Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (6): 1028-1032. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.06.011
Previous Articles Next Articles
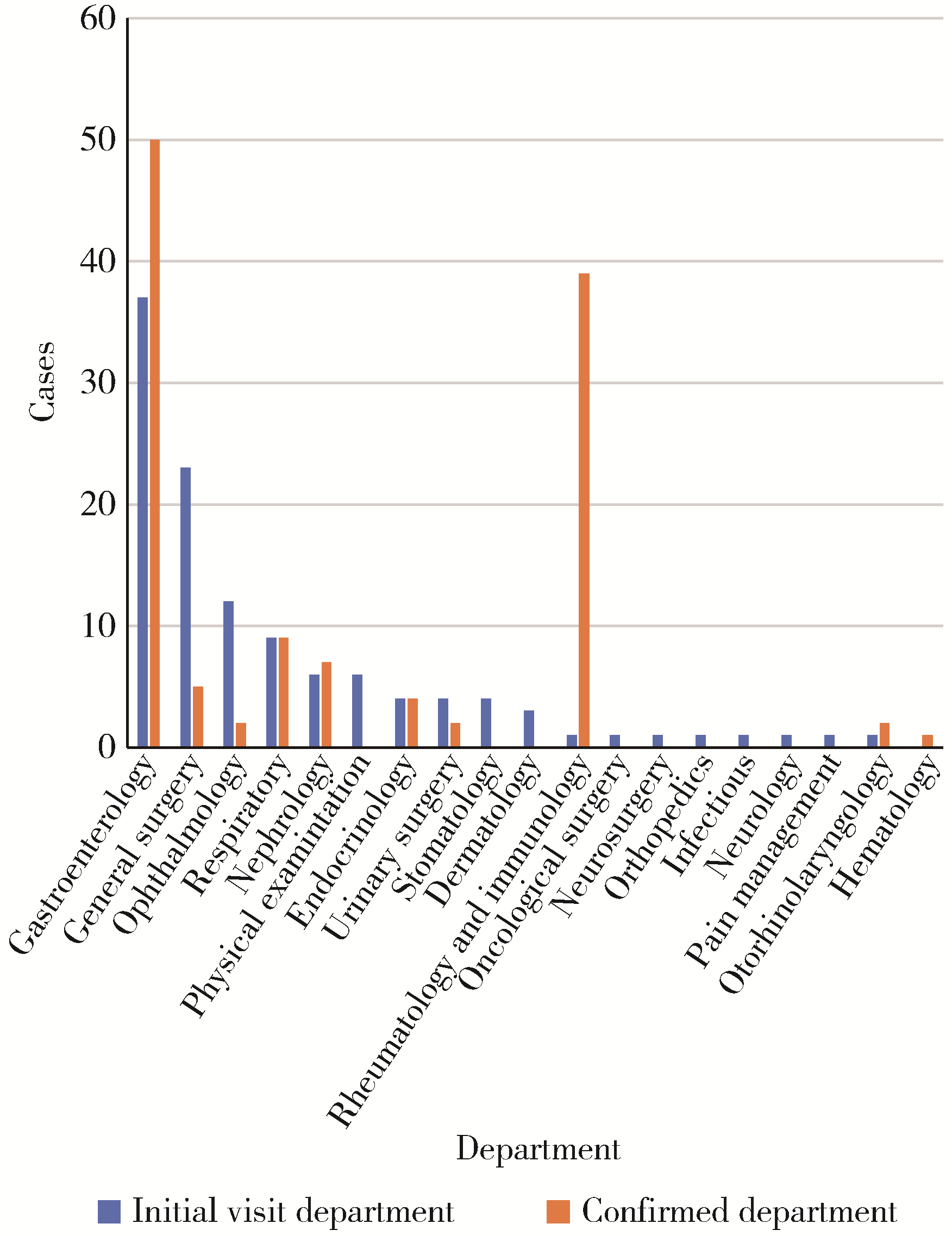
Medical visit status and clinical features in patients with IgG4 related disease
Lu FENG1,2,Jia-yu ZHAI1,Jin-xia ZHAO1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
2. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Liaoning Health Industry Group Bengang General Hospital, Benxi 117000, Liaoning, China
CLC Number:
- R593.2
| 1 |
Denton CP , Khanna D . Systemic sclerosis[J]. Lancet, 2017, 390 (10103): 1685- 1699.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30933-9 |
| 2 |
Szabo I , Muntean L , Crisan T , et al. Novel concepts in systemic sclerosis pathogenesis: Role for miRNAs[J]. Biomedicines, 2021, 9 (10): 1471.
doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9101471 |
| 3 |
Liu Y , Cheng L , Zhan H , et al. The roles of noncoding RNAs in systemic sclerosis[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13, 856036.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.856036 |
| 4 |
Henry TW , Mendoza FA , Jimenez SA . Role of microRNA in the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis tissue fibrosis and vasculopathy[J]. Autoimmun Rev, 2019, 18 (11): 102396.
doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2019.102396 |
| 5 |
Zhao M , Qi Q , Liu S , et al. MicroRNA-34a: A novel therapeutic target in fibrosis[J]. Front Physiol, 2022, 13, 895242.
doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.895242 |
| 6 |
Wuttge DM , Carlsen AL , Teku G , et al. Specific autoantibody profiles and disease subgroups correlate with circulating micro-RNA in systemic sclerosis[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2015, 54 (11): 2100- 2107.
doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kev234 |
| 7 |
Jafarinejad-Farsangi S , Gharibdoost F , Farazmand A , et al. MicroRNA-21 and microRNA-29a modulate the expression of collagen in dermal fibroblasts of patients with systemic sclerosis[J]. Autoimmunity, 2019, 52 (3): 108- 116.
doi: 10.1080/08916934.2019.1621856 |
| 8 | Shi J , Li F , Luo M , et al. Distinct roles of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in the pathogenesis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis[J]. Mediators Inflamm, 2017, 2017, 3520581. |
| 9 |
Cottin V , Brown KK . Interstitial lung disease associated with systemic sclerosis (SSc-ILD)[J]. Respir Res, 2019, 20 (1): 13.
doi: 10.1186/s12931-019-0980-7 |
| 10 |
Duan W , Zhang W , Jia J , et al. Exosomal microRNA in autoimmunity[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2019, 16 (12): 932- 934.
doi: 10.1038/s41423-019-0319-9 |
| 11 |
Mirzaei R , Zamani F , Hajibaba M , et al. The pathogenic, therapeutic and diagnostic role of exosomal microRNA in the autoimmune diseases[J]. J Neuroimmunol, 2021, 358, 577640.
doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2021.577640 |
| 12 | Wermuth PJ , Piera-Velazquez S , Jimenez SA . Exosomes isolated from serum of systemic sclerosis patients display alterations in their content of profibrotic and antifibrotic microRNA and induce a profibrotic phenotype in cultured normal dermal fibroblasts[J]. Clin Exp Rheumatol, 2017, 35 (Suppl 106): 21- 30. |
| 13 |
Cui H , Ge J , Xie N , et al. miR-34a inhibits lung fibrosis by inducing lung fibroblast senescence[J]. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol, 2017, 56 (2): 168- 178.
doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2016-0163OC |
| 14 |
Bulvik R , Biton M , Berkman N , et al. Forefront: MiR-34a-knockout mice with wild type hematopoietic cells, retain persistent fibrosis following lung injury[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21 (6): 2228.
doi: 10.3390/ijms21062228 |
| 15 |
Disayabutr S , Kim EK , Cha SI , et al. miR-34 miRNAs regulate cellular senescence in type Ⅱ alveolar epithelial cells of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11 (6): e0158367.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0158367 |
| 16 |
Yang G , Yang L , Wang W , et al. Discovery and validation of extracellular/circulating microRNAs during idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis disease progression[J]. Gene, 2015, 562 (1): 138- 144.
doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2015.02.065 |
| 17 |
Blumer S , Fang L , Chen WC , et al. IPF-Fibroblast Erk1/2 acti-vity is independent from microRNA cluster 17-92 but can be inhibited by treprostinil through DUSP1[J]. Cells, 2021, 10 (11): 2836.
doi: 10.3390/cells10112836 |
| 18 |
Steen SO , Iversen LV , Carlsen AL , et al. The circulating cell-free microRNA profile in systemic sclerosis is distinct from both healthy controls and systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. J Rheumatol, 2015, 42 (2): 214- 221.
doi: 10.3899/jrheum.140502 |
| 19 |
黄赛赛, 王丹丹, 张卓亚, 等. 系统性硬化症患者血浆7种miRNA水平与脏器累及和临床指标的相关性[J]. 临床检验杂志, 2021, 39 (5): 358- 361.
doi: 10.13602/j.cnki.jcls.2021.05.09 |
| 20 |
Sing T , Jinnin M , Yamane K , et al. microRNA-92a expression in the sera and dermal fibroblasts increases in patients with scleroderma[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2012, 51 (9): 1550- 1556.
doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kes120 |
| 21 |
Guiot J , Cambier M , Boeckx A , et al. Macrophage-derived exosomes attenuate fibrosis in airway epithelial cells through delivery of antifibrotic miR-142-3p[J]. Thorax, 2020, 75 (10): 870- 881.
doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2019-214077 |
| 22 |
Njock MS , Guiot J , Henket MA , et al. Sputum exosomes: Promising biomarkers for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis[J]. Thorax, 2019, 74 (3): 309- 312.
doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2018-211897 |
| [1] | Min FENG,Zhe CHEN,Yong-jing CHENG. A case of duodenal ulcer as prominent manifestation of IgG4-related disease [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1125-1129. |
| [2] | Min LI,Lin-qing HOU,Yue-bo JIN,Jing HE. Clinical and immunological characteristics of systemic lupus erythematosus with retinopathy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1106-1111. |
| [3] | WEI Hui,Luo-zeng ##,Ci-dan-yang-zong ##,Bai-ma-yang-jin ##. Analysis of clinical characteristics of Henoch-Schonlein purpura patients from different altitudes in plateau areas [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(6): 1072-1077. |
| [4] | Zi-qiao WANG,Yan-ying LIU,Xia ZHANG,Tian LIU,Li-min REN,Dan-hua SHEN,Yi WANG,Zhan-guo LI. Analysis of the clinical features and misdiagnosis reasons of 17 patients misdiagnosed with IgG4-related disease [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(6): 1025-1031. |
| [5] | Xiao-peng ZHANG,Zi-xiong HUANG,Lu-ping YU,Xiao-wei ZHANG,Qing LI,Shi-jun LIU,Tao XU. Clinical and pathological analysis of small renal cell carcinoma [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(4): 623-627. |
| [6] | Guang-ya YU,Xia HONG,Wei LI,Yan-yan ZHANG,Yan GAO,Yan CHEN,Zu-yan ZHANG,Xiao-yan XIE,Zhan-guo LI,Yan-ying LIU,Jia-zeng SU,Wen-xuan ZHU,Zhi-peng SUN. Clinicopathological characteristics and diagnosis of IgG4-related sialadenitis [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(1): 1-3. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 159
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 238
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cited |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shared | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discussed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||