Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (3): 548-551. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.03.022
Previous Articles Next Articles
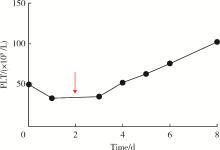
Effect of artificial liver with double plasma molecular absorb system model on patients' platelets and corresponding treatment strategy
Jin-feng JIA,Fei LIANG*( ),Jian-wei HUANG,Hao WANG,Pu-qing HAN
),Jian-wei HUANG,Hao WANG,Pu-qing HAN
- Department of Gastroenterology, the Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510700, China
CLC Number:
- R575.3
| 1 |
Stravitz RT , Lee WM . Acute liver failure[J]. Lancet, 2019, 394 (10201): 869- 881.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31894-X |
| 2 |
Dong V , Nanchal R , Karvellas CJ . Pathophysiology of acute liver failure[J]. Nutr Clin Pract, 2020, 35 (1): 24- 29.
doi: 10.1002/ncp.10459 |
| 3 |
Kok B , Dong V , Karvellas CJ . Graft dysfunction and management in liver transplantation[J]. Crit Care Clin, 2019, 35 (1): 117- 133.
doi: 10.1016/j.ccc.2018.08.002 |
| 4 |
Larsen FS . Artificial liver support in acute and acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Curr Opin Crit Care, 2019, 25 (2): 187- 191.
doi: 10.1097/MCC.0000000000000584 |
| 5 |
Larsen FS , Schmidt LE , Bernsmeier C , et al. High-volume plasma exchange in patients with acute liver failure: An open randomised controlled trial[J]. J Hepatol, 2016, 64 (1): 69- 78.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.08.018 |
| 6 |
Wan YM , Li YH , Xu ZY , et al. Therapeutic plasma exchange versus double plasma molecular absorption system in hepatitis B virus-infected acute-on-chronic liver failure treated by entercavir: A prospective study[J]. J Clin Apher, 2017, 32 (6): 453- 461.
doi: 10.1002/jca.21535 |
| 7 |
García Martínez JJ , Bendjelid K . Artificial liver support systems: What is new over the last decade[J]. Ann Intensive Care, 2018, 8 (1): 109.
doi: 10.1186/s13613-018-0453-z |
| 8 |
Huang K , Ji F , Xie Z , et al. Artificial liver support system therapy in acute-on-chronic hepatitis B liver failure: Classification and regression tree analysis[J]. Sci Rep, 2019, 9 (1): 16462.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-53029-0 |
| 9 |
Wu G , Wu D , Lo J , et al. A bioartificial liver support system integrated with a DLM/GelMA-based bioengineered whole liver for prevention of hepatic encephalopathy via enhanced ammonia reduction[J]. Biomater Sci, 2020, 8 (10): 2814- 2824.
doi: 10.1039/C9BM01879D |
| 10 |
Gundamaraju R , Vemuri R , Chong WC , et al. Bilirubin attenuates ER stress-mediated inflammation, escalates apoptosis and reduces proliferation in the LS174T colonic epithelial cell line[J]. Int J Med Sci, 2019, 16 (1): 135- 144.
doi: 10.7150/ijms.29134 |
| 11 |
Lee Y , Sugihara K , Gillilland MG 3rd , et al. Hyaluronic acid-bilirubin nanomedicine for targeted modulation of dysregulated intestinal barrier, microbiome and immune responses in colitis[J]. Nat Mater, 2020, 19 (1): 118- 126.
doi: 10.1038/s41563-019-0462-9 |
| 12 |
Yao J , Li S , Zhou L , et al. Therapeutic effect of double plasma molecular adsorption system and sequential half-dose plasma exchange in patients with HBV-related acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. J Clin Apher, 2019, 34 (4): 392- 398.
doi: 10.1002/jca.21690 |
| 13 | 农村立, 郭堑, 韦秋芳, 等. 双重血浆分子吸附系统序贯血浆置换治疗肝衰竭的临床疗效[J]. 现代医药卫生, 2018, 34 (12): 22- 24. |
| 14 |
Tang B , Huang L , Liu H , et al. Recombinant human thrombo-poietin promotes platelet engraftment after umbilical cord blood transplantation[J]. Blood Adv, 2020, 4 (16): 3829- 3839.
doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020002257 |
| 15 | Zhang J , Lu Z , Xiao W , et al. Efficacy and safety of recombinant human thrombopoietin on sepsis patients with thrombocytopenia: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2020, 11 (3): 940. |
| [1] | Hong-yu GAO,Jing-ling XU,Huan-xin MENG,Lu HE,Jian-xia HOU. Effect of initial periodontal therapy on blood parameters related to erythrocyte and platelet in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic periodontitis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(4): 750-754. |
|
||