Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (6): 1097-1100. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.06.024
Previous Articles Next Articles
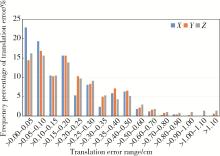
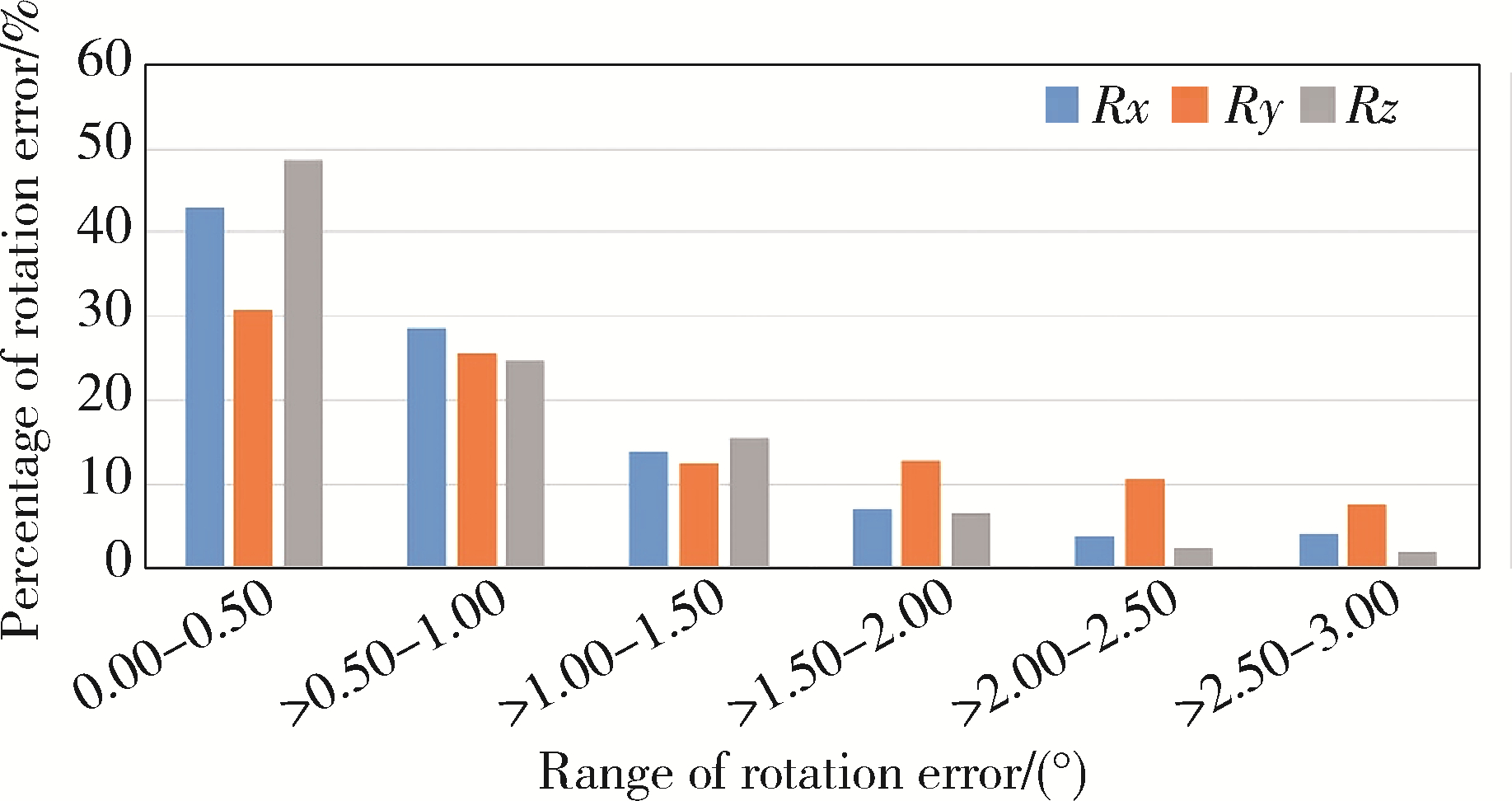
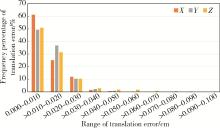
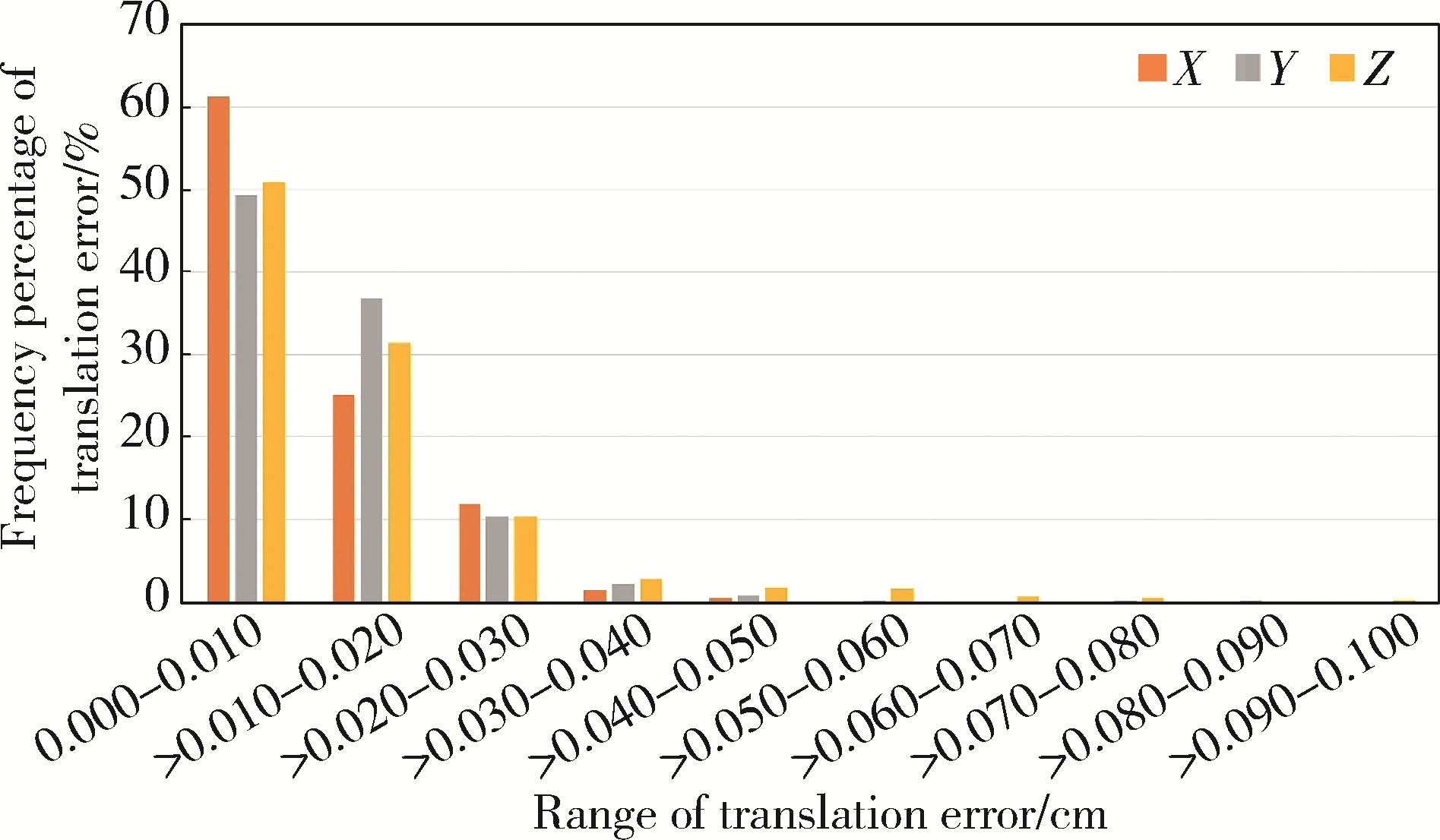
Analysis of positioning errors in head and neck cancers during radiotherapy assisted by the 6D treatment couch and image-guided radiation therapy
Suqing TIAN, Haitao SUN*( ), Tiandi ZHAO, Wei WANG
), Tiandi ZHAO, Wei WANG
- Department Of Radiation Oncology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
CLC Number:
- R730.55
| 1 | 中国医师协会放射肿瘤治疗医师分会, 中华医学会放射肿瘤治疗学分会, 中国抗癌协会肿瘤放射治疗专业委员会. 中国头颈部肿瘤放射治疗指南(2021年版)[J]. 国际肿瘤学杂志, 2022, 49 (2): 65- 72. |
| 2 |
Alfouzan AF . Radiation therapy in head and neck cancer[J]. Saudi Med J, 2021, 42 (3): 247- 254.
doi: 10.15537/smj.2021.42.3.20210660 |
| 3 |
Abshire D , Lang MK . The evolution of radiation therapy in treating cancer[J]. Semin Oncol Nurs, 2018, 34 (2): 151- 157.
doi: 10.1016/j.soncn.2018.03.006 |
| 4 |
Zhou J , Li S , Ye C , et al. Analysis of local setup errors of sub-regions in cone-beam CT-guided post-mastectomy radiation therapy[J]. Radiat Res, 2020, 61 (3): 457- 463.
doi: 10.1093/jrr/rraa007 |
| 5 |
Park J , Yea JW , Park JW , et al. Evaluation of the setup discrepancy between 6D ExacTrac and cone beam computed tomography in spine stereotactic body radiation therapy[J]. PLoS One, 2021, 16 (5): e0252234.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0252234 |
| 6 |
Hadj Henni A , Gensanne D , Roge M , et al. Evaluation of inter- and intra-fraction 6D motion for stereotactic body radiation therapy of spinal metastases: Influence of treatment time[J]. Radiat Oncol, 2021, 16 (1): 168.
doi: 10.1186/s13014-021-01892-5 |
| 7 |
Fu W , Yang Y , Yue NJ , et al. Dosimetric influences of rotational setup errors on head and neck carcinoma intensity-modulated radiation therapy treatments[J]. Med Dosim, 2013, 38 (2): 125- 132.
doi: 10.1016/j.meddos.2012.09.003 |
| 8 | 曹倩倩, 朱丽红, 王俊杰, 等. 6D治疗床对原发宫颈癌放疗摆位误差及靶区边界的影响[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2015, 95 (9): 689- 692. |
| 9 | 姚丽红, 朱丽红, 王俊杰, 等. 6D治疗床联合锥形束CT引导下妇科肿瘤摆位误差及计划靶区外放边界研究[J]. 中华放射医学与防护杂志, 2015, 35 (3): 206- 209. |
| 10 |
江萍, 周舜, 王俊杰, 等. 影像引导下放射治疗脊柱肿瘤六自由度摆位误差分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015, 47 (6): 952- 956.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-167X.2015.06.011 |
| 11 |
Zeidan OA , Langen KM , Meeks SL , et al. Evaluation of image-guidance protocols in the treatment of head and neck cancers[J]. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2007, 67 (3): 670- 677.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.09.040 |
| 12 |
Ohira S , Ueda Y , Nishiyama K , et al. Couch height-based patient setup for abdominal radiation therapy[J]. Med Dosim, 2016, 41 (1): 59- 63.
doi: 10.1016/j.meddos.2015.08.003 |
| 13 |
Aristophanous M , Chi PM , Kao J , et al. Deep-inspiration breath-hold intensity modulated radiation therapy to the mediastinum for lymphoma patients: Setup uncertainties and margins[J]. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2018, 100 (1): 254- 262.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2017.09.036 |
| 14 | Islam MK , Purdie TG , Norrlinger BD , et al. Patient dose from kilovoltage cone beam computed tomography imaging in radiation therapy[J]. Med Phys, 2006, 33 (6): 1573- 1582. |
| [1] | YE Ke-qiang, HUANG Ming-wei, LI Jun-li, TANG Jin-tian, ZHANG Jian-guo. Simulation of dose distribution in bone medium of 125I photon emitting source with Monte Carlo method [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(1): 131-135. |
| [2] | SUN Hai-tao, YANG Rui-jie, JIANG Ping, JIANG Wei-juan, LI Jin-na, MENG Na, WANG Jun-jie. Dosimetric analysis of volumetric modulated arc therapy and intensity modulated radiotherapy for patients undergone breast-conserving operation [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(1): 188-192. |
| [3] | GUO Fu-xin, JIANG Yu-liang, JI Zhe, PENG Ran, SUN Hai-tao, WANG Jun-jie. 3D printed template-assisted and computed tomography image-guided 125-iodine seed implantation for supraclavicular metastatic tumor: a dosimetric study [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(3): 506-511. |
| [4] | JIANG Ping, ZHOU Shun,WANG Jun-jie, YANG Rui-jie, LIU Zi-yi, JIANG Shu-kun, WANG Wei. Errors in six degree-of-freedom pose estimation of spine tumors assessed by image guided radiotherapy [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2015, 47(6): 952-956. |
|
||