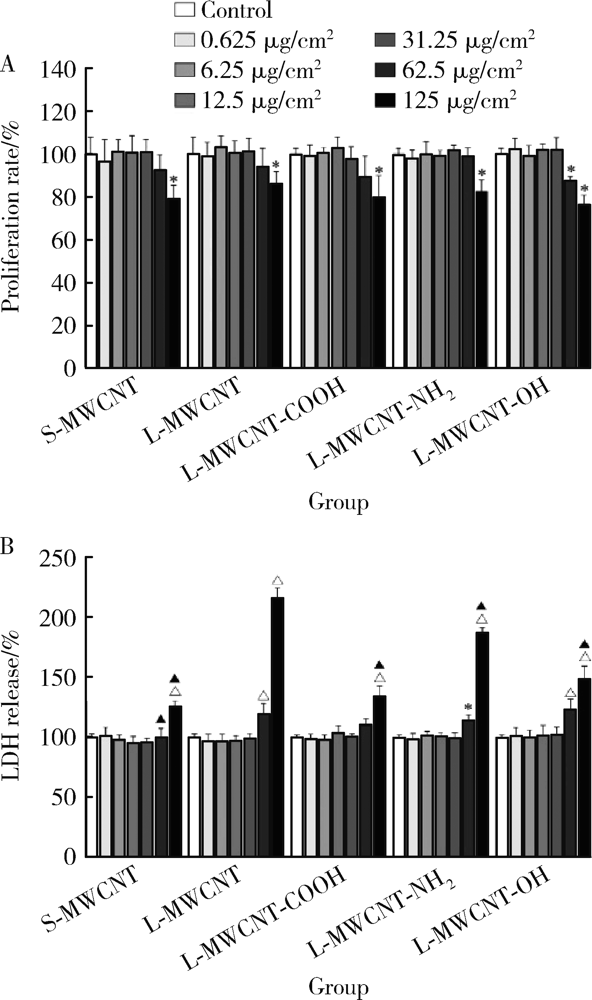
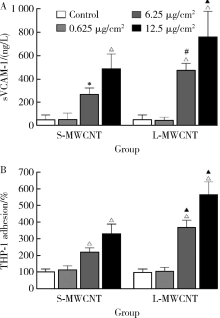
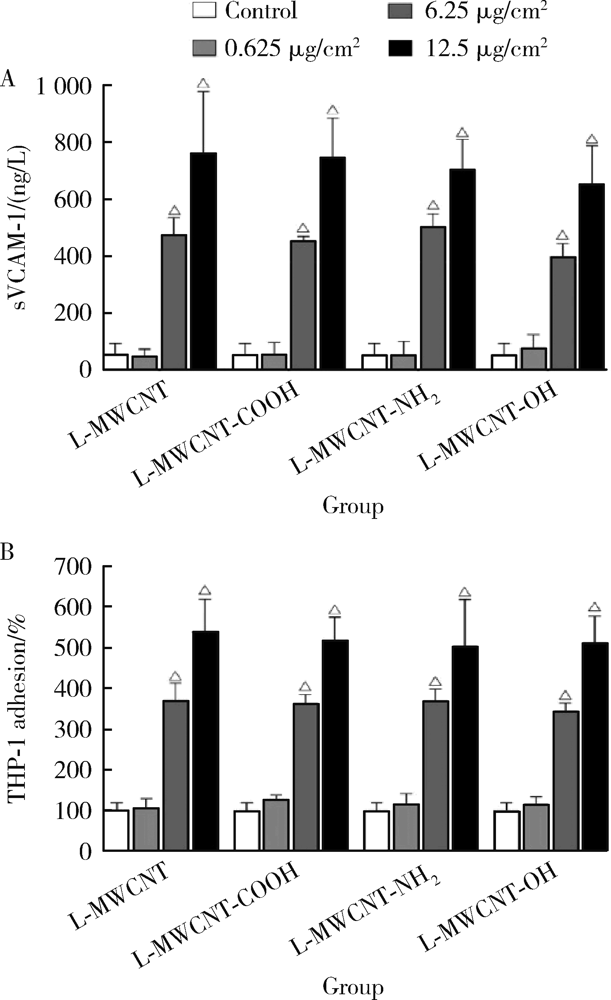
Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (3): 439-446. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.03.001
Effects of length and chemical modification on the activation of vascular endothelial cells induced by multi-walled carbon nanotubes
SHEN Jie,YANG Di,CHEN Meng-yuan,GUO Xin-biaoΔ( )
)
- Department of Occupational and Environmental Health, Peking University School of Public Health, Beijing 100191, China
CLC Number:
- R12
| [1] | He H, Pham-Huy LA, Dramou P, et al. Carbon nanotubes: applications in pharmacy and medicine[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2013,2013:578290. |
| [2] |
Aschberger K, Johnston HJ, Stone V, et al. Review of carbon nanotubes toxicity and exposure: appraisal of human health risk assessment based on open literature[J]. Crit Rev Toxicol, 2010,40(9):759-790.
doi: 10.3109/10408444.2010.506638 |
| [3] |
Amenta V, Aschberger K. Carbon nanotubes: potential medical applications and safety concerns[J]. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol, 2015,7(3):371-386.
doi: 10.1002/wnan.2015.7.issue-3 |
| [4] | John AA, Subramanian AP, Vellayappan MV, et al. Carbon nanotubes and graphene as emerging candidates in neuroregeneration and neurodrug delivery[J]. Int J Nanomedicine, 2015,10:4267-4277. |
| [5] |
Gonzalez-Carter D, Goode AE, Kiryushko D, et al. Quantification of blood-brain barrier transport and neuronal toxicity of unlabelled multiwalled carbon nanotubes as a function of surface charge[J]. Nanoscale, 2019,11(45):22054-22069.
doi: 10.1039/c9nr02866h pmid: 31720664 |
| [6] |
Setyawati MI, Tay CY, Docter D, et al. Understanding and exploiting nanoparticles’ intimacy with the blood vessel and blood[J]. Chem Soc Rev, 2015,44(22):8174-8199.
doi: 10.1039/c5cs00499c pmid: 26239875 |
| [7] |
Hunt BJ, Jurd KM. Endothelial cell activation. A central pathophysiological process[J]. BMJ, 1998,316(7141):1328-1329.
pmid: 9563977 |
| [8] |
Zhang J, Defelice AF, Hanig JP, et al. Biomarkers of endothelial cell activation serve as potential surrogate markers for drug-induced vascular injury[J]. Toxicol Pathol, 2010,38(6):856-871.
doi: 10.1177/0192623310378866 pmid: 20716788 |
| [9] |
Schroder K, Tschopp J. The inflammasomes[J]. Cell, 2010,140(6):821-832.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.01.040 pmid: 20303873 |
| [10] |
van der Heijden T, Kritikou E, Venema W, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition by MCC950 reduces atherosclerotic lesion development in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice-brief report[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2017,37(8):1457-1461.
doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.117.309575 |
| [11] |
Yang WL, Sharma A, Wang Z, et al. Cold-inducible RNA-binding protein causes endothelial dysfunction via activation of NLRP3 inflammasome[J]. Sci Rep, 2016,6:26571.
doi: 10.1038/srep26571 |
| [12] |
Yang D, Shen J, Fan J, et al. Paracellular permeability changes induced by multi-walled carbon nanotubes in brain endothelial cells and associated roles of hemichannels[J]. Toxicology, 2020,440:152491.
doi: S0300-483X(20)30130-X pmid: 32413421 |
| [13] |
Fan J, Chen Y, Yang D, et al. Multi-walled carbon nanotubes induce IL-1β secretion by activating hemichannels-mediated ATP release in THP-1 macrophages[J]. Nanotoxicology, 2020,14(7):929-946.
doi: 10.1080/17435390.2020.1777476 |
| [14] |
Bicker J, Alves G, Fortuna A, et al. Blood-brain barrier models and their relevance for a successful development of CNS drug delivery systems: a review[J]. Eur J Pharm Biopharm, 2014,87(3):409-432.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2014.03.012 pmid: 24686194 |
| [15] |
Constantinescu CA, Fuior EV, Rebleanu D, et al. Targeted transfection using PEGylated cationic liposomes directed towards P-selectin increases siRNA delivery into activated endothelial cells[J]. Pharmaceutics, 2019,11(1):47.
doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics11010047 |
| [16] |
Li Y, Cao J. The impact of multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) on macrophages: contribution of MWCNT characteristics[J]. Sci China Life Sci, 2018,61(11):1333-1351.
doi: 10.1007/s11427-017-9242-3 |
| [17] | 龙继敏. 多壁碳纳米管的长度及功能化对血管健康效应的影响及其作用机制[D]. 湖南湘潭: 湘潭大学, 2019. |
| [18] |
Mallakpour S, Khodadadzadeh L. Ultrasonic-assisted fabrication of starch/MWCNT-glucose nanocomposites for drug delivery[J]. Ultrason Sonochem, 2018,40(Pt A):402-409.
doi: S1350-4177(17)30336-X pmid: 28946439 |
| [19] |
Wang JT, Rubio N, Kafa H, et al. Kinetics of functionalised carbon nanotube distribution in mouse brain after systemic injection: Spatial to ultra-structural analyses[J]. J Control Release, 2016,224:22-32.
doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.12.039 |
| [20] |
Badea MA, Prodana M, Dinischiotu A, et al. Cisplatin loaded multiwalled carbon nanotubes induce resistance in triple negative breast cancer cells[J]. Pharmaceutics, 2018,10(4):228.
doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics10040228 |
| [21] |
Chen H, Shi Y, Sun L, et al. Electrospun composite nanofibers with all-trans retinoic acid and MWCNTs-OH against cancer stem cells[J]. Life Sci, 2020,258:118152.
doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118152 |
| [22] |
Kafa H, Wang JT, Rubio N, et al. The interaction of carbon nanotubes with an in vitro blood-brain barrier model and mouse brain in vivo[J]. Biomaterials, 2015,53:437-452.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.02.083 |
| [23] |
Cao Y, Jacobsen NR, Danielsen PH, et al. Vascular effects of multiwalled carbon nanotubes in dyslipidemic ApoE-/- mice and cultured endothelial cells[J]. Toxicol Sci, 2014,138(1):104-116.
doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kft328 |
| [24] |
Long J, Li X, Kang Y, et al. Internalization, cytotoxicity, oxidative stress and inflammation of multi-walled carbon nanotubes in human endothelial cells: influence of pre-incubation with bovine serum albumin[J]. RSC Advances, 2018,8(17):9253-9260.
doi: 10.1039/C8RA00445E |
| [25] |
Li Z, Liu T, Long J, et al. The toxicity of hydroxylated and carboxylated multi-walled carbon nanotubes to human endothelial cells was not exacerbated by ER stress inducer[J]. Chin Chem Lett, 2019,30(3):582-586.
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2018.12.011 |
| [26] |
Svadlakova T, Hubatka F, Turanek Knotigova P, et al. Proinflammatory effect of carbon-based nanomaterials: in vitro study on stimulation of inflammasome NLRP3 via destabilisation of lysosomes[J]. Nanomaterials (Basel), 2020,10(3):418.
doi: 10.3390/nano10030418 |
| [27] |
Sun B, Wang X, Ji Z, et al. NADPH oxidase-dependent NLRP3 inflammasome activation and its important role in lung fibrosis by multiwalled carbon nanotubes[J]. Small, 2015,11(17):2087-2097.
doi: 10.1002/smll.v11.17 |
| [1] | Min ZHEN,Huan-xin MENG,Wen-jie HU,Deng-cheng WU,Yi-ping WEI. Healing of the dento-gingival junction following modified crown lengthening procedure in beagle dogs [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(5): 927-935. |
| [2] | Hai-long HE,Qing LI,Tao XU,Xiao-wei ZHANG. Treatment of adult-acquired buried penis with suprapubic liposuction combined with modified Devine operation [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(4): 741-745. |
| [3] | ZHANG Fan,CHEN Qu,HAO Yi-chang,YAN Ye,LIU Cheng,HUANG Yi,MA Lu-lin. Relationship between recovery of urinary continence after laparoscopic radical prostatectomy and preoperative/postoperative membranous urethral length [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(2): 299-303. |
| [4] | WU Jing-yi,LIN Yu,LIN Ke,HU Yong-hua,KONG Gui-lan. Predicting prolonged length of intensive care unit stay via machine learning [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(6): 1163-1170. |
| [5] | ZHEN Min, HU Wen-jie, RONG Qi-guo. Finite element analysis of the maxillary central incisor with crown lengthening surgery and post-core restoration in management of crown-root fracture [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2015, 47(6): 1015-1021. |
| [6] | JIA Xue-ting, ZHEN Min, HU Wen-jie, LIU Yun-song. Different multidisciplinary approaches of two traumatic teeth fractures in the esthetic zone: a case report [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2015, 47(5): 878-882. |
|
||