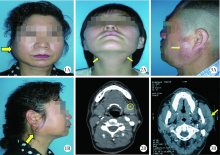
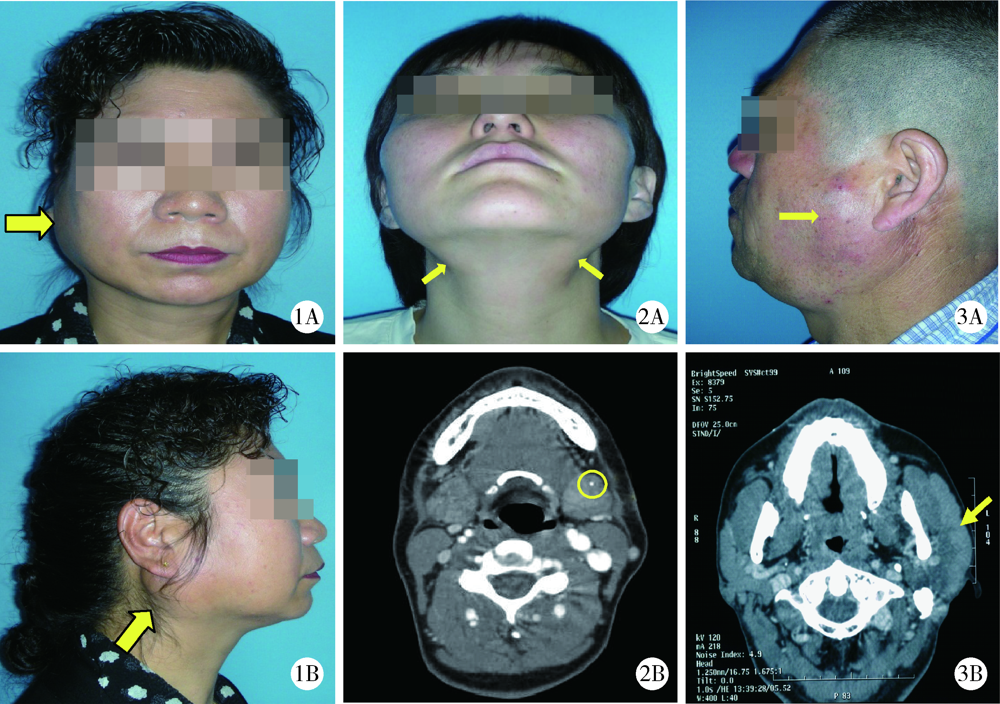
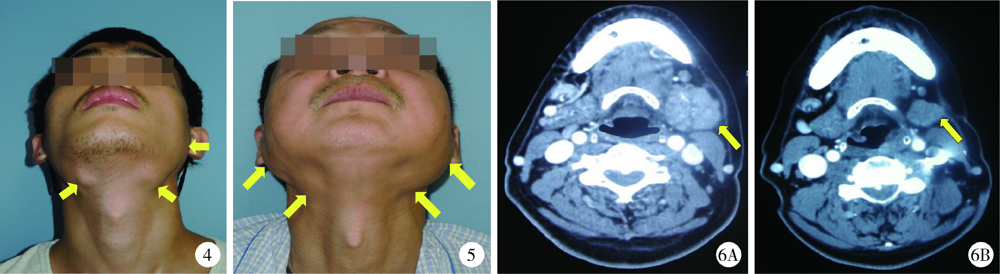
CLC Number:
- R780.2
| [1] |
Li W, Chen Y, Sun ZP, et al. Clinicopathological characteristics of immunoglobulin G4-related sialadenitis[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2015,17(1):186.
doi: 10.1186/s13075-015-0698-y |
| [2] |
Hong X, Li W, Xie XY, et al. Differential diagnosis of IgG4-related sialadenitis, primary Sjögren syndrome, and chronic obstructive submandibular sialadenitis[J]. Brit J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2017,55(2):179-184.
doi: 10.1016/j.bjoms.2016.10.021 |
| [3] |
Hong X, Zhang YY, Wei L, et al. Treatment of immunoglobulin G4-related sialadenitis: outcomes of glucocorticoid therapy combined with steroid-sparing agents[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2018,20(1):12.
doi: 10.1186/s13075-017-1507-6 pmid: 29382364 |
| [4] | 俞光岩, 洪霞, 李巍, 等. IgG4相关唾液腺炎的临床病理特点及诊断[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018,50(6):6-8. |
| [5] |
Hong X, Sun ZP, Li W, et al. Comorbid diseases of IgG4-related sialadenitis in the head and neck region[J]. Laryngoscope, 2015,125(9):2113-2118.
doi: 10.1002/lary.25387 pmid: 25994602 |
| [6] | 宿骞, 彭歆, 周传香, 等. 原发性腮腺淋巴瘤的临床病理特点及预后分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019,51(1):35-42. |
| [7] | 俞光岩. 要重视下颌下腺功能器官的保护[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2017,52(4):204-205. |
| [1] | ZHOU Chuan-xiang,ZHOU Zheng,ZHANG Ye,LIU Xiao-xiao,GAO Yan. Clinicopathological study in 28 cases of oral basaloid squamous cell carcinomas [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(1): 62-67. |
| [2] | Guang-ya YU,Xia HONG,Wei LI,Yan-yan ZHANG,Yan GAO,Yan CHEN,Zu-yan ZHANG,Xiao-yan XIE,Zhan-guo LI,Yan-ying LIU,Jia-zeng SU,Wen-xuan ZHU,Zhi-peng SUN. Clinicopathological characteristics and diagnosis of IgG4-related sialadenitis [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(1): 1-3. |
| [3] | JIA Wei-qian, ZHAO Yu-ming, GE Li-hong. Recombinant human transforming growth factor β1 promotes dental pulp stem cells proliferation and mineralization [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(4): 680-681. |
| [4] | SIMA Zi-han, HONG Ying-ying, LI Tie-jun△. Effects of PTCH1 mutations on the epithelial proliferation derived from keratocystic odontogenic tumour [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(3): 522-526. |
| [5] | GAO Li, YU Xiao-qian, CAI Yu. Effect of molar ligation and local Porphyromonas gingivalis inoculation on alveolar bone loss in the mouse [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(1): 31-035. |
| [6] | HUANG Zhen, LUAN Qing-xian. Evaluation of dental plaque by quantitative digital image analysis system [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2016, 48(2): 320-323. |
|
||