Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (4): 705-710. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.04.021
Previous Articles Next Articles
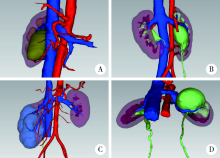
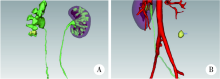
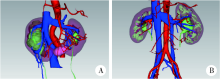
Application of preoperative three-dimensional image reconstruction in the treatment of ureteropelvic junction obstruction
Meng-meng ZHENG1,2,Guang-pu DING1,Wei-jie ZHU1,Kun-lin YANG1,Shu-bo FAN1,Bao GUAN1,Xin-fei LI1,Yu-kun CAI1,Jin-sheng ZHANG2,Xue-song LI1,△( ),Li-qun ZHOU1
),Li-qun ZHOU1
- 1. Department of Urology, Peking University First Hospital, Institute of Urology, Peking University, National Urological Cancer Centre,Beijing 100034, China
2. Department of Urology, Fu Xing Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100038, China
CLC Number:
- R691.2
| [1] | 黄强, 杨骥, 林先盛, 等. CT三维重建在肝门部胆管癌的诊疗中的应用价值[J]. 中国普通外科杂志, 2017,26(8):960-967. |
| [2] | 中华医学会数字医学分会, 中国研究型医院学会数字医学临床外科专业委员会. 复杂性肝脏肿瘤三维可视化精准诊治专家共识[J]. 中国实用外科杂志, 2017,37(1):53-59. |
| [3] | 李学松, 杨昆霖, 周利群. IUPU经腹腹腔镜肾盂成型术治疗成人肾盂输尿管连接处梗阻(附视频)[J]. 现代泌尿外科杂志, 2015,20(6):369-372. |
| [4] |
Yang K, Yao L, Li X, et al. A modified suture technique for transperitoneal laparoscopic dismembered pyeloplasty of pelviureteric junction obstruction[J]. Urology, 2015,85(1):263-267.
doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2014.09.031 pmid: 25530399 |
| [5] | Klingler HC, Remzi M, Janetschek G, et al. Comparison of open versus laparoscopic pyeloplasty techniques in treatment of uretero-pelvic junction obstruction[J]. Eur Urol, 2003,44(3):340-345. |
| [6] | 贾晨尧, 陈柯, 刘奇, 等. 基于CT的肾脏可视化三维重建模型在肾蒂血管变异的肾癌根治术中的应用[J]. 广东医学, 2017,38(9):81-84. |
| [7] |
Wang Z, Qi L, Yuan P, et al. Application of three-dimensional visualization technology in laparoscopic partial nephrectomy of renal tumor: a comparative study[J]. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A, 2017,27(5):516-523.
pmid: 28186431 |
| [8] |
Tolkach Y, Thomann S, Kristiansen G. Three-dimensional reconstruction of prostate cancer architecture with serial immunohistochemical sections: hallmarks of tumour growth, tumour compartmentalisation, and implications for grading and heterogeneity[J]. Histopathology, 2018,72(6):1051-1059.
pmid: 29323728 |
| [9] | Rydberg J, Kopecky KK, Tann M, et al. Evaluation of prospective living renal donors for laparoscopic nephrectomy with multisection CT: the marriage of minimally invasive imaging with minimally invasive surgery[J]. Radiographics, 2001,21(Supp1 1):S223-S236. |
| [10] |
Ukimura O. Image-guided surgery in minimally invasive urology[J]. Curr Opin Urol, 2010,20(2):136-140.
doi: 10.1097/MOU.0b013e3283362610 |
| [11] | 赵海岳, 叶雄俊, 陈伟男, 等. 腹腔镜肾盂成型术中异位血管的处理方法[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019,51(4):660-664. |
| [12] |
Berkman DS, Landman J, Gupta M. Treatment outcomes after endopyelotomy performed with or without simultaneous nephrolithotomy: 10-year experience[J]. J Endourol, 2009,23(9):1409-1413.
doi: 10.1089/end.2009.0379 pmid: 19694529 |
| [13] | 陈远波, 李虎林, 刘春晓, 等. 数字化肾结石三维模型的建立及虚拟手术仿真[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2013,33(2):267-270. |
| [14] |
Li HL, Chen YB, Liu C, et al. Construction of a three-dimensional model of renal stones: comprehensive planning for percutaneous nephrolithotomy and assistance in surgery[J]. World J Urol, 2013,31(6):1587-1592.
doi: 10.1007/s00345-012-0998-7 pmid: 23223963 |
| [15] | 杨昆霖, 李学松, 周利群. IUPU经腹腹腔镜联合膀胱软镜肾盂取石及肾盂成型术[J]. 泌尿外科杂志: 电子版, 2015,7(3):4-6. |
| [16] | Simonato A, Gregori A, Lissiani A, et al. The tongue as an alternative donor site for graft urethroplasty: a pilot study[J]. J Urol, 2006,175(2):589-592. |
| [17] |
Singh PB, Das SK, Kumar A, et al. Dorsal onlay lingual mucosal graft urethroplasty: comparison of two techniques[J]. Int J Urol, 2010,15(11):1002-1005.
pmid: 18808427 |
| [18] | Xu YM, Feng C, Sa YL, et al. Outcome of 1-stage urethroplasty using oral mucosal grafts for the treatment of urethral strictures associated with genital lichen sclerosus[J]. Urology, 2014,83(1):232-236. |
| [19] |
Li B, Xu YJ, Hai B, et al. Laparoscopic onlay lingual mucosal graft ureteroplasty for proximal ureteral stricture: initial experience and 9-month follow-up[J]. Int Urol Nephrol, 2016,48(8):1275-1279.
doi: 10.1007/s11255-016-1289-9 pmid: 27115158 |
| [1] | Li-zhe AN,Liu-lin XIONG,Liang CHEN,Huan-rui WANG,Wei-nan CHEN,Xiao-bo HUANG. Laparoscopic pyeloplasty combined with ultrasonic lithotripsy via nephroscope for treatment of ureteropelvic junction obstruction with renal calculi [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(4): 746-750. |
| [2] | Sheng-wei XIONG,Jie WANG,Wei-jie ZHU,Si-da CHENG,Lei ZHANG,Xue-song LI,Li-qun ZHOU. Advance in re-do pyeloplasty for the management of recurrent ureteropelvic junction obstruction after surgery [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(4): 794-798. |
| [3] | Hai-yue ZHAO,Xiong-jun YE,Wei-nan CHEN,Li-zhe AN,Jun LIU,Liu-lin XIONG,Xiao-bo HUANG. Treatment of crossing vessels in laparoscopic pyeloplasty [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(4): 660-664. |
| [4] | CHEN Wei-nan, YE Xiong-jun, LIU Shi-jun, XIONG Liu-lin, HUANG Xiao-bo, XU Tao, WANG Xiao-feng. Comparison of three surgical methods of ureteropelvic junction obstruction in therapeutic effect and complication [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2016, 48(5): 817-821. |
|
||