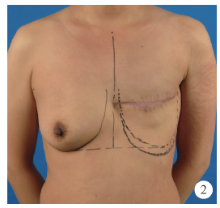
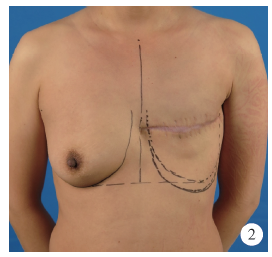
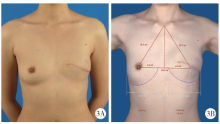
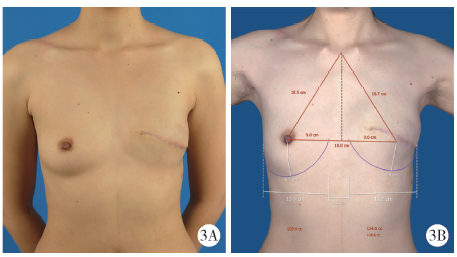
Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (1): 169-176. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.01.027
Previous Articles Next Articles
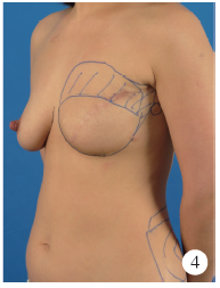
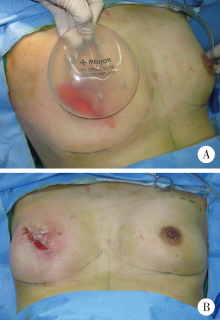
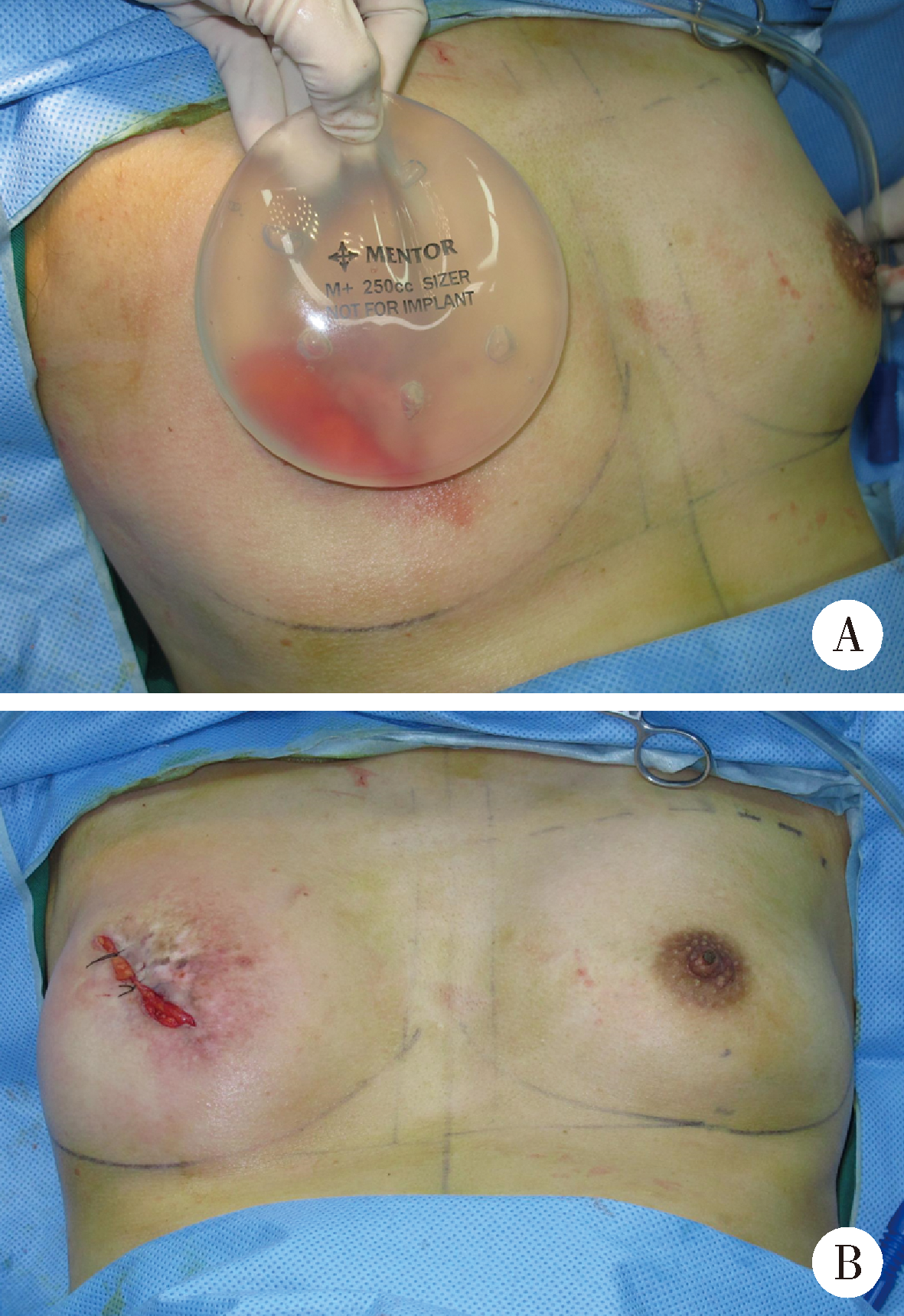
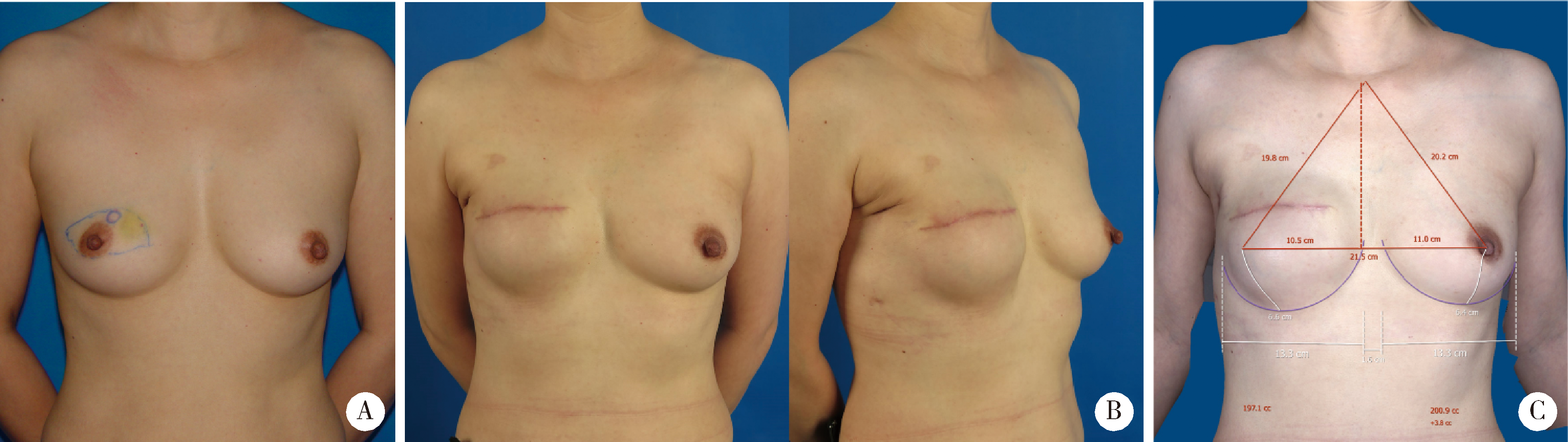
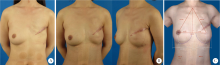
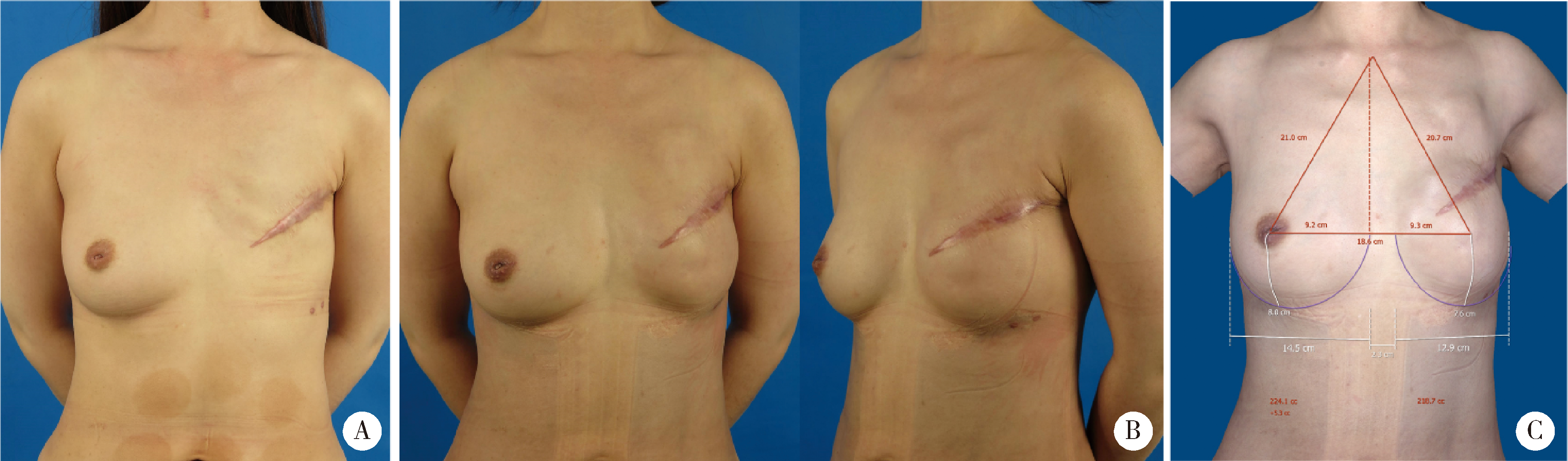
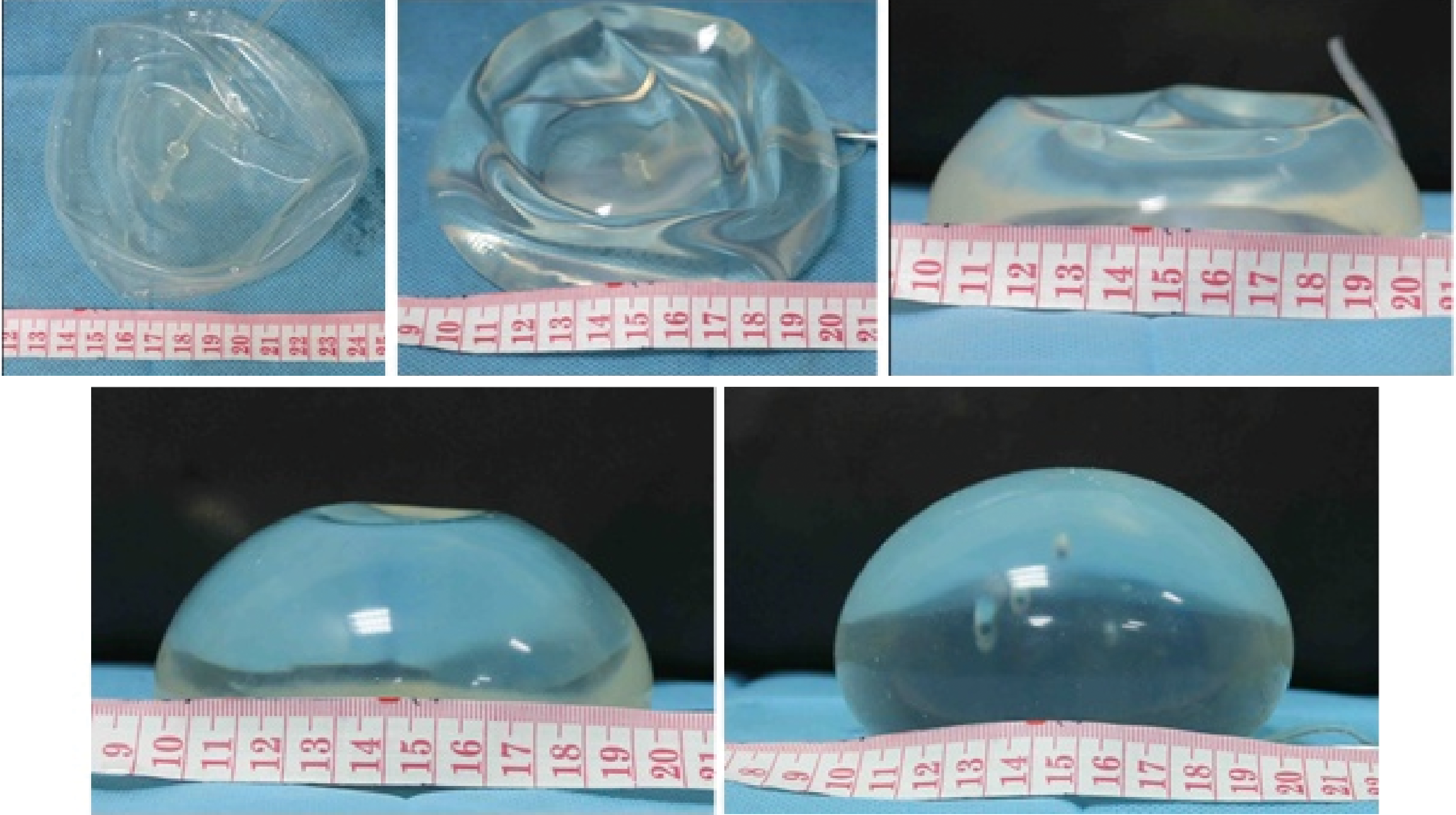
Techniques enhancement for tissue expander/implant two-stage breast reconstruction
Jian-xun MA1,You-chen XIA1,Bi LI1,△( ),Hong-mei ZHAO2,Yu-tao LEI2
),Hong-mei ZHAO2,Yu-tao LEI2
- 1. Department of Plastic Surgery, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
2. Department of General Surgery, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
CLC Number:
- R622
| [1] | Bertozzi N, Pesce M, Santi P . Tissue expansion for breast reconstruction: methods and techniques[J]. Ann Med Surg (Lond), 2017,21:34-44. |
| [2] | Jabo B, Lin AC, Aljehani MA , et al. Impact of breast reconstruction on time to definitive surgical treatment, adjuvant therapy, and breast cancer outcomes[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2018,25(10):3096-3105. |
| [3] | Susarla SM, Ganske I, Helliwell L , et al. Comparison of clinical outcomes and patient satisfaction in immediate single-stage versus two-stage implant-based breast reconstruction[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 2015,135(1):1e-8e. |
| [4] | Lee KT, Mun GH . Comparison of one-stage vs two-stage prosjournal-based breast reconstruction: a systematic review and meta-ana-lysis[J]. Am J Surg, 2016,212(2):336-344. |
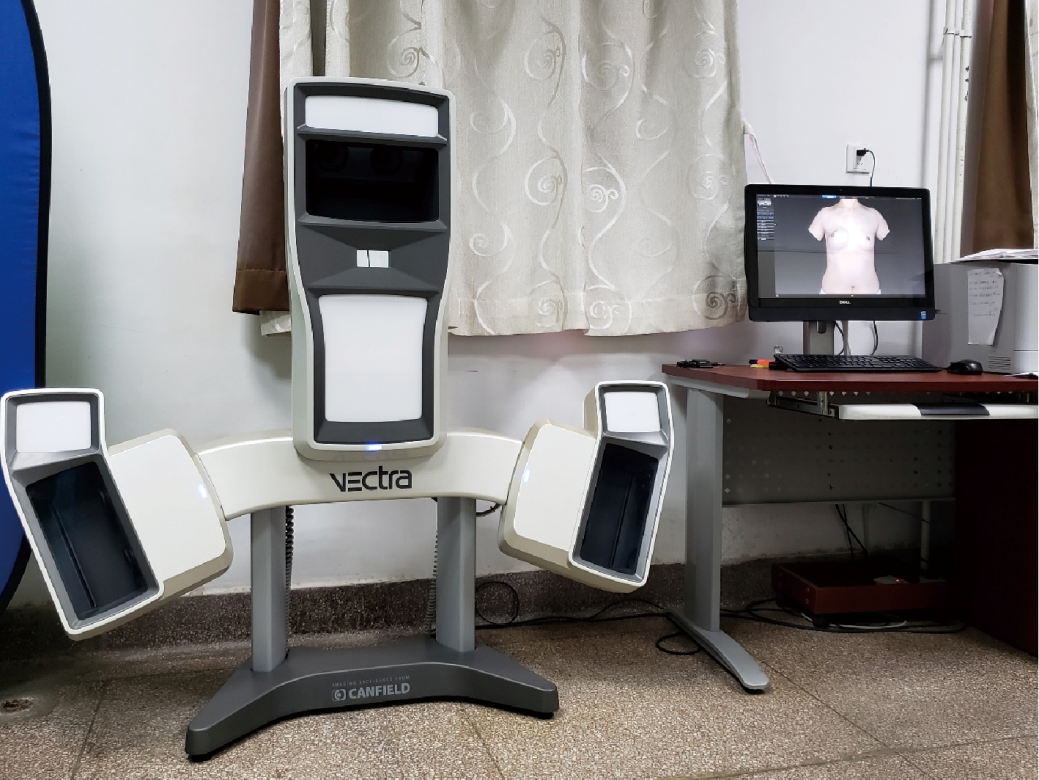
| [5] | Hameeteman M, Verhulst AC, Maal TJ , et al. An analysis of pose in 3D stereophotogrammetry of the breast[J]. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg, 2016,69(12):1609-1613. |
| [6] | Liu C, Ji K, Sun J , et al. Does respiration influence breast volumetric change measurement with the three-dimensional scanning technique?[J]. Aesthetic Plast Surg, 2014,38(1):115-119. |
| [7] | 刘荫华, 刘真真, 王翔 , 等. 乳腺癌改良根治术专家共识及手术操作指南(2018版)[J]. 中国实用外科杂志, 2018,38(8):851-854. |
| [8] | Cordeiro PG, Jazayeri L . Two-stage implant-based breast reconstruction: an evolution of the conceptual and technical approach over a two-decade period[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 2016,138(1):1-11. |
| [9] | Coleman SR, Mazzola RF. Fat injection: From filling to regeneration [M]. Florida: CRC Press LLC, 2009. |
| [10] | 王振宇, 姜晓曼, 杜彤华 , 等. Ⅰ期乳房重建中扩张器的应用[J]. 中华内分泌外科杂志, 2019,13(2):93-96. |
| [11] | 李尚善, 穆大力, 栾杰 , 等. 乳腺肿瘤切除术后二期组织扩张术假体植入乳房再造术的临床效果[J]. 中华医学美学美容杂志, 2018,24(1):32-34. |
| [12] | Pacella SJ . Evolution in tissue expander design for breast reconstruction: technological innovation to optimize patient outcomes[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 2018,142(4S The Science of Breast Implants):21S-30S. |
| [13] | Yang CE, Chung SW, Lee DW , et al. Evaluation of the relationship between flap tension and tissue perfusion in implant-based breast reconstruction using laser-assisted indocyanine green angiography[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2018,25(8):2235-2240. |
| [14] | Kato H, Nakagami G, Iwahira Y , et al. Risk factors and risk scoring tool for infection during tissue expansion in tissue expander and implant breast reconstruction[J]. Breast J, 2013,19(6):618-626. |
| [15] | Lam TC, Borotkanics R, Hsieh F , et al. Immediate two-stage prosthetic breast reconstruction failure: radiation is not the only culprit[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 2018,141(6):1315-1324. |
| [16] | Woo KJ, Paik JM, Bang SI , et al. The impact of expander inflation/deflation status during adjuvant radiotherapy on the complications of immediate two-stage breast reconstruction[J]. Aesthetic Plast Surg, 2017,41(3):551-559. |
| [17] | Sue GR, Sun BJ, Lee GK . Complications after two-stage expander implant breast reconstruction requiring reoperation: a critical ana-lysis of outcomes[J]. Ann Plast Surg, 2018,80(5S Suppl 5):S292-S294. |
| [18] | Pusic AL, Cordeiro PG . An accelerated approach to tissue expansion for breast reconstruction: experience with intraoperative and rapid postoperative expansion in 370 reconstructions[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 2003,111(6):1871-1875. |
| [19] | Liang X, Huang X, Zhou Y , et al. Mechanical stretching promotes skin tissue regeneration via enhancing mesenchymal stem cell homing and transdifferentiation[J]. Stem Cells Transl Med, 2016,5(7):960-969. |
| [20] | Makiguchi T, Atomura D, Nakamura H , et al. Quantitative assessment and risk factors for chest wall deformity resulting from tissue expansion for breast reconstruction[J]. Breast Cancer, 2019,26(4):446-451. |
| [21] | 刘晨, 栾杰, 丛中 , 等. 乳房再造手术对乳房缺失者的心理影响[J]. 中华医学美学美容杂志, 2008,14(3):187-189. |
| [22] | Agochukwu-Nwubah N, Boustany A, Wetzel M , et al. Anatomic implants in breast reconstruction: a comparison of outcomes and aesthetic results compared to smooth round silicone implants [J]. Aesthet Surg J, 2019, 39(8): NP322-NP330. |
| [23] | Petit JY, Maisonneuve P, Rotmensz N , et al. Fat grafting after invasive breast cancer: a matched case-control study[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 2017,139(6):1292-1296. |
| [24] | Krastev T, van Turnhout A, Vriens E , et al. Long-term follow-up of autologous fat transfer vs conventional breast reconstruction and association with cancer relapse in patients with breast cancer[J]. JAMA Surg, 2019,154(1):56-63. |
| [25] | Kim MS, Sbalchiero JC, Reece GP , et al. Assessment of breast aesthetics[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 2008,121(4):186e-194e. |
| [26] | Lee WY, Kim MJ, Lew DH , et al. Three-dimensional surface imaging is an effective tool for measuring breast volume: a validation study[J]. Arch Plast Surg, 2016,43(5):430-437. |
| [27] | Howes BH, Watson DI, Fosh B , et al. Magnetic resonance imaging versus 3-dimensional laser scanning for breast volume assessment after breast reconstruction[J]. Ann Plast Surg, 2017,78(4):455-459. |
| [28] | O’Connell RL, Di Micco R, Khabra K , et al. The potential role of three-dimensional surface imaging as a tool to evaluate aesthetic outcome after breast conserving therapy(BCT)[J]. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 2017,164(2):385-393. |
| [29] | Chae MP, Rozen WM, Spychal RT , et al. Breast volumetric ana-lysis for aesthetic planning in breast reconstruction: a literature review of techniques[J]. Gland Surg, 2016,5(2):212-226. |
| [30] | Razdan SN, Panchal H, Albornoz CR , et al. Impact of contrala-teral symmetry procedures on long-term patient-reported outcomes following unilateral prosthetic breast reconstruction[J]. J Reconstr Microsurg, 2019,35(2):124-128. |
| [1] | Xin-ling ZHANG,Zhi-yu LIN,Yu-jie CHEN,Wen-fang DONG,Xin YANG. Plastic and reconstruction surgery for non-healing wound after posterior spinal surgery [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 910-914. |
| [2] | ZHAO Jian-fang,LI Dong,AN Yang. Roles of ten eleven translocation proteins family and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in epigenetic regulation of stem cells and regenerative medicine [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(2): 420-424. |
| [3] | . [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2015, 47(5): 891-封三. |
|
||