Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (2): 293-297. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.02.010
Previous Articles Next Articles
Multivariate analysis of varus after Oxford unicompartmental knee arthroplasty
JI Song-jie,HUANG Ye,WANG Xing-shan,LIU Jian,DOU Yong,JIANG Xu,ZHOU Yi-xin( )
)
- Department of Adult Joint Reconstruction Surgery, Beijing Jishuitan Hospital, Beijing 100035, China
CLC Number:
- R687.4
| [1] |
Berger RA, Meneghini RM, Jacobs JJ, et al. Results of unicom-partmental knee arthroplasty at a minimum of ten years of follow-up[J]. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2005,87(5):999-1006.
doi: 10.2106/JBJS.C.00568 pmid: 15866962 |
| [2] |
Kim MS, Koh IJ, Choi YJ, et al. Differences in patient-reported outcomes between unicompartmental and total knee arthroplasties: a propensity score-matched analysis[J]. J Arthroplasty, 2017,32(5):1453-1459.
doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2016.11.034 pmid: 27979407 |
| [3] |
van der List JP, Chawla H, Zuiderbaan HA, et al. Patients with isolated lateral osteoarthritis: Unicompartmental or total knee arthroplasty[J]. Knee, 2016,23(6):968-974.
doi: 10.1016/j.knee.2016.06.007 |
| [4] |
Ko YB, Gujarathi MR, Oh KJ. Outcome of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: a systematic review of comparative studies between fixed and mobile bearings focusing on complications[J]. Knee Surg Relat Res, 2015,27(3):141-148.
doi: 10.5792/ksrr.2015.27.3.141 pmid: 26389066 |
| [5] |
Kim KT, Lee S, Kim TW, et al. The influence of postoperative tibiofemoral alignment on the clinical results of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty[J]. Knee Surg Relat Res, 2012,24(2):85-90.
doi: 10.5792/ksrr.2012.24.2.85 pmid: 22708108 |
| [6] |
Bruni D, Iacono F, Russo A, et al. Minimally invasive unicom-partmental knee replacement: retrospective clinical and radiographic evaluation of 83 patients[J]. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc, 2010,18(6):710-717.
doi: 10.1007/s00167-009-0895-9 pmid: 19763541 |
| [7] | Ewald FC. The knee society total knee arthroplasty roentgenographic evaluation and scoring system[J]. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1989,248(11):9-12. |
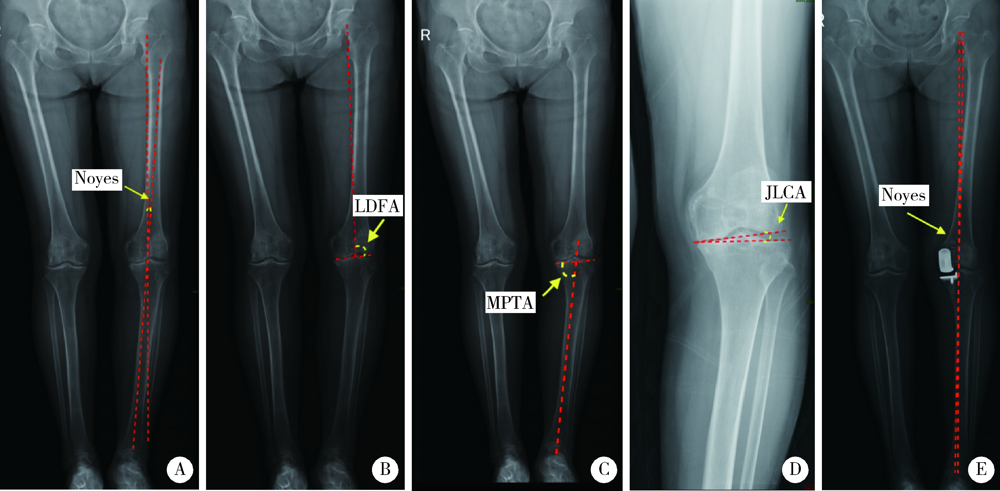
| [8] | Dugdale TW, Noyes FR, Styer D. Preoperative planning for high tibial osteotomy. The effect of lateral tibiofemoral separation and tibiofemoral length[J]. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1992,274(1):248-264. |
| [9] |
Price AJ, O’Connor JJ, Murray DW, et al. A history of Oxford unicompartmental knee arthroplasty[J]. Orthopedics, 2007,30(Suppl 5):7-10.
doi: 10.3928/01477447-20070101-01 |
| [10] |
Choy WS, Kim KJ, Lee SK, et al. Mid-term results of oxford medial unicompartmental knee arthroplasty[J]. Clin Orthop Surg, 2011,3(3):178-183.
doi: 10.4055/cios.2011.3.3.178 pmid: 21909464 |
| [11] |
Mercier N, Wimsey S, Saragaglia D. Long-term clinical results of the Oxford medial unicompartmental knee arthroplasty[J]. Int Orthop, 2010,34(8):1137-1143.
doi: 10.1007/s00264-009-0869-z pmid: 19838707 |
| [12] |
Kuipers BM, Kollen BJ, Bots PC, et al. Factors associated with reduced early survival in the Oxford phase III medial unicompartment knee replacement[J]. Knee, 2010,17(1), 48-52.
doi: 10.1016/j.knee.2009.07.005 |
| [13] | 及松洁, 黄野, 王达成, 等. 胫骨高位闭合截骨与开放截骨对胫骨后倾及髌骨高度的影响[J]. 基础医学与临床, 2020,40(10):1394-1398. |
| [14] |
Aleto TJ, Berend ME, Ritter MA, et al. Early failure of unicom-partmental knee arthroplasty leading to revision[J]. J Arthroplasty, 2008,23(2):159-163.
doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2007.03.020 |
| [15] |
Hernigou P, Deschamps G. Alignment influences wear in the knee after medial unicompartmental arthroplasty[J]. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 2004,423(6):161-165.
doi: 10.1097/01.blo.0000128285.90459.12 |
| [16] | Squire MW, Callaghan JJ, Goetz DD, et al. Unicompartmental knee replacement. A minimum 15 year followup study[J]. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1999,367(10):61-72. |
| [17] |
Cartier P, Sanouiller JL, Grelsamer RP. Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty surgery. 10-year minimum follow-up period[J]. J Arthroplasty, 1996,11(7):782-788.
doi: 10.1016/s0883-5403(96)80177-x pmid: 8934317 |
| [18] |
Tashiro Y, Matsuda S, Okazaki K, et al. The coronal alignment after medial unicompartmental knee arthroplasty can be predicted: usefulness of full-length valgus stress radiography for evaluating correctability[J]. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc, 2014,22(12):3142-3249.
doi: 10.1007/s00167-014-3248-2 pmid: 25155051 |
| [19] |
Robinson BJ, Rees JL, Price AJ, et al. Dislocation of the bearing of the Oxford lateral unicompartmental arthroplasty. A radiological assessment[J]. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 2002,84(5):653-657.
doi: 10.1302/0301-620x.84b5.12950 pmid: 12188479 |
| [20] |
Scott CE, Eaton MJ, Nutton RW, et al. Proximal tibial strain in medial unicompartmental knee replacements: a biomechanical study of implant design[J]. Bone Joint J, 2013,95B(10):1339-1347.
doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.95B10.31644 |
| [21] |
Sawatari T, Tsumura H, Iesaka K, et al. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: the influence of tibial component inclination[J]. J Orthop Res, 2005,23(3):549-554.
doi: 10.1016/j.orthres.2004.06.007 pmid: 15885474 |
| [22] |
Simpson DJ, Price AJ, Gulati A, et al. Elevated proximal tibial strains following unicompartmental knee replacement: a possible cause of pain[J]. Med Eng Phys, 2009,31(7):752-757.
doi: 10.1016/j.medengphy.2009.02.004 pmid: 19278893 |
| [23] |
Pandit HG, Campi S, Hamilton TW, et al. Five-year experience of cementless Oxford unicompartmental knee replacement[J]. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc, 2017,25(3):694-702.
doi: 10.1007/s00167-015-3879-y pmid: 26611902 |
| [1] | Silan AN,Qunyi ZHENG,Kai WANG,Shan GAO. Characteristics and influencing factors of early pain in patients after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 167-173. |
| [2] | Ran ZHAO,Yan-qing LIU,Hua TIAN. Cumulative sum control chart analysis of soft tissue balance in total knee replacement assisted by electronic pressure sensor [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 658-664. |
| [3] | Yi-lin YE,Heng LIU,Li-ping PAN,Wei-bing CHAI. Periprosthetic gout flare after total knee arthroplasty: A misdiagnostic case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 362-365. |
| [4] | Yan-chao TANG,Wen-kui ZHAO,Miao YU,Xiao-guang LIU. Normative values of cervical sagittal alignment according to the whole spine balance: Based on 126 asymptomatic Chinese young adults [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(4): 712-718. |
| [5] | LI Zhi-chang,HOU Yun-fei,ZHOU Zhi-wei,JIANG Long,ZHANG Shu,LIN Jian-hao. Patient factors influencing preoperative expectations of patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(1): 170-176. |
| [6] | Hao WU,Li-ping PAN,Heng LIU,Hong-bin WANG,Tai-guo NING,Yong-ping CAO. Effect of posterior tibial slope on the short-term outcome in mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(5): 877-882. |
| [7] | WANG Xin-guang,GENG Xiao,LI Yang,WU Tian-chen,LI Zi-jian,TIAN Hua. Comparison of alignment and operative time between portable accelerometer-based navigation device and computer assisted surgery in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(4): 728-733. |
| [8] | CAO Ze,WANG Le-tong,LIU Zhen-ming. Homologous modeling and binding ability analysis of Spike protein after point mutation of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 to receptor proteins and potential antiviral drugs [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(1): 150-158. |
| [9] | KE Yan,ZHANG Qiang,MA Yun-qing,LI Ru-jun,TAO Ke,GUI Xian-ge,LI Ke-peng,ZHANG Hong,LIN Jian-hao. Short-term outcomes of total hip arthroplasty in the treatment of Tönnis grade 3 hip osteoarthritis in patients with spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(1): 175-182. |
| [10] | Zhong-di LIU,Hao LU,Yu-song YUAN,Hai-lin XU. Evaluation of therapeutic efficacy of arthroplasty with Swanson prosthesis in the surgical treatment of 2-5 metatarsophalangeal joint diseases [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(4): 726-729. |
| [11] | Sen-lei LI,Xian-teng YANG,Xiao-bin TIAN,Li SUN. Early functional recovery of direct anterior approach versus anterolateral approach for total hip arthroplasty [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(2): 268-272. |
| [12] | LIU Heng, LI Zhuo-yang, CAO Yong-ping, CUI Yun-peng, WU Hao. Measurement of the tibial alignment after total knee replacement without the extramedullary cutting guide [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(5): 850-854. |
| [13] | LI Yang, LI Bang-guo, ZHAO Ran, TIAN Hua, ZHANG Ke. Effect of autologous blood transfusion device on preventing blood loss in primary total knee arthroplasty using comprehensive hemostatic methods [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(4): 651-656. |
| [14] | WANG Jun-feng, LI Zhao, ZHANG Ke-shi, YUAN Feng, LI Ru-jun, ZHONG Qun-jie, GUAN Zhen-peng. Unilateral patellar resurfacing in bilateral total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled study [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(5): 861-866. |
| [15] | GONG Xiao-feng, LYU Yan-wei, WANG Jin-hui, WANG Yan, WU Yong, WANG Man-yi. A correlation analysis of the ankle CT and ankle fracture classification [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(2): 281-285. |
|
||