Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (6): 1025-1031. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.06.008
Previous Articles Next Articles
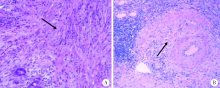
Analysis of the clinical features and misdiagnosis reasons of 17 patients misdiagnosed with IgG4-related disease
Zi-qiao WANG1,Yan-ying LIU1,△( ),Xia ZHANG1,Tian LIU1,Li-min REN1,Dan-hua SHEN2,Yi WANG3,Zhan-guo LI1
),Xia ZHANG1,Tian LIU1,Li-min REN1,Dan-hua SHEN2,Yi WANG3,Zhan-guo LI1
- 1. Department of Rheumatology & Immunology, Beijing 100044, China
2. Department of Pathology, Beijing 100044, China
3. Department of Radiology, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
CLC Number:
- R593.2
| [1] | Yamamoto M, Takahashi H, Shinomura Y . Mechanisms and assessment of IgG4-related disease: Lessons for the rheumatologist[J]. Nat Rev Rheumatol, 2013,10(3):148-159. |
| [2] | Umehara H, Okazaki K, Masaki Y , et al. Comprehensive diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD), 2011[J]. Nihon Naika Gakkai Zasshi, 2012,22(1):21-30. |
| [3] | Brito-Zerón P, Ramos-Casals M, Bosch X , et al. The clinical spectrum of IgG4-related disease[J]. Autoimmun Rev, 2014,13(12):1203-1210. |
| [4] | Carruthers MN, Khosroshahi A, Augustin T , et al. The diagnostic utility of serum IgG4 concentrations in IgG4-related disease[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2015,74(1):14-18. |
| [5] | El-Monayeri M, Nadim A, Abdel-Fattah I , et al. Pathologies associated with serum IgG4 elevation[J]. Int J Rheumatol, 2012,2012(8):1-6. |
| [6] | Vikram D, Yoh Z, John KC , et al. Consensus statement on the pathology of IgG4-related disease[J]. Mod Pathol, 2012,25(9):1181-1192. |
| [7] | Hart S, Horsman JM, Radstone CR , et al. Localised extranodal lymphoma of the head and neck: The Sheffield Lymphoma Group Experience (1971—2000)[J]. Clin Oncol, 2004,16(3):186-192. |
| [8] | 陈利红, 施若非, 郑捷 , 等. 托珠单抗成功治疗误诊为IgG4相关性疾病的多中心Castleman病2例国内首报[J]. 中国皮肤性病学杂志, 2017,31(12):1285-1289. |
| [9] | Vivino FB . Sjogren’s syndrome: clinical aspects[J]. Clin Immunol, 2017,9(182):48-54. |
| [10] | 吴靖林, 陈秉良, 贾强 . ANCA相关性小血管炎25例诊断及误诊分析[J]. 中国误诊学杂志, 2009,9(6):1367-1368. |
| [11] | Chari ST, Kloeppel G, Zhang L , et al. Histopathologicand clinical subtypes of autoimmune pancreatitis: The Honolulu Consensus Document[J]. Pancreas, 2010,39(5):549-554. |
| [12] | Cai Y, Shi Z, Bai Y . Review of Rosai-Dorfman disease: new insights into the pathogenesis of this rare disorder[J]. Acta Haematol, 2017,138(1):14-23. |
| [13] | Taylor TV, Sosa J . Bilateral breast fibromatosis: case report and review of the literature[J]. J Surg Educ, 2011,68(4):320-325. |
| [1] | Min FENG,Zhe CHEN,Yong-jing CHENG. A case of duodenal ulcer as prominent manifestation of IgG4-related disease [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1125-1129. |
| [2] | Lu FENG,Jia-yu ZHAI,Jin-xia ZHAO. Medical visit status and clinical features in patients with IgG4 related disease [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1028-1032. |
| [3] | Guang-ya YU,Xia HONG,Wei LI,Yan-yan ZHANG,Yan GAO,Yan CHEN,Zu-yan ZHANG,Xiao-yan XIE,Zhan-guo LI,Yan-ying LIU,Jia-zeng SU,Wen-xuan ZHU,Zhi-peng SUN. Clinicopathological characteristics and diagnosis of IgG4-related sialadenitis [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(1): 1-3. |
| [4] | WANG Yun-yun, SUN Wei, HUANG Yi-ning. Cervical spondylosis misdiagnosed as cerebral infarction: a case report [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2015, 47(5): 883-884. |
|
||