Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (4): 697-700. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.04.019
Previous Articles Next Articles
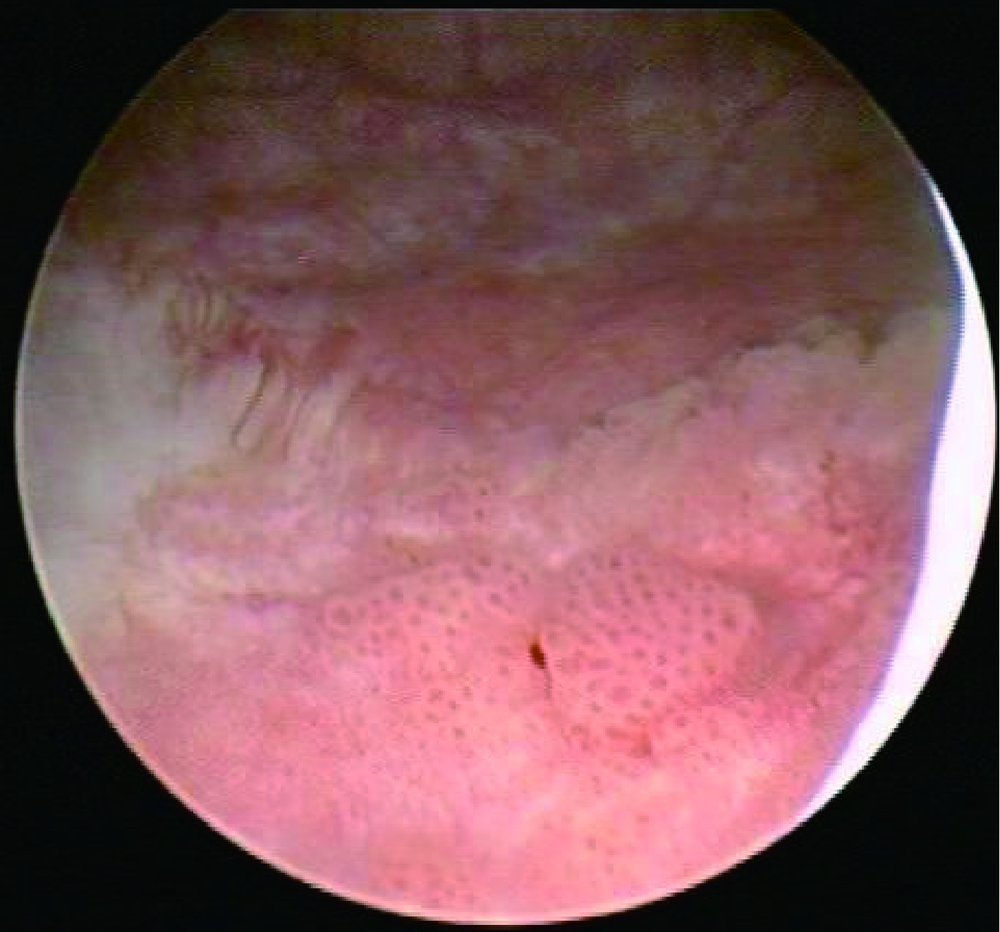
Analysis of self-control trial results of narrow band imaging and white light in transurethral resection of bladder tumor
Min QIU,Chu-xiao XU,Bin-shuai WANG,Ye YAN,Shao-hui DENG,Chun-lei XIAO,Cheng LIU,Jian LU,Xiao-jun TIAN( ),Lu-lin MA
),Lu-lin MA
- Department of Urology,Peking University Third Hospital,Beijing 100191, China
CLC Number:
- R737.14
| [1] | Li K, Lin T, Xue W, et al. Current status of diagnosis and treatment of bladder cancer in China: analyses of Chinese bladder cancer consortium database[J]. Asian J Urol, 2015,2(2):63-69. |
| [2] |
Naselli A, Introini C, Timossi L, et al. A randomized prospective trial to assess the impact of transurethral resection in narrow band imaging modality on non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer recurrence[J]. Eur Urol, 2012,61(5):908-913.
pmid: 22280855 |
| [3] | 廖洪, 李汉忠, 张玉石, 等. 单中心尿路上皮癌2 115例临床特点分析[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2014,35(12):900-904. |
| [4] | Bryan RT, Billingham LJ, Wallace DM. Narrow-band imaging flexible cystoscopy in the detection of recurrent urothelial cancer of the bladder[J]. BJU Int, 2008,101(6):702-705. |
| [5] |
Cauberg ECC, Mamoulakis C, de la Rosette JJMC, et al. Narrow band imaging-assisted transurethral resection for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer significantly reduces residual tumour rate[J]. World J Urol, 2011,29(4):503-509.
pmid: 21350871 |
| [6] |
Malik K, Raja A, Mahalingam S, et al. Usefulness of narrow-band imaging in transurethral resection of bladder tumor: early experience from a tertiary center in India[J]. South Asian J Cancer, 2019,8(4):226.
pmid: 31807483 |
| [7] | 邱敏, 颜野, 田晓军, 等. 窄带成像技术辅助经尿道膀胱肿瘤切除术[J]. 中国微创外科杂志, 2018,18(10):888-890. |
| [8] |
Naito S, Algaba F, Babjuk M, et al. The clinical research office of the endourological society (CROES) multicentre randomised trial of narrow band imaging-assisted transurethral resection of bladder tumour (TURBT) versus conventional white light imaging-assisted TURBT in primary non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer patients: trial protocol and 1-year results[J]. Eur Urol, 2016,70(3):506-515.
pmid: 27117749 |
| [9] | Shadpour P, Emami M, Haghdani S. A Comparison of the progression and recurrence risk index in non-muscle-invasive bladder tumors detected by narrow-band imaging versus white light cystoscopy, based on the EORTC scoring system[J]. Nephro-Urol Mon, 2016,8(1):e33240. |
| [10] | 唐兴国, 颜野, 邱敏, 等. 单中心16年青年膀胱尿路上皮癌患者的诊治[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018,50(4):630-633. |
| [11] | Dalgaard LP, Zare R, Gaya JM, et al. Prospective evaluation of the performances of narrow-band imaging flexible videoscopy relative to white-light imaging flexible videoscopy, in patients scheduled for transurethral resection of a primary NMIBC[J]. World J Urol, 2018,37(8):1615-1621. |
| [1] | Tian WANG,Xin HONG,Xiao-feng WANG. Clinical application of the needle electrode in transurethral plasmakinetic resection of bladder tumor around ureteral orifice: A report of 16 cases [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(4): 632-636. |
| [2] | Shi-ming ZHAO,Tie-jun YANG,Chun-miao XU,Xiao-feng GUO,Yong-kang MA,Xue-jun CHEN,Xiang LI,Chao-hong HE. Bladder cancer local staging about muscle invasion: 3.0T MRI performance following transurethral resection [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(4): 701-704. |
| [3] | Hai-wen HUANG,Bing YAN,Mei-xia SHANG,Li-bo LIU,Han HAO,Zhi-jun XI. Propensity-matched comparison of laparoscopic and open radical cystectomy for female patients with bladder cancer [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(4): 698-705. |
| [4] | . [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(2): 372-373. |
| [5] | . [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(4): 565-568. |
| [6] | MENG Yi-sen, WANG Yu, FAN Yu, SU Yang, LIU Zhen-hua, YU Wei, CHEN Cheng, ZHOU Li-qun, ZHANG Qian, HE Zhi-song, JIN Jie. Impact of different surgical methods of radical cystectomy on the perioperative complications in patients over 75 years [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2016, 48(4): 632-637. |
| [7] | YE Hai-yun, XU Qing-quan, HUANG Xiao-bo, MA Kai, WANG Xiao-feng. Tuberculous prostatic abscess following intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guérin immunotherapy: a case report [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2015, 47(6): 1039-1041. |
| [8] | LIU Yu-Qing, LU Jian, ZHAO Lei, HOU Xiao-Fei, MA Lu-Lin. Prognostic factors for intravesical recurrence after surgery for upper tract urothelial carcinoma in renal transplant recipients [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2015, 47(4): 605-610. |
| [9] | MENG Yi-Sen, Su-Yang, Fan-Yu, Yu-Wei, Wang-Yu, Zheng-Wei, Chen-Cheng, Zhou-Li-Qun, Zhang-Qian, Li-Xue-Song, . Risk factors for the development of postoperative paralytic ileus after radical cystectomy: a report of 740 cases [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2015, 47(4): 628-633. |
|
||