Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (6): 1020-1025. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.06.002
Previous Articles Next Articles
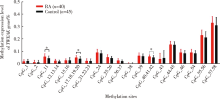
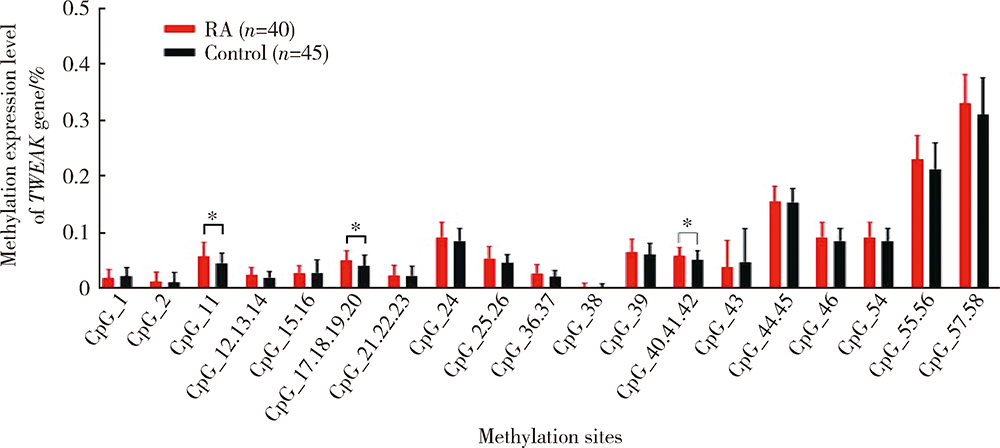
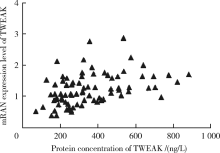
Methylation status and expression of TWEAK gene promoter region in peripheral blood of patients with rheumatoid arthritis
LOU Xue,LIAO Li,LI Xing-jun,WANG Nan,LIU Shuang,CUI Ruo-mei,XU Jian( )
)
- Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650032, China
CLC Number:
- R593.22
| [1] |
Firestein GS. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Nature, 2003, 423(6937):356-361.
doi: 10.1038/nature01661 |
| [2] | Sánchez-Ramón S, López-Longo FJ, Carreño L. Interleukins network in rheumatoid arthritis pathophysiology: Beyond proinflammatory cytokines[J]. Reumatol Clin, 2011, 6(S3):S20-S24. |
| [3] |
Song X, Lin Q. Genomics, transcriptomics and proteomics to elucidate the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Rheumatol Int, 2017, 37(8):1257-1265.
doi: 10.1007/s00296-017-3732-3 |
| [4] |
Karami J, Aslani S, Jamshidi A, et al. Genetic implications in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis: An updated review[J]. Gene, 2019, 702:8-16.
doi: S0378-1119(19)30290-2 pmid: 30904715 |
| [5] |
Park J, Kwok S, Lim M, et al. TWEAK promotes osteoclastogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Am J Pathol, 2013, 183(3):857-867.
doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2013.05.027 |
| [6] |
Chicheportiche Y, Chicheportiche R, Sizing I, et al. Proinflammatory activity of TWEAK on human dermal fibroblasts and synoviocytes: Blocking and enhancing effects of anti-TWEAK monoclonal antibodies[J]. Arthritis Res, 2002, 4(2):126-133.
pmid: 11879548 |
| [7] |
Karami J, Aslani S, Tahmasebi MN, et al. Epigenetics in rheumatoid arthritis; fibroblast-like synoviocytes as an emerging paradigm in the pathogenesis of the disease[J]. Immunol Cell Biol, 2020, 98(3):171-186.
doi: 10.1111/imcb.12311 pmid: 31856314 |
| [8] |
Singer BD. A practical guide to the measurement and analysis of DNA methylation[J]. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol, 2019, 61(4):417-428.
doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2019-0150TR |
| [9] |
Hua XM, Wang J, Qian DM, et al. DNA methylation level of promoter region of activating transcription factor 5 in glioma[J]. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B, 2015, 16(9):757-762.
doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1500067 |
| [10] |
Fuso A, Raia T, Orticello M, et al. The complex interplay between DNA methylation and miRNAs in gene expression regulation[J]. Biochimie, 2020, 173:12-16.
doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2020.02.006 |
| [11] | 中华医学会风湿病学分会. 类风湿关节炎诊断及治疗指南[J]. 中华风湿病学杂志, 2010(4):265-270. |
| [12] |
Schwartz N, Su L, Burkly LC, et al. Urinary TWEAK as a biomarker of lupus nephritis: A multicenter cohort study[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2009, 11(5):R143.
doi: 10.1186/ar2816 |
| [13] |
Xu W, Zhao Y, Liu Y. Role of the TWEAK/Fn14 pathway in autoimmune diseases[J]. Immunol Res, 2016, 64(1):44-50.
doi: 10.1007/s12026-015-8761-y |
| [14] |
Kamijo S, Nakajima A, Kamata K, et al. Involvement of TWEAK/Fn14 interaction in the synovial inflammation of RA[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2008, 47(4):442-450.
doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/ken006 pmid: 18310134 |
| [15] | Bertin D, Stephan D, Khrestchatisky M, et al. Is TWEAK a biomarker for autoimmune/chronic inflammatory diseases[J]. Front Immunol, 2013(4):489. |
| [16] |
van Kuijk AW, Wijbrandts CA, Vinkenoog M, et al. TWEAK and its receptor Fn14 in the synovium of patients with rheumatoid arthritis compared to psoriatic arthritis and its response to tumour necrosis factor blockade[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2010, 69(1):301-304.
doi: 10.1136/ard.2008.090548 pmid: 19147618 |
| [17] |
Park MC, Chung SJ, Jung SJ, et al. Relationship of serum TWEAK level to cytokine level, disease activity, and response to anti-TNF treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Scand J Rheumatol, 2008, 37(3):173-178.
doi: 10.1080/03009740801898608 pmid: 18465450 |
| [18] |
Dharmapatni A, Smith MD, Crotti TN, et al. TWEAK and Fn14 expression in the pathogenesis of joint inflammation and bone erosion in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2011, 13(2):R51.
doi: 10.1186/ar3294 |
| [19] |
Maecker H, Varfolomeev E, Kischkel F, et al. TWEAK attenuates the transition from innate to adaptive immunity[J]. Cell, 2005, 123(5):931-944.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.09.022 |
| [20] |
Guo SC, Zhu Q, Jiang T, et al. Genome-wide DNA methylation patterns in CD4+ T cells from Chinese Han patients with rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Mod Rheumatol, 2017, 27(3):441-447.
doi: 10.1080/14397595.2016.1218595 |
| [21] |
Zhu H, Wu LF, Mo XB, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis-associated DNA methylation sites in peripheral blood mononuclear cells[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2019, 78(1):36-42.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-213970 |
| [1] | GAO Chao,CHEN Li-hong,WANG Li,YAO Hong,HUANG Xiao-wei,JIA Yu-bo,LIU Tian. Validation of the Pollard’s classification criteria (2010) for rheumatoid arthritis patients with fibromyalgia [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(2): 278-282. |
| [2] | ZHANG Lu,HU Xiao-hong,CHEN Cheng,CAI Yue-ming,WANG Qing-wen,ZHAO Jin-xia. Analysis of cervical instability and clinical characteristics in treatment-naive rheumatoid arthritis patients [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(6): 1049-1054. |
| [3] | LUO Liang,HUO Wen-gang,ZHANG Qin,LI Chun. Clinical characteristics and risk factors of rheumatoid arthritis with ulcerative keratitis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(6): 1032-1036. |
| [4] | ZHONG Hua,XU Li-ling,BAI Ming-xin,SU Yin. Effect of chemokines CXCL9 and CXCL10 on bone erosion in patients with rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(6): 1026-1031. |
| [5] | CAO Di,WANG Yan,WANG Liu-qing,SUN Xiao-lin,HUANG Fei,MENG Yang,REN Li-li,ZHANG Xue-wu. Expression of plasma Dickkopf-1 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and its correlation with peripheral blood T cell subsets [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(2): 255-260. |
| [6] | ZHAO Kai,CHANG Zhi-fang,WANG Zhi-hua,PANG Chun-yan,WANG Yong-fu. Therapeutic effect of gene silencing peptidyl arginine deaminase 4 on pulmonary interstitial lesions induced by collagen-induced arthritis mice [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(2): 235-239. |
| [7] | Guo TANG,Li LONG,Ya-xin HAN,Qing PENG,Jia-jun LIU,Hua SHANG. Clinical characteristics and related factors of rheumatoid arthritis complicated with tuberculosis infection [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(6): 1029-1033. |
| [8] | Jing-feng ZHANG,Xiu-ling YE,Meng DUAN,Xiao-li ZHOU,Zhong-qiang YAO,Jin-xia ZHAO. Clinical and laboratory characteristics of rheumatoid arthritis with positive antinuclear antibody [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(6): 1023-1028. |
| [9] | Lu ZHANG,Xiao-hong HU,Qing-wen WANG,Yue-ming CAI,Jin-xia ZHAO,Xiang-yuan LIU. Population distribution and clinical characteristics in rheumatoid arthritis patients with cervical spine instability [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(6): 1034-1039. |
| [10] | Jia-li CHEN,Yue-bo JIN,Yi-fan WANG,Xiao-ying ZHANG,Jing LI,Hai-hong YAO,Jing HE,Chun LI. Clinical characteristics and risk factors of cardiovascular disease in patients with elderly-onset rheumatoid arthritis: A large cross-sectional clinical study [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(6): 1040-1047. |
| [11] | Jia-jing PENG,Tian LIU. Rheumatoid arthritis combined with pigmented villonodular synovitis: A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(6): 1135-1139. |
| [12] | Cai-nan LUO,Zheng-fang LI,Li-jun WU,Hai-juan CHEN,Chun-mei YANG,Wen-hui XU,Xiao-ling LIU,Wei TANG,Ping QIAO,Baihetiya Rena. Multicenter performance of the different classification criteria for rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(5): 897-901. |
| [13] | Zhao-nian WANG,Wen-jing GAO,Bi-qi WANG,Wei-hua CAO,Jun LV,Can-qing YU,Zeng-chang PANG,Li-ming CONG,Hua WANG,Xian-ping WU,Yu LIU,Li-ming LI. Correlation between fasting plasma glucose, HbA1c and DNA methylation in adult twins [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(3): 425-431. |
| [14] | Hong ZHU,Li-juan ZHAO,Yan ZHOU,Yao CHEN. Significance of anti-carbamylated protein antibodies in patients with rheumatoid arthritis-associated intersitial lung disease [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(6): 1003-1007. |
| [15] | Xiao-ying ZHANG,Jia-yang JIN,Jing HE,Yu-zhou GAN,Jia-li CHEN,Xiao-zhen ZHAO,Jia-jia LIU,Xu-jie YOU,Xue LI,Jian-ping GUO,Xiao-feng LI,Jing LI,Ru LI,Zhan-guo LI. Family history of rheumatic diseases in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a large scale cross-sectional study [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(3): 439-444. |
|