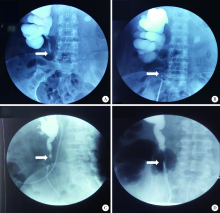
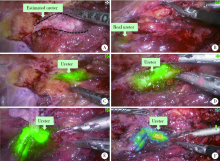
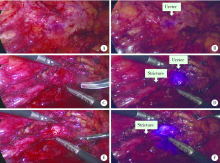
Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (4): 651-656. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.04.010
Previous Articles Next Articles
Application of indocyanine green in complex upper urinary tract repair surgery
Bing-wei HUANG1,2,Jie WANG1,Peng ZHANG2,Zhe LI2,Si-cheng BI2,Qiang WANG2,Cai-bo YUE2,Kun-lin YANG1,△( ),Xue-song LI1,△(
),Xue-song LI1,△( ),Li-qun ZHOU1
),Li-qun ZHOU1
- 1. Department of Urology, Peking University First Hospital; Institute of Urology, Peking University, Beijing 100034, China
2. Department of Urology, Emergency General Hospital, Beijing 100028, China
CLC Number:
- R693.5
| [1] | Asghar AM, Lee RA, Yang KK, et al. Robot-assisted distal ureteral reconstruction for benign pathology: Current state[J]. Investig Clin Urol, 2020,61(Suppl 1):23-32. |
| [2] | Kaplan-Marans E, Fulla J, Tomer N, et al. Indocyanine green (ICG) in urologic surgery[J]. Urology, 2019,132:10-17. |
| [3] | Lee Z, Moore B, Giusto L, et al. Use of indocyanine green during robot-assisted ureteral reconstructions[J]. Eur Urol, 2015,67(2):291-298. |
| [4] | 李锟, 张中林, 刘权焰, 等. 三维可视化技术联合术中ICG荧光显像在腹腔镜肝癌肝切除术中的应用[J]. 中华肝脏外科手术学电子杂志, 2019,8(3):226-229. |
| [5] | 杨昆霖, 李学松, 周利群. IUPU经腹腹腔镜联合膀胱软镜肾盂取石及肾盂成型术[J]. 泌尿外科杂志(电子版), 2015,7(3):4-6. |
| [6] | 李学松, 钟文龙, 吴帅, 等. 回肠代输尿管术临床应用及手术技巧(附光盘)[J]. 现代泌尿外科杂志, 2016,21(04):245-248. |
| [7] | Cherrick GR, Stein SW, Leevy CM, et al. Indocyanine green: observations on its physical properties, plasma decay, and hepatic extraction[J]. J Clin Invest, 1960,39(4):592-600. |
| [8] |
Gioux S, Choi HS, Frangioni JV. Image-guided surgery using invisible near-infrared light: fundamentals of clinical translation[J]. Mol Imaging, 2010,9(5):237-255.
pmid: 20868625 |
| [9] | Vahrmeijer AL, Hutteman M, van der Vorst JR, et al. Image-guided cancer surgery using near-infrared fluorescence[J]. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2013,10(9):507-518. |
| [10] | Chu W, Chennamsetty A, Toroussian R, et al. Anaphylactic shock after intravenous administration of indocyanine green during robotic partial nephrectomy[J]. Urol Case Rep, 2017,12:37-38. |
| [11] |
Tobis S, Knopf JK, Silvers CR, et al. Near infrared fluorescence imaging after intravenous indocyanine green: initial clinical experience with open partial nephrectomy for renal cortical tumors[J]. Urology, 2012,79(4):958-964.
pmid: 22336035 |
| [12] | Ramirez BM, Calatrava-Fons A, Gomez-Ferrer A, et al. ICG lymphography and fluorescence in pelvic lymphadenectomy for bladder and prostate cancer[J]. Arch Esp Urol, 2019,72(8):831-841. |
| [13] | Manny TB, Pompeo AS, Hemal AK. Robotic partial adrenalec-tomy using indocyanine green dye with near-infrared imaging: the initial clinical experience[J]. Urology, 2013,82(3):738-742. |
| [14] | Selzman AA, Spirnak JP. Iatrogenic ureteral injuries: a 20-year experience in treating 165 injuries[J]. J Urol, 1996,155(3):878-881. |
| [15] | Razdan S, Silberstein IK, Bagley DH. Ureteroscopic endouretero-tomy[J]. BJU Int, 2005,95(Suppl 2):94-101. |
| [16] | Zhong W, Du Y, Yang K, et al. Ileal ureter replacement combined with boari flap-psoas hitch to treat full-length ureteral defects: Technique and initial experience[J]. Urology, 2017,108:201-206. |
| [17] | 王帅军, 李胜文. 长段输尿管修复重建研究的进展[J]. 现代泌尿外科杂志, 2019,24(6):496-501. |
| [18] | 熊盛炜, 杨昆霖, 丁光璞, 等. 输尿管损伤外科修复治疗的研究进展[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019,51(4):783-789. |
| [19] | Low RK, Moran ME. Laparoscopic use of the ureteral illuminator[J]. Urology, 1993,42(4):455-457. |
| [20] | Verbeek FP, van der Vorst JR, Schaafsma BE, et al. Intraoperative near infrared fluorescence guided identification of the ureters using low dose methylene blue: a first in human experience[J]. J Urol, 2013,190(2):574-579. |
| [21] | Abboudi H, Ahmed K, Royle J, et al. Ureteric injury: a challenging condition to diagnose and manage[J]. Nat Rev Urol, 2013,10(2):108-115. |
| [22] |
Bjurlin MA, Gan M, McClintock TR, et al. Near-infrared fluore-scence imaging: emerging applications in robotic upper urinary tract surgery[J]. Eur Urol, 2014,65(4):793-801.
pmid: 24099660 |
| [1] | Yicen YING,Yicong DU,Zhihua LI,Yiming ZHANG,Xinfei LI,Bing WANG,Peng ZHANG,Hongjian ZHU,Liqun ZHOU,Kunlin YANG,Xuesong LI. Robot-assisted laparoscopic ureteroplasty with buccal mucosa graft for complex ureteral stricture [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 640-645. |
| [2] | Zhan-yi ZHANG,Fan ZHANG,Ye YAN,Cai-guang CAO,Chang-jian LI,Shao-hui DENG,Yue-hao SUN,Tian-liang HUANG,Yun-he GUAN,Nan LI,Min LU,Zhen-hua HU,Shu-dong ZHANG. Near-infrared targeted probe designed for intraoperative imaging of prostatic neurovascular bundles [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 843-850. |
| [3] | Chun-long ZHANG,Ming-rui WANG,Ming-rui WANG,Ke-xin XU,Tao XU,Hao HU. Long-term efficacy evaluation of coated metal stent implantation for ureteroscopic lithotripsy related refractory ureteral stricture [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(4): 674-679. |
| [4] | Shu-dong ZHANG,Peng HONG,Bin-shuai WANG,Shao-hui DENG,Fan ZHANG,Li-yuan TAO,Cai-guang CAO,Zhen-hua HU,Lu-lin MA. Usefulness of the indocyanine green fluorescence imaging technique in laparoscopic partial nephrectomy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(4): 657-662. |
| [5] | HAO Yi-chang, HOU Xiao-fei, ZHAO Lei, XIAO Chun-lei, LIU Zhuo, ZHANG fan, MA Lu-lin. Laparoscopic ureterovesical reimplantation for ureteral stricture after renal transplantation [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(4): 705-710. |
|
||