Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (3): 552-556. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.03.023
Previous Articles Next Articles
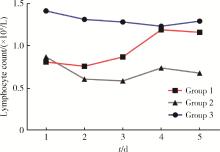
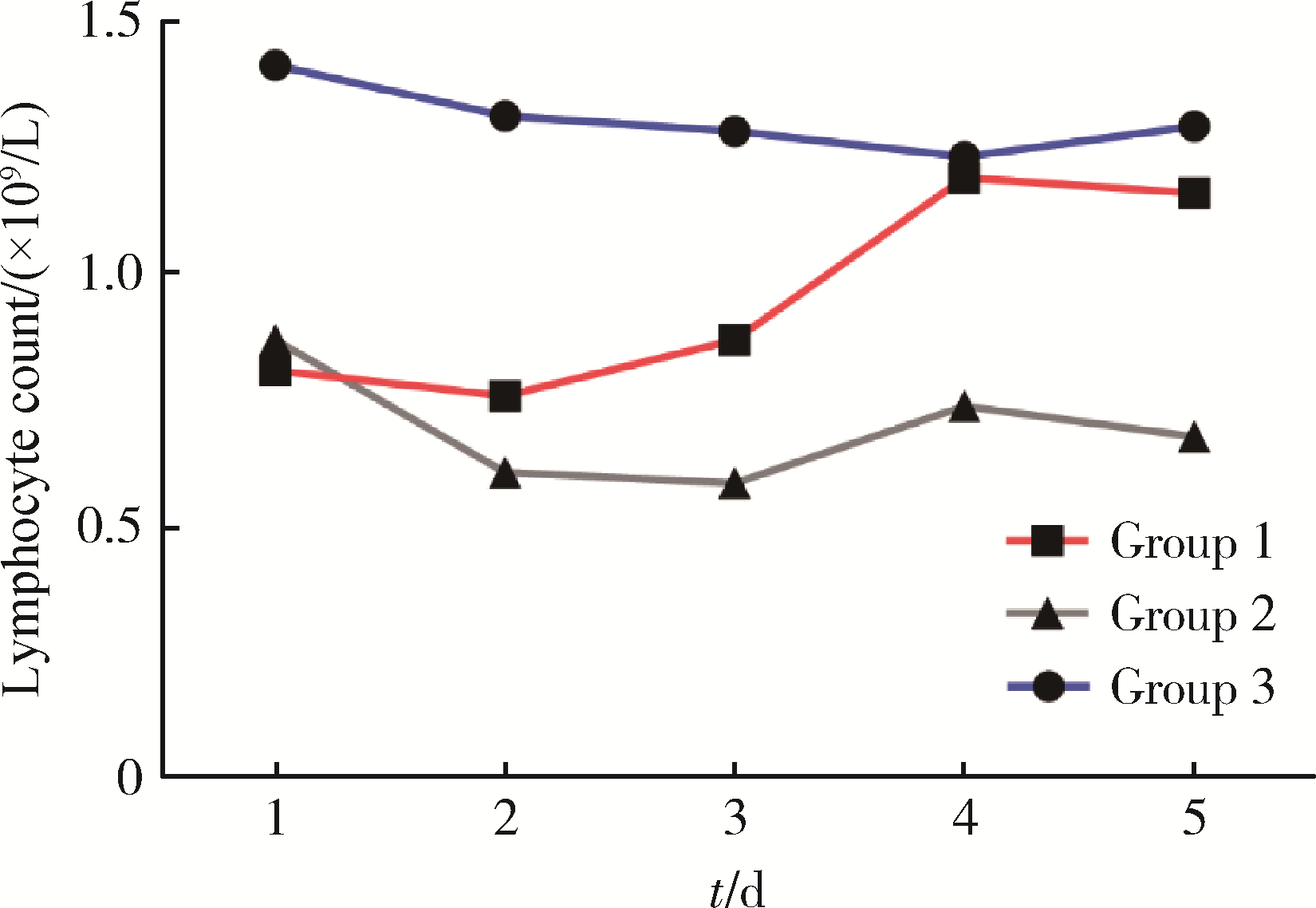
Early changes within the lymphocyte population are associated with the long term prognosis in severely injured patients
Fu-zheng GUO,Xiu-juan ZHAO,Jiu-xu DENG,Zhe DU,Tian-bing WANG,Feng-xue ZHU*( )
)
- Trauma Medicine Center, Peking University People′s Hospital, Bejing 10044, China
CLC Number:
- R641
| 1 |
姜保国. 我国严重创伤救治的现状和救治规范的建立[J]. 中华外科杂志, 2012, 50 (7): 577- 578.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0529-5815.2012.07.001 |
| 2 | Hillman PE , Scott NR , van Tienhoven A . Effect of 5-hydroxytryptamine and acetylcholine on the energy budget of chickens[J]. Am J Physiol, 1980, 239 (1): R57- R61. |
| 3 |
Cotton BA , Reddy N , Hatch QM , et al. Damage control resuscitation is associated with a reduction in resuscitation volumes and improvement in survival in 390 damage control laparotomy patients[J]. Ann Surg, 2011, 254 (4): 598- 605.
doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e318230089e |
| 4 |
Minei JP , Cuschieri J , Sperry J , et al. The changing pattern and implications of multiple organ failure after blunt injury with hemorrhagic shock[J]. Crit Care Med, 2012, 40 (4): 1129- 1135.
doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e3182376e9f |
| 5 |
Lord JM , Midwinter MJ , Chen YF , et al. The systemic immune response to trauma: an overview of pathophysiology and treatment[J]. Lancet, 2014, 384 (9952): 1455- 1465.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60687-5 |
| 6 |
Manson J , Hoffman R , Chen S , et al. Innate-like lymphocytes are immediate participants in the hyper-acute immune response to trauma and hemorrhagic shock[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10, 1501.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01501 |
| 7 |
Deitch EA , Landry KN , McDonald JC . Postburn impaired cell-mediated immunity may not be due to lazy lymphocytes but to overwork[J]. Ann Surg, 1985, 201 (6): 793- 802.
doi: 10.1097/00000658-198506000-00018 |
| 8 |
Hotchkiss RS , Tinsley KW , Swanson PE , et al. Prevention of lymphocyte cell death in sepsis improves survival in mice[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1999, 96 (25): 14541- 14546.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.25.14541 |
| 9 |
Heffernan DS , Monaghan SF , Thakkar RK , et al. Failure to normalize lymphopenia following trauma is associated with increased mortality, independent of the leukocytosis pattern[J]. Crit Care, 2012, 16 (1): R12.
doi: 10.1186/cc11157 |
| 10 |
Nacionales DC , Szpila B , Ungaro R , et al. A detailed charac-terization of the dysfunctional immunity and abnormal myelopoiesis induced by severe shock and trauma in the aged[J]. J Immunol, 2015, 195 (5): 2396- 2407.
doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1500984 |
| 11 |
Manson J , Cole E , de Ath HD , et al. Early changes within the lymphocyte population are associated with the development of multiple organ dysfunction syndrome in trauma patients[J]. Crit Care, 2016, 20 (1): 176.
doi: 10.1186/s13054-016-1341-2 |
| 12 |
Brakenridge SC , Efron PA , Stortz JA , et al. The impact of age on the innate immune response and outcomes after severe sepsis/septic shock in trauma and surgical intensive care unit patients[J]. J Trauma Acute Care Surg, 2018, 85 (2): 247- 255.
doi: 10.1097/TA.0000000000001921 |
| 13 |
Vanzant EL , Hilton RE , Lopez CM , et al. Advanced age is associated with worsened outcomes and a unique genomic response in severely injured patients with hemorrhagic shock[J]. Crit Care, 2015, 19, 77.
doi: 10.1186/s13054-015-0788-x |
| 14 |
Girardot T , Rimmele T , Venet F , et al. Apoptosis-induced lymphopenia in sepsis and other severe injuries[J]. Apoptosis, 2017, 22 (2): 295- 305.
doi: 10.1007/s10495-016-1325-3 |
| 15 |
Kasten KR , Goetzman HS , Reid MR , et al. Divergent adaptive and innate immunological responses are observed in humans following blunt trauma[J]. BMC Immunol, 2010, 11, 4.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-11-4 |
| 16 |
Servia L , Jove M , Sol J , et al. A prospective pilot study using metabolomics discloses specific fatty acid, catecholamine and tryptophan metabolic pathways as possible predictors for a negative outcome after severe trauma[J]. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med, 2019, 27 (1): 56.
doi: 10.1186/s13049-019-0631-5 |
| 17 |
Ploder M , Spittler A , Schroecksnadel K , et al. Tryptophan degradation in multiple trauma patients: survivors compared with non-survivors[J]. Clin Sci (Lond), 2009, 116 (7): 593- 598.
doi: 10.1042/CS20080319 |
| 18 |
Kahloul M , Bouida W , Boubaker H , et al. Value of anatomic and physiologic scoring systems in outcome prediction of trauma patients[J]. Eur J Emerg Med, 2014, 21 (2): 125- 129.
doi: 10.1097/MEJ.0b013e32836188ce |
| [1] | Yifan CHEN,Zhongdi LIU,Peng ZHANG,Wei HUANG. Consistency of injury severity score in severe trauma patients [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 157-160. |
| [2] | Zhe DU,Wei HUANG,Zhi-wei WANG,Jing ZHOU,Jian XIONG,Ming LI,Peng ZHANG,Zhong-di LIU,Feng-xue ZHU,Chuan-lin WANG,Bao-guo JIANG,Tian-bing WANG. Application of multidisciplinary team (MDT) in the treatment of severe trauma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(2): 298-301. |
| [3] | ZHU Zhen-jie, XU Qing-quan, HUANG Xiao-bo, HONG Yang, YANG Qing-ya, WANG Shu, AN Li-zhe, XU Tao. Risk factor analysis of systemic inflammatory response syndrome in type 2 diabetics after percutaneous nephrolithotomy [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2016, 48(4): 643-649. |
| [4] | CHEN Liang, LI Jian-Xing, HUANG Xiao-Bo, WANG Xiao-Feng. Analysis for risk factors of systemic inflammatory response syndrome after onephase treatment for apyrexic calculous pyonephrosis by percutaneous nephrolithotomy [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2014, 46(4): 566-569. |
|
||