fan WANG,Xin-yao ZHOU,Yu-hui LI. Clinical analysis of 5 cases of dermatomyositis complicated with macrophage activation syndrome [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1214-1218. |
| [2] | ZHANG Pu-li,YANG Hong-xia,ZHANG Li-ning,GE Yong-peng,PENG Qing-lin,WANG Guo-chun,LU Xin. Value of serum YKL-40 in the diagnosis of anti-MDA5-positive patients with dermatomyositis complicated with severe pulmonary injury [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(6): 1055-1060. |
| [3] | Jing XU,Jing XU,He LI,Jie TANG,Jian-long SHU,Jing ZHANG,Lian-jie SHI,Sheng-guang LI. Dermatomyositis combined with IgA vasculitis: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(6): 1173-1177. |
| [4] | Yi-ying YANG,Xiao-xia ZUO,Hong-lin ZHU,Si-jia LIU. Advances in epigenetic markers of dermatomyositis/polymyositis [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(2): 374-377. |
| [5] | YU Jian-feng, JIN Yue-bo, HE Jing, AN Yuan, LI Zhan-guo. Changes of serum Krebs von den Lungen-6 levels in interstitial lung disease associated with dermatomyositis and secondary Sjögren’s syndrome: a case report [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(5): 910-914. |
| [6] | LIU Shuang, AN Yuan, JIA Yuan, LI Zhan-Guo. A case of clinical overlap syndrome of rheumatoid arthritis and amyopathic dermatomyositis with multiple pulmonary injuries [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2014, 46(5): 805-808. |
|
||