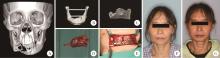
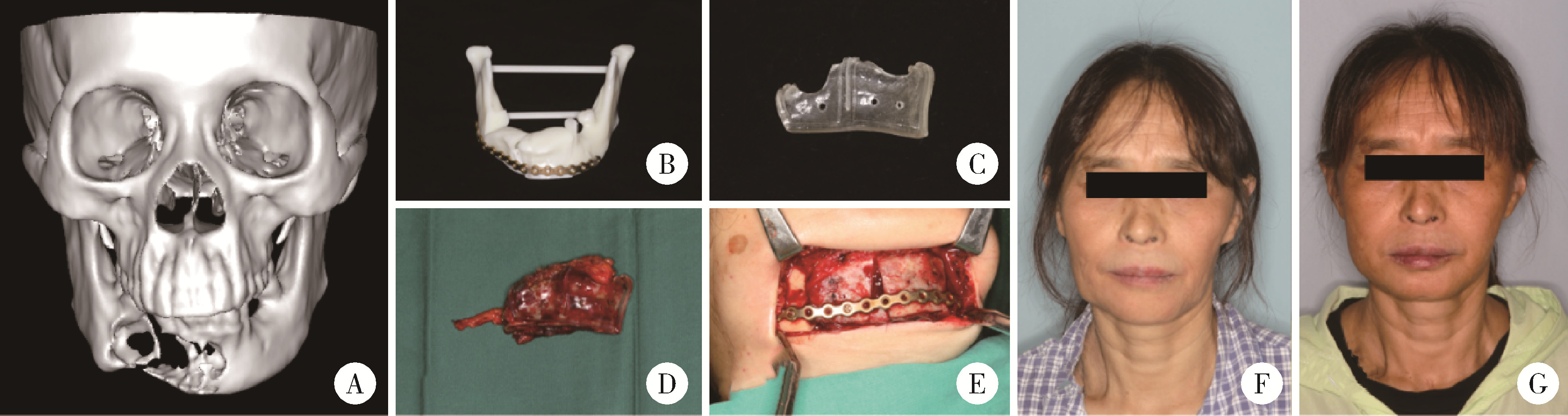
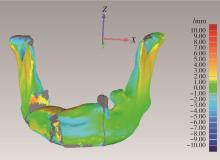
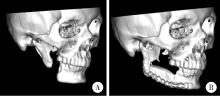
Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (2): 360-368. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.02.022
Previous Articles Next Articles
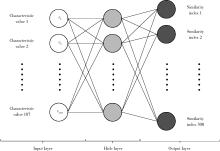
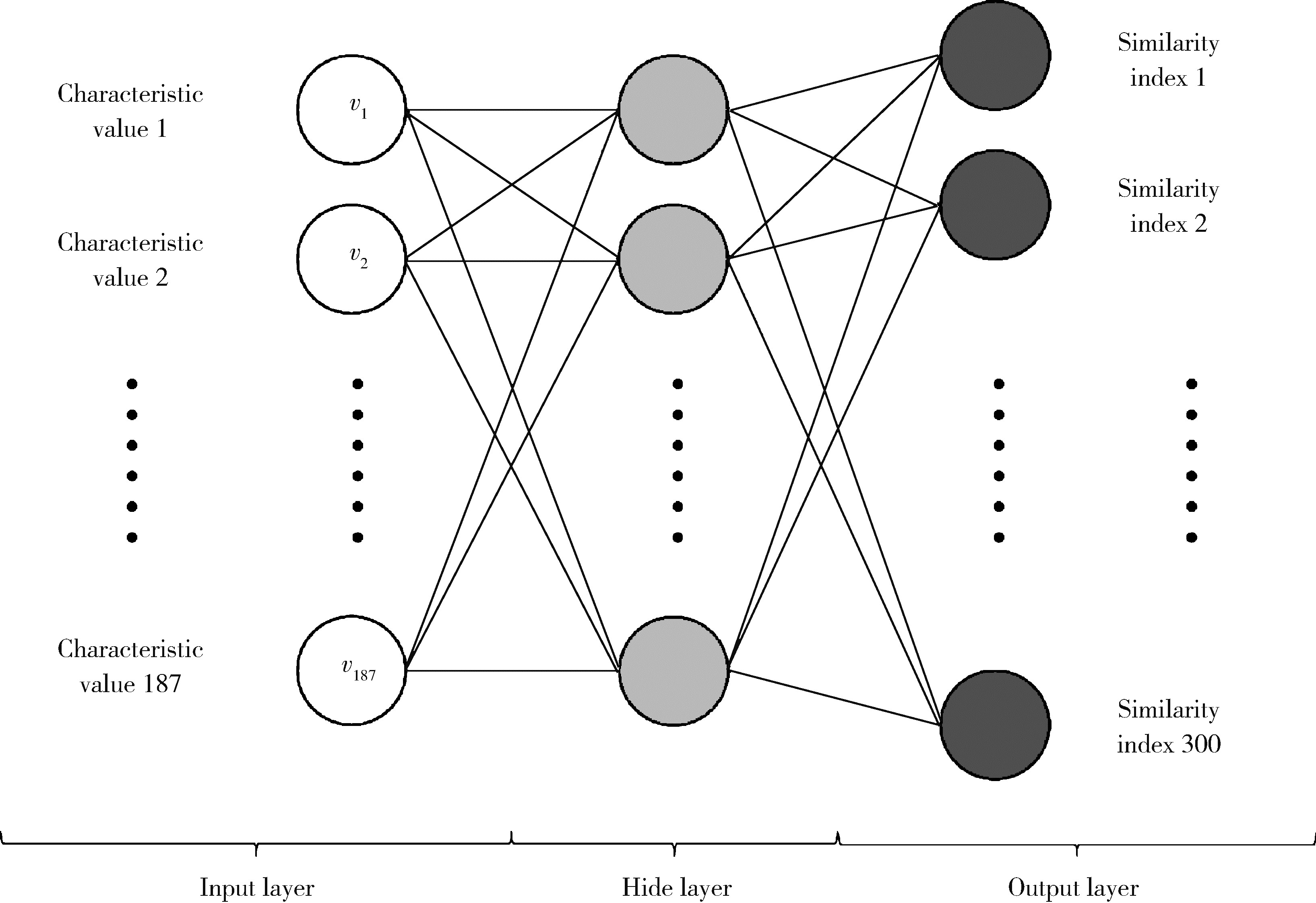
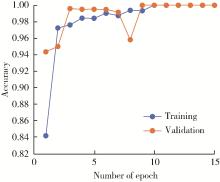
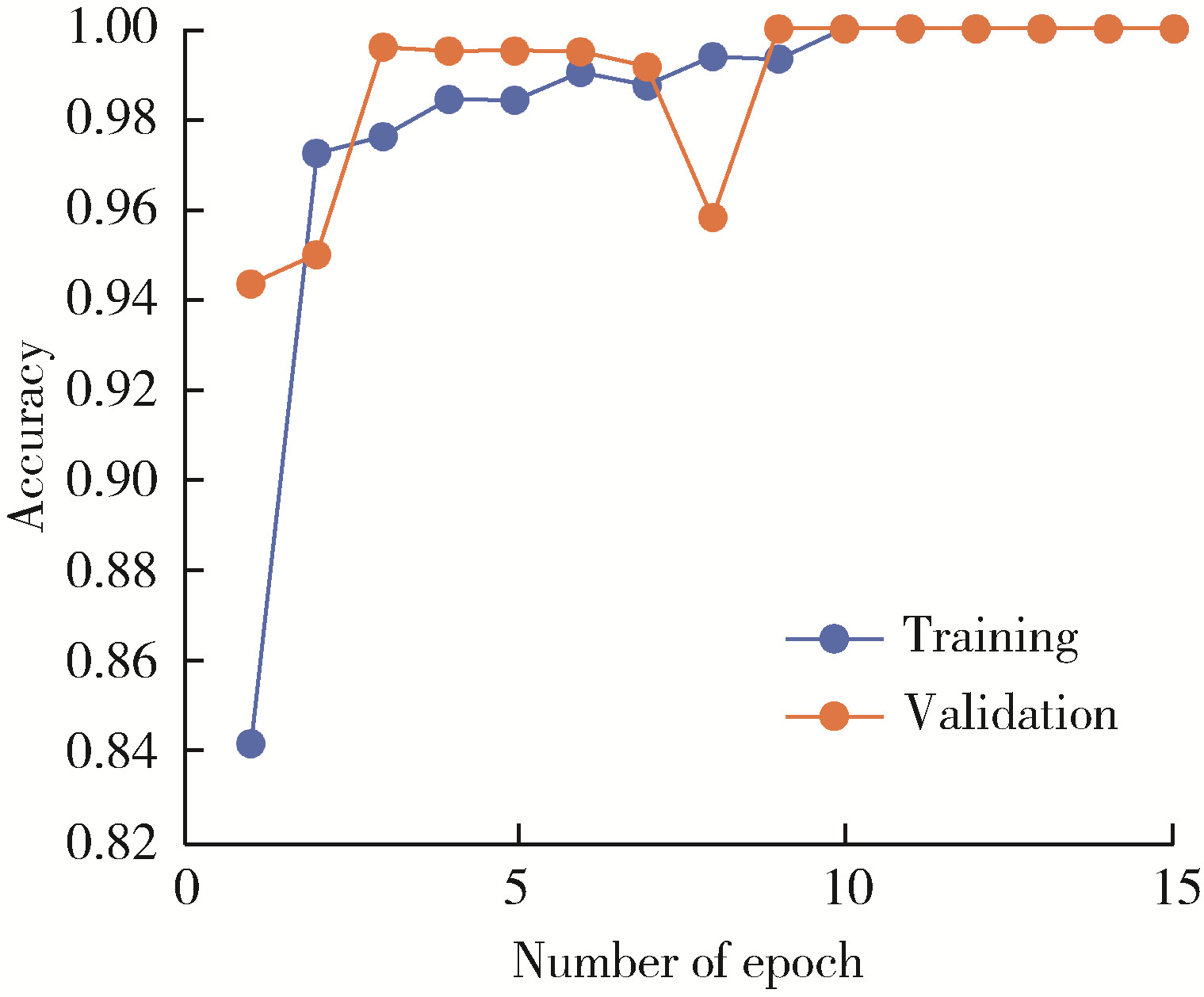
Personalized mandibular reconstruction assisted by three-dimensional retrieval model based on fully connected neural network and a database of mandibles
Shiyu QIU1, Yang LIAN2, Yifan KANG1, Lei ZHANG1, Yiwang CAI2, Xiaofeng SHAN1,*( ), Zhigang CAI1,*(
), Zhigang CAI1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
2. Byte-king Technology, Beijing 102629, China
CLC Number:
- R782.1
| 1 |
Kakarala K , Shnayder Y , Tsue TT , et al. Mandibular reconstruction[J]. Oral Oncol, 2018, 77, 111- 117.
doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2017.12.020 |
| 2 |
Hanasono MM , Skoracki RJ . Computer-assisted design and rapid prototype modeling in microvascular mandible reconstruction[J]. Laryngoscope, 2013, 123 (3): 597- 604.
doi: 10.1002/lary.23717 |
| 3 |
Zhang L , Liu Z , Li B , et al. Evaluation of computer-assisted mandibular reconstruction with vascularized fibular flap compared to conventional surgery[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol, 2016, 121 (2): 139- 148.
doi: 10.1016/j.oooo.2015.10.005 |
| 4 | Ren W , Gao L , Li S , et al. Virtual planning and 3D printing modeling for mandibular reconstruction with fibula free flap[J]. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal, 2018, 98 (33): 2666- 2670. |
| 5 |
Moiduddin K , Al-Ahmari A , Nasr ES , et al. A comparison study on the design of mirror and anatomy reconstruction technique in maxillofacial region[J]. Tech Health Care, 2016, 24 (3): 377- 389.
doi: 10.3233/THC-161136 |
| 6 |
陈全, 蔡志刚, 彭歆, 等. 下颌骨大范围缺损修复重建设计可变形模型的建立[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2014, 49 (7): 414- 419.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1002-0098.2014.07.008 |
| 7 | Wang E , Tran KL , D'heygere E , et al. Predicting the premorbid shape of a diseased mandible[J]. Laryngoscope, 2021, 131 (3): E781- E786. |
| 8 | 周子疌, 朱向阳, 韩婧, 等. 基于机器学习的颌骨特征点还原法辅助跨中线颌骨缺损重建[J]. 中国口腔颌面外科杂志, 2020, 18 (4): 323- 327. |
| 9 |
Yao BC , He Y , Jie BM , et al. Reconstruction of bilateral post-traumatic midfacial defects assisted by three-dimensional craniomaxillofacial data in normal chinese people: A preliminary study[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2019, 77 (11): 2302. e1- 2302. e13.
doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2019.04.030 |
| 10 | 傅民魁, 林久祥, 周彦恒, 等. 口腔正畸学[M]. 2版 北京: 北京大学医学出版社, 2014: 63- 78. |
| 11 |
Shnayder Y , Lin D , Desai SC , et al. Reconstruction of the lateral mandibular defect: A review and treatment algorithm[J]. JAMA Facial Plast Surg, 2015, 17 (5): 367- 373.
doi: 10.1001/jamafacial.2015.0825 |
| 12 | Cannon TY , Strub GM , Yawn RJ , et al. Oromandibular reconstruction[J]. Clin Anat, 2011, 25 (1): 108- 119. |
| 13 |
Mazzola F , Smithers F , Cheng K , et al. Time and cost-analysis of virtual surgical planning for head and neck reconstruction: A matched pair analysis[J]. Oral Oncol, 2020, 100, 104491.
doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2019.104491 |
| 14 |
Tarsitano A , Mazzoni S , Cipriani R , et al. The CAD/CAM technique for mandibular reconstruction: An 18 patients oncological case-series[J]. J Craniomaxillofac Surg, 2014, 42 (7): 1460- 1464.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2014.04.011 |
| 15 |
Chang EI , Boukovalas S , Liu J , et al. Reconstruction of posterior mandibulectomy defects in the modern era of virtual planning and three-dimensional modeling[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 2019, 144 (3): 453- 462.
doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000005954 |
| 16 | 蔡志刚. 数字化外科技术在下颌骨缺损修复重建中的应用[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2012, 47 (8): 474- 478. |
| 17 |
Yu HB , Shen GF , Wang XD , et al. The indication and application of computer-assisted navigation in oral and maxillofacial surgery: Shanghai' s experience based on 104 cases[J]. J Craniomaxillofac Surg, 2013, 41 (8): 770- 774.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2013.01.016 |
| 18 |
Davies JC , Chan HH , Jozaghi Y , et al. Analysis of simulated mandibular reconstruction using a segmental mirroring technique[J]. J Craniomaxillofac Surg, 2019, 47 (3): 468- 472.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2018.12.016 |
| [1] | Yifan KANG, Yanjun GE, Xiaoming LV, Shang XIE, Xiaofeng SHAN, Zhigang CAI. One-stage mandibular reconstruction combining iliac flap with immediate implant-based denture [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2025, 57(1): 78-84. |
| [2] | Congwei WANG,Min GAO,Yao YU,Wenbo ZHANG,Xin PENG. Clinical analysis of denture rehabilitation after mandibular fibula free-flap reconstruction [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 66-73. |
|
||