Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (3): 414-419. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.03.003
Previous Articles Next Articles
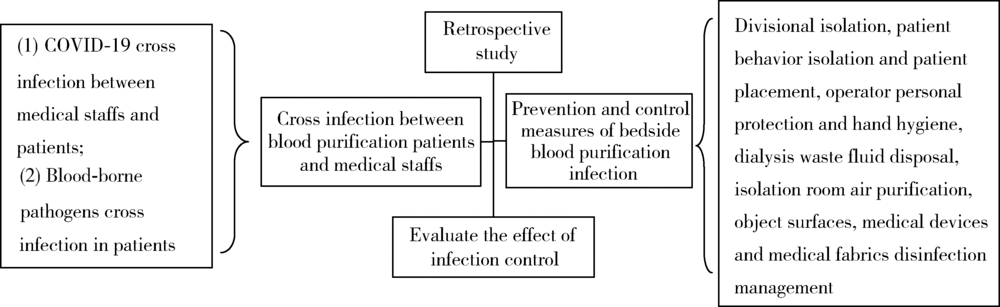
Infection prevention and control of bedside blood purification treatment in patients with COVID-19
Mei-lian CHEN1,Yan GAO1,2,△( ),Wei GUO3,Li ZUO4,Tian-bing WANG3
),Wei GUO3,Li ZUO4,Tian-bing WANG3
- 1. Department of Infection Control
2. Department of Infectious Disease
3. Trauma center
4. Department of Nephrology, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
CLC Number:
- R563.1
| [1] | 王文峰, 吴岚, 水华, 等. 新型冠状病毒肺炎疫情区域血液净化中心的防控策略[J/OL]. 武汉大学学报(医学版), 2020, 2 (2020- 02- 19)[2020-04-02]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1677.R.20200218.1642.002.html. |
| [2] | 中华医学会肾脏病学分会专家组. 中华医学会肾脏病学分会关于血液净化中心(室)新型冠状病毒感染的防控建议[J]. 中华肾脏病杂志, 2020,36(2):82-84 |
| [3] | 国家卫生健康委办公厅. 关于印发医疗机构内新型冠状病毒感染预防与控制技术指南(第一版)的通知[EB/OL]. ( 2020- 01- 22)[2020-04-02]. http://www.nhc.gov.cn/yzygj/s7659/202001/b91fdab7c304431eb082d67847d27e14.shtml |
| [4] | 卫生部. 医院隔离技术规范: WS/T 311—2009 [S/OL]. ( 2009- 04- 01)[2020-04-02]. http://www.nhc.gov.cn/wjw/s9496/200904/40116/files/3f2c129ec8d74c1ab1d40e16c1ebd321.pdf. |
| [5] | 国家卫生计生委办公厅. 关于印发血液透析中心基本标准和管理规范(试行)的通知[EB/OL].( 2016- 12- 21)[2020-04-02]. http://www.nhc.gov.cn/yzygj/s3594q/201612/69a95ec-0335c4a45883713094c8ef10d.shtml. |
| [6] | 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会. 医务人员手卫生规范: WS/T 313—2019 [S/OL].( 2019- 11- 26)[2020-04-05]. http://www.nhc.gov.cn/wjw/s9496/202002/dbd143c44abd4de8-b59a235feef7d75e/files/6a3e2bf3d82b4ee8a718dbfc3cde8338.pdf. |
| [7] | 国家卫生健康委办公厅. 新型冠状病毒感染的肺炎诊疗方案(试行第七版)[EB/OL]. ( 2020- 03- 04)[2020-04-05]. http://www.nhc.gov.cn/yzygj/s7653p/202003/46c9294a7dfe4-cef80dc7f5912eb1989.shtml. |
| [8] | Ling Y, Xu Sh B, Lin Y X, et al. Persistence and clearance of viral RNA in 2019 novel coronavirus disease rehabilitation patients[J/OL]. Chin Med J, 2020, 2 (2020-02-28)[2020-04-05]. https://journals.lww.com/cmj/Abstract/publishahead/Persis-tence_and_clearance_of_viral_RNA_in_2019.99362.aspx. |
| [9] | Eeeltjevan D, Trenton B, Dylan M, et al. Aerosol and surface stability of HCoV-19 (SARS-CoV-2) compared to SARS-CoV-1. N Engl J Med [EB/OL]. ( 2020-03-09)[2020-04-05]. https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.03.09.20033217v2. |
| [10] |
Sahli F, Feidjel R, Laalaoui R. Hemodialysis catheter-related infection: rates, risk factors and pathogens[J]. J Infect Public Health, 2017,10(4):403-408.
pmid: 27423929 |
| [11] | Smith S, Hobbs D, Ennis-Davis R, et al. Outbreak of influenza B at a hemodialysis unit[J]. Int J Antimicrob Agents, 2009,34(Supple 2):71. |
| [12] | 吕春燕. 血液透析期间合并甲型H1N1流感患者的感染管理[J]. 中国消毒学杂志, 2010,27(6):760-761. |
| [13] | 任南, 文细毛, 吴安华, 等. 全国医院感染监测网对持续血液透析患者丙型肝炎病毒感染现况调查[J]. 中国感染控制杂志, 2011, 11, ( 6):412-415. |
| [14] | 陈群, 陈燕芝, 何丽. 终末期尿毒症血液透析者乙肝和丙肝感染情况调查分析[J]. 中国地方病防治杂志, 2019,34(05):574-576. |
| [15] | 邹杨, 洪大情, 何强, 李贵森. 血液透析患者乙肝病毒感染情况及影响因素分析[J]. 中国误诊学杂志, 2018,13(09):389-393. |
| [16] | 国家卫生健康委办公厅. 新型冠状病毒肺炎防控方案(第六版)[EB/OL]. ( 2020- 03- 07)[2020-04-05]. http://www.nhc.gov.cn/xcs/zhengcwj/202003/4856d5b0458141fa9f376853-224-d41d7.shtml. |
| [17] | WHO. Infection prevention and control during health care when novel coronavirus (nCoV) infection is suspectted: interim gui-dance [S/OL]. ( 2020-03-19)[2020-04-05]. https://www.who.int/publications-detail/infection-prevention-and-control-during-health-care-when-novel-coronavirus-(ncov)-infection-is-suspected-20200125. |
| [18] | Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology. Guide to the elimination of infection in hemodialysis [S/OL]. ( 2010- 07- 05)[2020-04-05]. http://www.apic.org/AM/Template.cfm?Section=APIC_Elimination_Guides&Template=/CM/HTMLDisplay.cfm&ContentID=14743. |
| [1] | Xin LIU,Xueying SHI,Jun LI. A case of COVID-19 associated ischemic colitis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 362-365. |
| [2] | Jinrong ZHU,Yana ZHAO,Wei HUANG,Weiwei ZHAO,Yue WANG,Song WANG,Chunyan SU. Clinical characteristics of COVID-19 infection in patients undergoing hemodialysis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 267-272. |
| [3] | Jian-bin LI,Meng-na LYU,Qiang CHI,Yi-lin PENG,Peng-cheng LIU,Rui WU. Early prediction of severe COVID-19 in patients with Sjögren’s syndrome [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1007-1012. |
| [4] | Jin-hui LAI,Qi WANG,Jia-xiang JI,Ming-rui WANG,Xin-wei TANG,Ke-xin XU,Tao XU,Hao HU. Effects of delayed ureteral stents removal during the COVID-19 pandemic on the quality of life and psychological status of postoperative patients with urinary calculi [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 857-864. |
| [5] | Zhi-yu KANG,Lei-lei WANG,Yong-zheng HAN,Xiang-yang GUO. Anesthesia management of athletes' operation in Beijing Olympic Winter Games [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(4): 770-773. |
| [6] | Ming-long CHEN,Xiao-han LIU,jing GUO. Relationship between social support and parental burnout in COVID-19 among Chinese young parents [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(3): 520-525. |
| [7] | Hong MENG,Li-na JI,Jing HUANG,Shuang CHAO,Jia-wen ZHOU,Xue-jun LI,Xiao-mei YIN,Li-rong FAN. Analysis of the changes and characteristics of pediatric outpatient visits in a general hospital in Beijing before and after the COVID-19 pandemic [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(5): 952-956. |
| [8] | HUANG Bing, WANG Hong-yuan. Analysis of the development trend and severity of the COVID-19 panidemic in the global world [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(3): 536-542. |
| [9] | Qiu WANG,Jin-yu GUO,Hong SUN,Ling WANG,Ju-su YING,Hui-xin LIU. Investigation of protective exposure risk events in nurses against corona virus disease 2019 in Wuhan [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(4): 711-714. |
| [10] | Hang YANG,Lin-cheng YANG,Rui-tao ZHANG,Yun-peng LING,Qing-gang GE. Risks factors for death among COVID-19 patients combined with hypertension, coronary heart disease or diabetes [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(3): 420-424. |
| [11] | Wen FENG,Liang-nan ZHANG,Jing-yuan LI,Tian WEI,Ting-ting PENG,Dong-xu ZHANG,Zai-xin GUO,Wei-song WANG. Analysis of special ehealth service for corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(2): 302-307. |
|
||