Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (6): 1150-1152. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.06.028
Previous Articles Next Articles
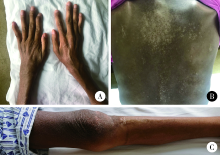
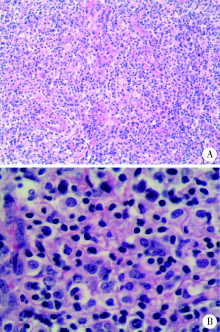
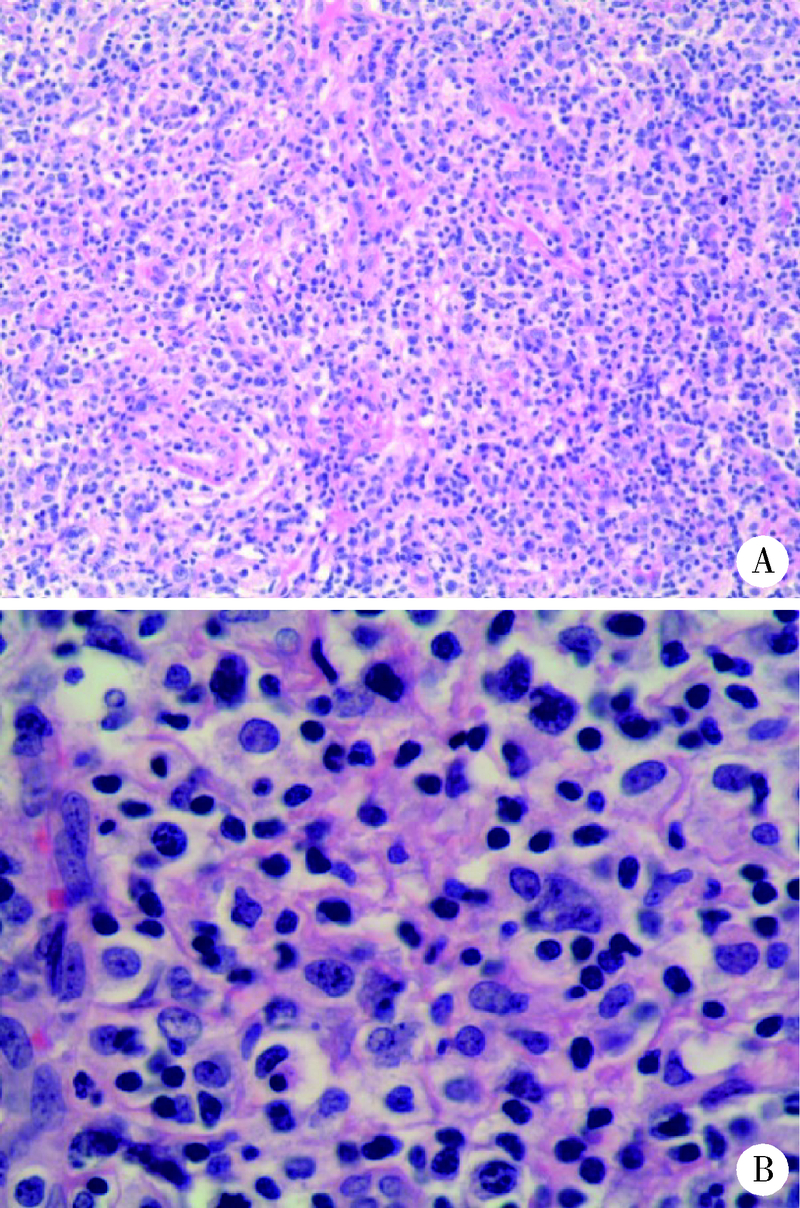
Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma with fever, arthritis and skin pigmentation: A case report
Gong CHENG1,Xia ZHANG1,Fei YANG2,Jia-yu CHENG3,Yan-ying LIU1,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Rheumatology & Immunology
2. Department of Department of Pathology
3. Department of Endocrinology, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
CLC Number:
- R733
| [1] |
Yabe M, Dogan A, Horwitz SM, et al. Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma[J]. Cancer Treat Res, 2019,176:99-126.
doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-99716-2_5 pmid: 30596215 |
| [2] |
Eng V, Kulkarni SK, Kaplan MS, et al. Hypereosinophilia with angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma[J]. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol, 2020,124(5):513-515.
doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2020.01.028 pmid: 32044452 |
| [3] | 于慧, 杜玉薪, 李玲, 等. 血管免疫母细胞性T细胞淋巴瘤的临床特点和预后分析[J]. 郑州大学学报(医学版), 2020,55(3):414-418. |
| [4] |
Lunning MA, Vose JM. Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma: the many-faced lymphoma[J]. Blood, 2017,129(9):1095-1102.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-09-692541 pmid: 28115369 |
| [5] | Chiba S, Sakata-Yanagimoto M. Advances in understanding of angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma[J/OL]. Leukemia, 2020(2020-07-23) [2020-07-29]. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41375-020-0990-y. |
| [6] |
Broccoli A, Zinzani PL. Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma[J]. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am, 2017,31(2):223-238.
doi: 10.1016/j.hoc.2016.12.001 pmid: 28340875 |
| [1] | Xinxin CHEN, Zhe TANG, Yanchun QIAO, Wensheng RONG. Caries experience and its correlation with caries activity of 4-year-old children in Miyun District of Beijing [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 833-838. |
| [2] | Hua ZHONG, Yuan LI, Liling XU, Mingxin BAI, Yin SU. Application of 18F-FDG PET/CT in rheumatic diseases [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 853-859. |
| [3] | Zhengfang LI,Cainan LUO,Lijun WU,Xue WU,Xinyan MENG,Xiaomei CHEN,Yamei SHI,Yan ZHONG. Application value of anti-carbamylated protein antibody in the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 729-734. |
| [4] | Hai-hong YAO,Fan YANG,Su-mei TANG,Xia ZHANG,Jing HE,Yuan JIA. Clinical characteristics and diagnostic indicators of macrophage activation syndrome in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and adult-onset Still's disease [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 966-974. |
| [5] | Hui WEI, Ci-dan-yang-zong, Yi-xi-la-mu, Bai-ma-yang-jin. Risk factors associated with different types of Henoch-Schönlein purpura in Tibetan patients at high altitude [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 923-928. |
| [6] | Yan XIONG,Xin LI,Li LIANG,Dong LI,Li-min YAN,Xue-ying LI,Ji-ting DI,Ting LI. Evaluation of accuracy of pathological diagnosis based on thyroid core needle biopsy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 234-242. |
| [7] | Xue-mei HA,Yong-zheng YAO,Li-hua SUN,Chun-yang XIN,Yan XIONG. Solid placental transmogrification of the lung: A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 357-361. |
| [8] | Bo-han NING,Qing-xia ZHANG,Hui YANG,Ying DONG. Endometrioid adenocarcinoma with proliferated stromal cells, hyalinization and cord-like formations: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 366-369. |
| [9] | Rui-jie CAO,Zhong-qiang YAO,Peng-qing JIAO,Li-gang CUI. Comparison of diagnostic efficacy of different classification criteria for Takayasu arteritis in Chinese patients [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1128-1133. |
| [10] | Zhe HAO,Shu-hua YUE,Li-qun ZHOU. Application of Raman-based technologies in the detection of urological tumors [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(4): 779-784. |
| [11] | Bo YU,Yang-yu ZHAO,Zhe ZHANG,Yong-qing WANG. Infective endocarditis in pregnancy: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(3): 578-580. |
| [12] | MENG Guang-yan,ZHANG Yun-xiao,ZHANG Yu-xin,LIU Yan-ying. Clinical characteristics of central nervous system involvement in IgG4 related diseases [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(6): 1043-1048. |
| [13] | ZHAI Li,QIU Nan,SONG Hui. Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(6): 1183-1187. |
| [14] | Mei-ge LIU,Pu FANG,Yan WANG,Lu CONG,Yang-yi FAN,Yuan YUAN,Yan XU,Jun ZHANG,Dao-jun HONG. Clinical, pathological and genetic characteristics of 8 patients with distal hereditary motor neuropathy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(5): 957-963. |
| [15] | YUAN Yuan,LANG Ning,YUAN Hui-shu. CT spectral curve in differentiating spinal tumor metastasis and infections [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(1): 183-187. |
|
||