Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (6): 1043-1048. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.06.006
Previous Articles Next Articles
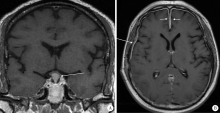
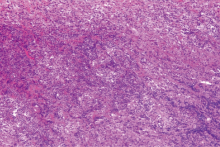
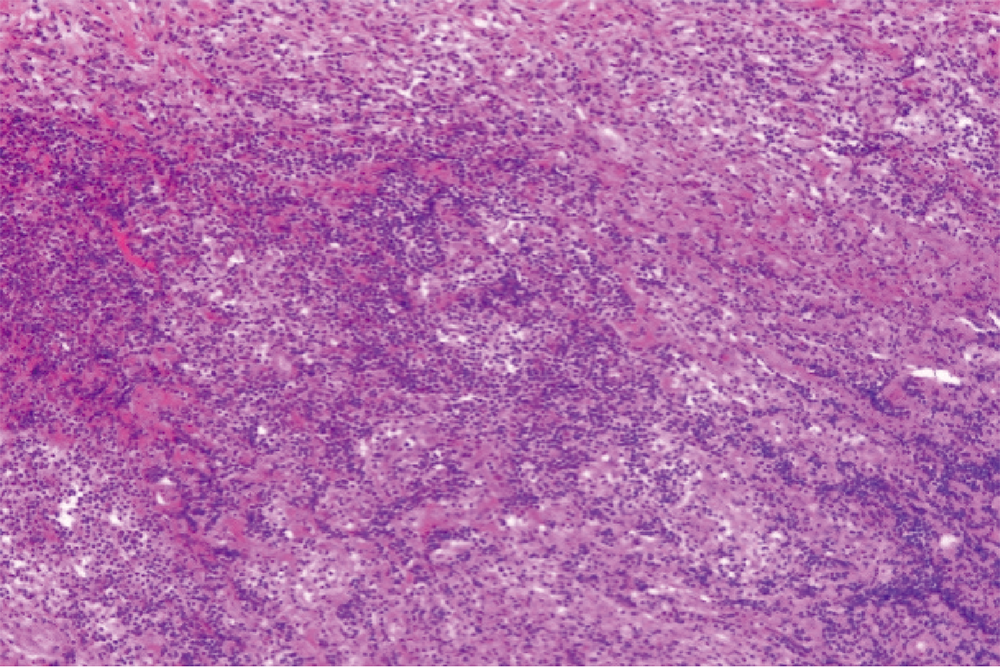
Clinical characteristics of central nervous system involvement in IgG4 related diseases
MENG Guang-yan1,2,ZHANG Yun-xiao1,3,ZHANG Yu-xin1,LIU Yan-ying1,4,△
- 1. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
2. Department of Clinical Laboratory, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
3. Department of Internal Medicine, Hospital of Qinghe Branch of Beijing Prison Administration, Tianjin 300481, China
4. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Beijing Friendship Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100050, China
CLC Number:
- R593.2
| [1] |
Kamisawa T, Funata N, Hayashi Y, et al. A new clinicopatholo-gical entity of IgG4-related autoimmune disease[J]. J Gastroenterol, 2003, 38(10):982-984.
pmid: 14614606 |
| [2] |
Umehara H, Okazaki K, Kawa S, et al. The 2020 revised comprehensive diagnostic (RCD) criteria for IgG4-RD[J]. Mod Rheumatol, 2021, 31(3):529-533.
doi: 10.1080/14397595.2020.1859710 |
| [3] | Peng L, Zhang P, Zhang X, et al. Clinical features of immunoglobulin G4-related disease with central nervous system involvement: An analysis of 15 cases[J]. Clin Exp Rheumatol, 2020, 38(4):626-632. |
| [4] |
Kamisawa T, Zen Y, Pillai S, et al. IgG4-related disease[J]. Lancet, 2015, 385(9976):1460-1471.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60720-0 pmid: 25481618 |
| [5] | 王子乔, 刘燕鹰, 张霞, 等. 17例误诊为IgG4相关疾病患者的临床特点及误诊原因分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(6):1025-1031. |
| [6] | 朱星昀, 刘燕鹰, 孙学娟, 等. 免疫球蛋白G4相关疾病患者发病形式及就诊行为特征分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018, 50(6):1039-1043. |
| [7] |
Iseda I, Hida K, Tone A, et al. Prednisolone markedly reduced serum IgG4 levels along with the improvement of pituitary mass and anterior pituitary function in a patient with IgG4-related infundibulo-hypophysitis[J]. Endocr J, 2014, 61(2):195-203.
doi: 10.1507/endocrj.EJ13-0407 |
| [8] | 李芊, 段炼, 李伟, 等. IgG4相关性垂体炎5例临床分析[J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2018, 38(9):861-864. |
| [9] |
Ohkubo Y, Sekido T, Takeshige K, et al. Occurrence of IgG4-related hypophysitis lacking IgG4-bearing plasma cell infiltration during steroid therapy[J]. Intern Med, 2014, 53(7):753-757.
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.53.0714 |
| [10] |
Christakis PG, Machado DG, Fattahi P. Idiopathic hypertrophic pachymeningitis mimicking neurosarcoidosis[J]. Clin Neurol Neurosurg, 2012, 114(2):176-178.
doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2011.10.011 |
| [11] | 苏玉莹, 王晨琼, 董凌莉. IgG4相关性疾病的发病机制及进展[J]. 中华临床医师杂志:电子版, 2014(14):2713-2717. |
| [12] | 纪宗斐. IgG4相关性疾病(IgG4-RD)发病机制的研究进展[J]. 复旦学报(医学版), 2019, 46(1):114-118. |
| [13] |
Leporati P, Landek-Salgado MA, Lupi I, et al. IgG4-related hypophysitis: A new addition to the hypophysitis spectrum[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2011, 96(7):1971-1980.
doi: 10.1210/jc.2010-2970 pmid: 21593109 |
| [14] |
Chan SK, Cheuk W, Chan KT, et al. IgG4-related sclerosing pachymeningitis: A previously unrecognized form of central nervous system involvement in IgG4-related sclerosing disease[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2009, 33(8):1249-1252.
doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181abdfc2 |
| [15] |
Lee YS, Lee HW, Park KS, et al. Immunoglobulin G4-related hypertrophic pachymeningitis with skull involvement[J]. Brain Tumor Res Treat, 2014, 2(2):87-91.
doi: 10.14791/btrt.2014.2.2.87 |
| [16] |
Peng Y, Li JQ, Zhang PP, et al. Clinical outcomes and predictive relapse factors of IgG4-related disease following treatment: A long-term cohort study[J]. J Intern Med, 2019, 286(5):542-552.
doi: 10.1111/joim.12942 pmid: 31121062 |
| [1] | Xinxin CHEN, Zhe TANG, Yanchun QIAO, Wensheng RONG. Caries experience and its correlation with caries activity of 4-year-old children in Miyun District of Beijing [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 833-838. |
| [2] | Hua ZHONG, Yuan LI, Liling XU, Mingxin BAI, Yin SU. Application of 18F-FDG PET/CT in rheumatic diseases [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 853-859. |
| [3] | Zhengfang LI,Cainan LUO,Lijun WU,Xue WU,Xinyan MENG,Xiaomei CHEN,Yamei SHI,Yan ZHONG. Application value of anti-carbamylated protein antibody in the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 729-734. |
| [4] | Hai-hong YAO,Fan YANG,Su-mei TANG,Xia ZHANG,Jing HE,Yuan JIA. Clinical characteristics and diagnostic indicators of macrophage activation syndrome in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and adult-onset Still's disease [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 966-974. |
| [5] | Ting WANG,Qiao-sheng LI,Hao-ran LIU,Wei-yan JIAN. Urban-rural differentials in the relationship between personality traits and changes in depressive symptoms [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(3): 385-391. |
| [6] | Yan XIONG,Xin LI,Li LIANG,Dong LI,Li-min YAN,Xue-ying LI,Ji-ting DI,Ting LI. Evaluation of accuracy of pathological diagnosis based on thyroid core needle biopsy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 234-242. |
| [7] | Xue-mei HA,Yong-zheng YAO,Li-hua SUN,Chun-yang XIN,Yan XIONG. Solid placental transmogrification of the lung: A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 357-361. |
| [8] | Bo-han NING,Qing-xia ZHANG,Hui YANG,Ying DONG. Endometrioid adenocarcinoma with proliferated stromal cells, hyalinization and cord-like formations: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 366-369. |
| [9] | Rui-jie CAO,Zhong-qiang YAO,Peng-qing JIAO,Li-gang CUI. Comparison of diagnostic efficacy of different classification criteria for Takayasu arteritis in Chinese patients [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1128-1133. |
| [10] | Zhe HAO,Shu-hua YUE,Li-qun ZHOU. Application of Raman-based technologies in the detection of urological tumors [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(4): 779-784. |
| [11] | Bo YU,Yang-yu ZHAO,Zhe ZHANG,Yong-qing WANG. Infective endocarditis in pregnancy: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(3): 578-580. |
| [12] | ZHAI Li,QIU Nan,SONG Hui. Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(6): 1183-1187. |
| [13] | YUAN Yuan,LANG Ning,YUAN Hui-shu. CT spectral curve in differentiating spinal tumor metastasis and infections [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(1): 183-187. |
| [14] | Qi KANG,Ji-xin ZHANG,Ying GAO,Jun-qing ZHANG,Xiao-hui GUO. Analysis of diagnosis and treatment of 100 patients with Hürthle cell adenoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(6): 1098-1101. |
| [15] | Gong CHENG,Xia ZHANG,Fei YANG,Jia-yu CHENG,Yan-ying LIU. Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma with fever, arthritis and skin pigmentation: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(6): 1150-1152. |
|
||