Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (5): 1002-1004. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.05.028
Previous Articles Next Articles
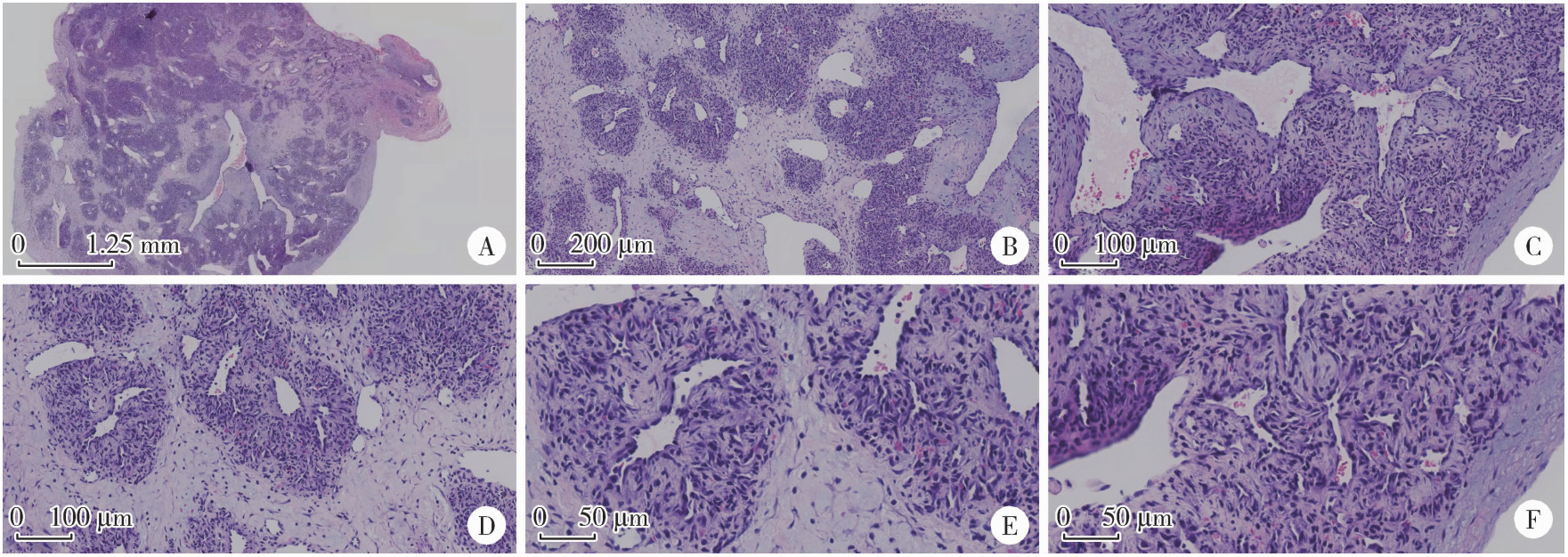
Left sided sternocleidomastoid interosseous intravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia: A case report
Xiaodi XIAO1, Youchen XIA1, Jianying LIU2, Peng FU3,*( )
)
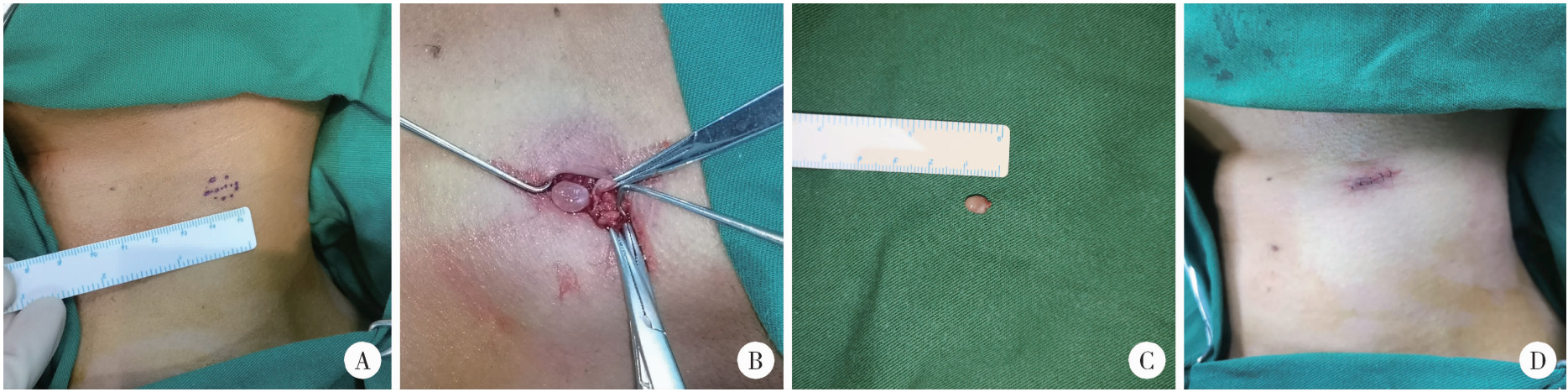
- 1. Department of Plastic Surgery, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
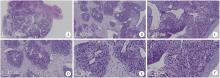
2. Department of Pathology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
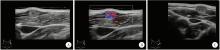
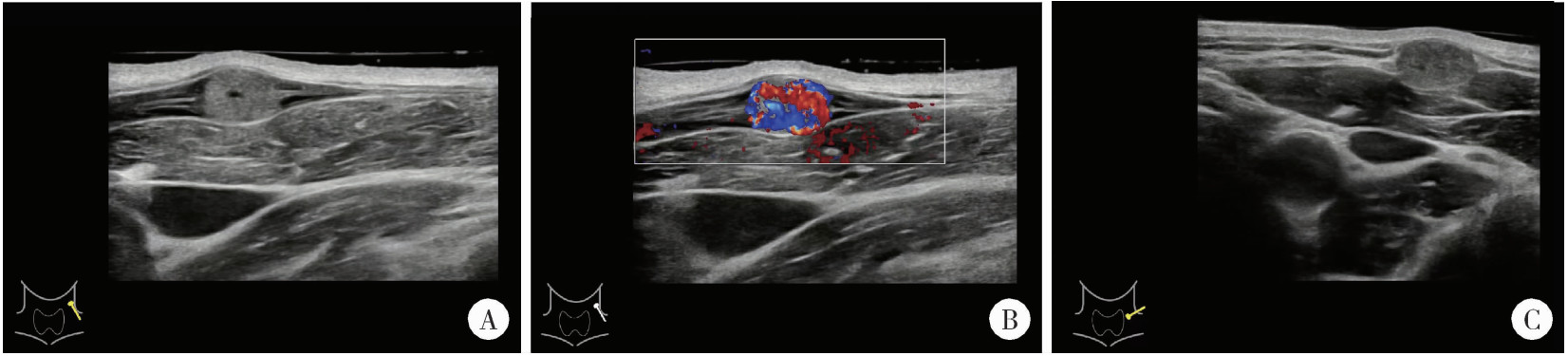
3. Department of Ultrasound, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
CLC Number:
- R730.262
| 1 |
doi: 10.7181/acfs.2018.02208 |
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1688925 |
| 4 |
doi: 10.3892/mco.2016.1117 |
| 5 |
doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2008.08.011 |
| 6 |
doi: 10.1007/s00256-015-2281-7 |
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
doi: 10.1016/0363-5023(94)90256-9 |
| 9 |
doi: 10.1097/00000372-198312000-00004 |
| 10 |
doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2005.11.095 |
| [1] | Chao ZUO, Guoli WANG, Kunlin YANG, Xinyan CHE, Yisen MENG, Kai ZHANG. Comparison of efficacy and safety of transurethral thulium fiber laser enucleation of prostate in patients with different prostate volumes [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2025, 57(4): 711-716. |
| [2] | Ning LIU, Libo MAN, Feng HE, Guanglin HUANG, Jianpo ZHAI. Correlation between urination intermittences and urodynamic parameters in benign prostatic hyperplasia patients [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2025, 57(2): 328-333. |
| [3] | Hua ZHONG, Yuan LI, Liling XU, Mingxin BAI, Yin SU. Application of 18F-FDG PET/CT in rheumatic diseases [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 853-859. |
| [4] | Xue-mei HA,Yong-zheng YAO,Li-hua SUN,Chun-yang XIN,Yan XIONG. Solid placental transmogrification of the lung: A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 357-361. |
| [5] | Chieko MORIMOTO,Yi-qin WANG,Rong ZHOU,Jian-liu WANG. Clinical analysis of fertility-sparing therapy of patients with complex atypical hyperplasia and endometrial cancer [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(5): 936-942. |
| [6] | HU Hao, XU Ke-Xin, ZHANG Xiao-Peng, FANG Zhi-Wei, CHEN Jing-Wen, HUO Fei, WANG Dong, WANG Xiao-Feng. Expression of brainderived neurotrophic factor in urine of patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia complicated overactive bladder symptoms [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2014, 46(4): 519-523. |
|
||