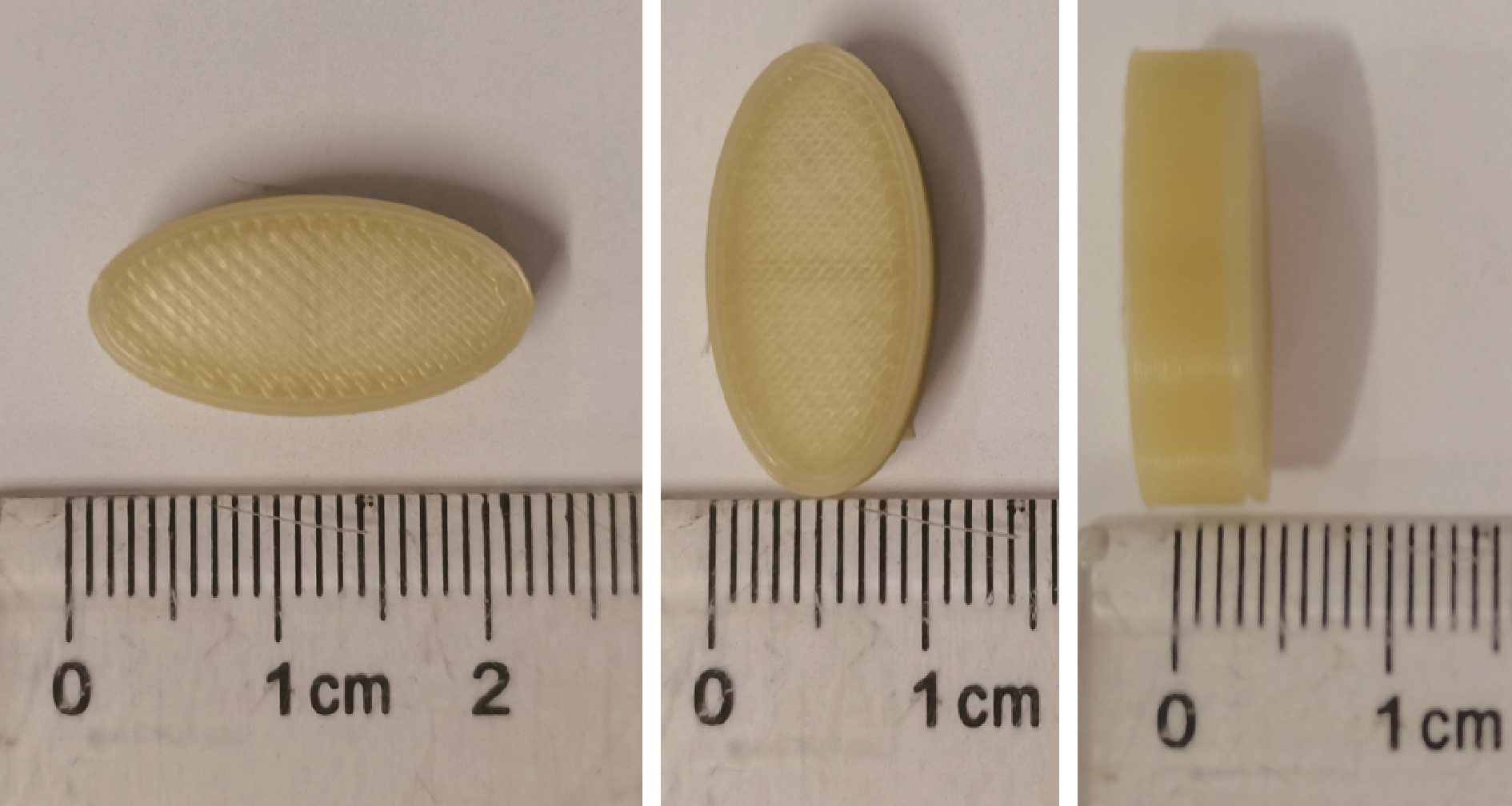
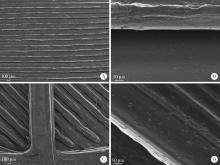
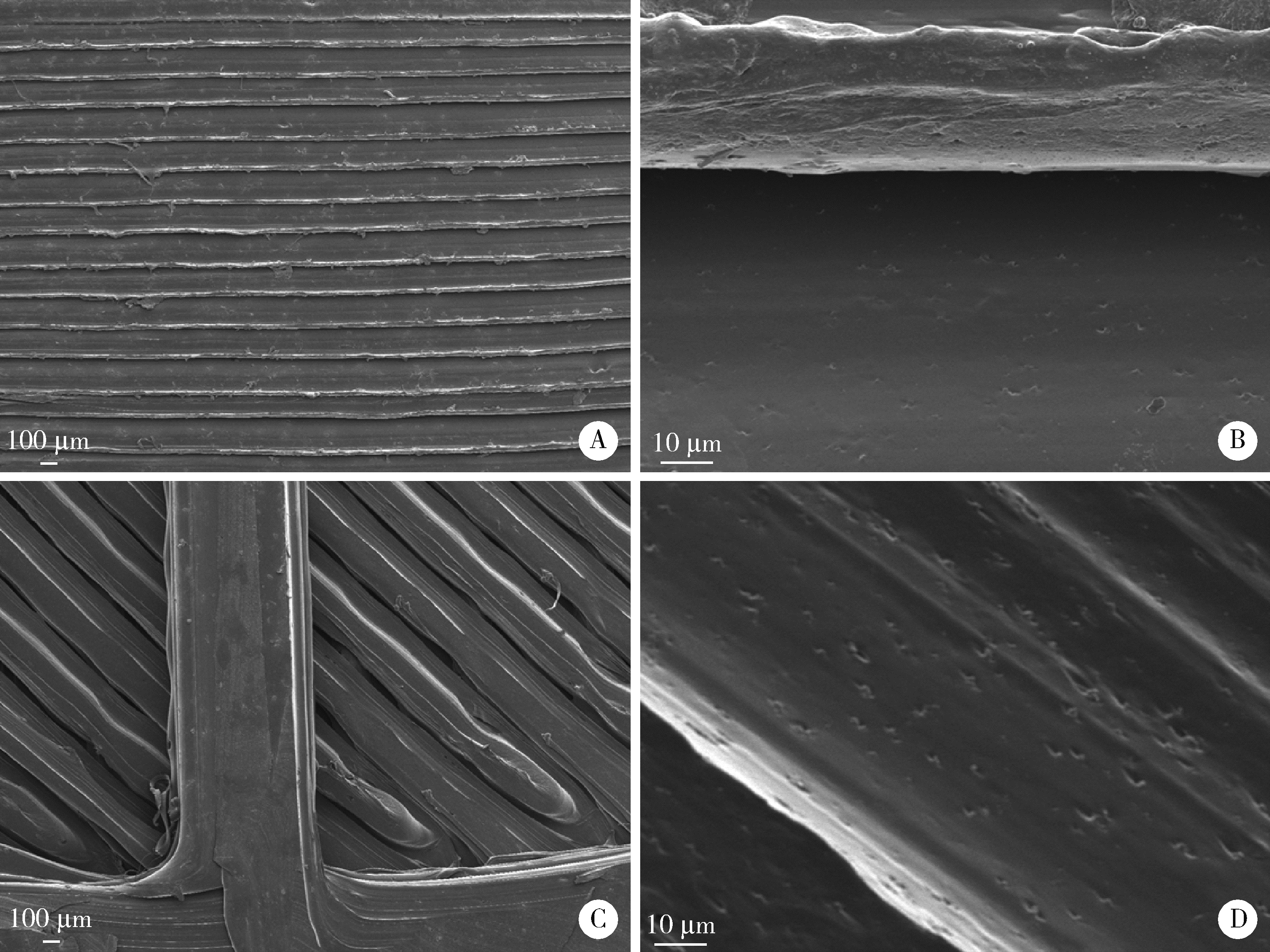
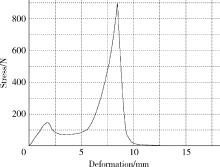
Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (3): 572-577. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.03.026
Previous Articles Next Articles
Preparation and in vitro evaluation of fused deposition modeling 3D printed compound tablets of captopril and hydrochlorothiazide
Zhi-sheng LI,Hao-nan QIAN,Tian-yuan FAN*( )
)
- Department of Pharmaceutics, Beijing Key Laboratory of Molecular Pharmaceutics and New Drug Delivery Systems, Peking University School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Beijing 100191, China
CLC Number:
- R944.4
| 1 |
Tan DK , Maniruzzaman M , Nokhodchi A . Advanced pharmaceutical applications of hot-melt extrusion coupled with fused deposition modelling (FDM) 3D printing for personalised drug delivery[J]. Pharmaceutics, 2018, 10 (4): 203.
doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics10040203 |
| 2 |
Okafor-Muo OL , Hassanin H , Kayyali R , et al. 3D printing of solid oral dosage forms: Numerous challenges with unique opportunities[J]. J Pharm Sci, 2020, 109 (12): 3535- 3550.
doi: 10.1016/j.xphs.2020.08.029 |
| 3 |
Brambilla CRM , Okafor-Muo OL , Hassanin H , et al. 3D printing of oral solid formulations: A systematic review[J]. Pharmaceutics, 2021, 13 (3): 358.
doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13030358 |
| 4 |
Melocchi A , Parietti F , Loreti G , et al. 3D printing by fused deposition modeling (FDM) of a swellable/erodible capsular device for oral pulsatile release of drugs[J]. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol, 2015, 30 (Part B): 360- 367.
doi: 10.1016/j.jddst.2015.07.016 |
| 5 |
Lu J , Lu Y , Wang X , et al. Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in China: Data from 1.7 million adults in a population-based screening study (China PEACE Million Persons Project)[J]. Lancet, 2017, 390 (10112): 2549- 2558.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32478-9 |
| 6 | 国家卫生计生委合理用药专家委员会, 中国医师协会高血压专业委员会. 高血压合理用药指南(第2版)[J]. 中国医学前沿杂志, 2017, 9 (7): 28- 126. |
| 7 |
An J , Derington CG , Luong T , et al. Fixed-dose combination medications for treating hypertension: A review of effectiveness, safety, and challenges[J]. Curr Hypertens Rep, 2020, 22 (11): 95.
doi: 10.1007/s11906-020-01109-2 |
| 8 | 国家药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典(二部)[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2020: 963 |
| 9 | 国家药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典(四部)[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2020: 112, 137, 478. |
| 10 |
Ghanizadeh Tabriz A , Nandi U , Hurt AP , et al. 3D printed bilayer tablet with dual controlled drug release for tuberculosis treatment[J]. Int J Pharm, 2021, 593, 120147.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2020.120147 |
| 11 | Charoenying T , Patrojanasophon P , Ngawhirunpat T , et al. Fabrication of floating capsule-in-3D-printed devices as gastro-retentive delivery systems of amoxicillin[J]. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol, 2020, 55, 100393. |
| 12 |
Wang Y , Sun L , Mei Z , et al. 3D printed biodegradable implants as an individualized drug delivery system for local chemotherapy of osteosarcoma[J]. Materials & Design, 2020, 186, 108336.
doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2019.108336 |
| 13 |
Kempin W , Domsta V , Grathoff G , et al. Immediate release 3D-printed tablets produced via fused deposition modeling of a thermo-sensitive drug[J]. Pharm Res, 2018, 35 (6): 124.
doi: 10.1007/s11095-018-2405-6 |
| 14 |
Homaee Borujeni S , Mirdamadian SZ , Varshosaz J , et al. Three-dimensional (3D) printed tablets using ethyl cellulose and hydroxypropyl cellulose to achieve zero order sustained release profile[J]. Cellulose, 2020, 27, 1573- 1589.
doi: 10.1007/s10570-019-02881-4 |
| 15 |
Fuenmayor E , Forde M , Healy AV , et al. Comparison of fused filament fabrication to direct compression and injection molding in the manufacture of oral tablets[J]. Int J Pharm, 2019, 558, 328- 340.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.01.013 |
| 16 |
Yang Y , Wang H , Li H , et al. 3D printed tablets with internal scaffold structure using ethyl cellulose to achieve sustained ibuprofen release[J]. Eur J Pharm Sci, 2018, 115, 11- 18.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2018.01.005 |
| 17 |
Mazzanti V , Malagutti L , Mollica F . FDM 3D printing of polymers containing natural fillers: A review of their mechanical properties[J]. Polymers (Basel), 2019, 11 (7): 1094.
doi: 10.3390/polym11071094 |
| 18 | Sadia M , Sosnicka A , Arafat B , et al. Adaptation of pharmaceutical excipients to FDM 3D printing for the fabrication of patient-tailored immediate release tablets[J]. Int J Pharm, 2016, 513 (1/2): 659- 668. |
| 19 |
Melocchi A , Uboldi M , Briatico-Vangosa F , et al. The ChronotopicTM system for pulsatile and colonic delivery of active molecules in the era of precision medicine: Feasibility by 3D printing via fused deposition modeling (FDM)[J]. Pharmaceutics, 2021, 13 (5): 759.
doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13050759 |
| 20 | The U.S. Food and Drug Administration. FDA-approved drugs: Captopril (018343): 2. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/020504s026lbl.pdf. |
| 21 | The U.S. Food and Drug Administration. FDA-approved drugs: Hydrochlorothiazide (084324): 2. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/018343s087lbl.pdf. |
| [1] | Chu-yun CHEN,Peng-fei SUN,Jing ZHAO,Jia JIA,Fang-fang FAN,Chun-yan WANG,Jian-ping LI,Yi-meng JIANG,Yong HUO,Yan ZHANG. Related factors of endogenous erythropoietin and its association with 10-year risks of cardiovascular disease in a community-based Chinese study [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1068-1073. |
| [2] | ABUDUREHEMAN Kaidierya,Rong-geng ZHANG,Hao-nan QIAN,Zhen-yang ZOU,YESITAO Danniya,Tian-yuan FAN. Preparation and in vitro evaluation of FDM 3D printed theophylline tablets with personalized dosage [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1202-1207. |
| [3] | Zhe LIANG,Fang-fang FAN,Yan ZHANG,Xian-hui QIN,Jian-ping LI,Yong HUO. Rate and characteristics of H-type hypertension in Chinese hypertensive population and comparison with American population [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(5): 1028-1037. |
| [4] | Yu-chao HUANG-FU,Yi-qing DU,Lu-ping YU,Tao XU. Risk factors of persistent hypertension in primary aldosteronism patients after surgery [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(4): 686-691. |
| [5] | XIAO Yun-shu,ZHU Feng-yun-zhi,LUO Lan,XING Xiao-yan,LI Yu-hui,ZHANG Xue-wu,SHEN Dan-hua. Clinical and immunological characteristics of 88 cases of overlap myositis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(6): 1088-1093. |
| [6] | CHEN Di,XU Xiang-yu,WANG Ming-rui,LI Rui,ZANG Gen-ao,ZHANG Yue,QIAN Hao-nan,YAN Guang-rong,FAN Tian-yuan. Preparation and in vitro evaluation of fused deposition modeling 3D printed verapa-mil hydrochloride gastric floating formulations [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(2): 348-354. |
| [7] | Hang YANG,Lin-cheng YANG,Rui-tao ZHANG,Yun-peng LING,Qing-gang GE. Risks factors for death among COVID-19 patients combined with hypertension, coronary heart disease or diabetes [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(3): 420-424. |
| [8] | Hong-chen ZHENG,En-ci XUE,Xue-heng WANG,Xi CHEN,Si-yue WANG,Hui HUANG,Jin JIANG,Ying YE,Chun-lan HUANG,Yun ZHOU,Wen-jing GAO,Can-qing YU,Jun LV,Xiao-ling WU,Xiao-ming HUANG,Wei-hua CAO,Yan-sheng YAN,Tao WU,Li-ming LI. Bivariate heritability estimation of resting heart rate and common chronic disease based on extended pedigrees [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(3): 432-437. |
| [9] | Wen-ying MENG,Wan-tong HUANG,Jie ZHANG,Ming-yuan JIAO,Lei JIN,Lei JIN. Relationship between serum vitamin E concentration in first trimester and the risk of developing hypertension disorders complicating pregnancy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(3): 470-478. |
| [10] | Ying LIU,Xiang-zhu ZENG,Zheng WANG,Han ZHANG,Xi-lin WANG,Hui-shu YUAN. Cerebral blood flow measurements in patients with comorbid hypertension and depression using 3D arterial spin labeling [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(2): 260-264. |
| [11] | Rong LI,Ke-long CHEN,Yong WANG,Yun-song LIU,Yong-sheng ZHOU,Yu-chun SUN. Establishment of a 3D printing system for bone tissue engineering scaffold fabrication and the evaluation of its controllability over macro and micro structure precision [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(1): 115-119. |
| [12] | GUO Xiao-yue, SHAO Hui, ZHAO Yang-yu. A case of systemic lupus erythematosus in pregnancy complicated by pulmonary hypertension [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(5): 928-931. |
| [13] | DONG Yan-hui, SONG Yi, DONG Bin, ZOU Zhi-yong, WANG Zheng-he, YANG Zhao-geng, WANG Xi-jie, LI Yan-hui, MA Jun. Association between the blood pressure status and nutritional status among Chinese students aged 7-18 years in 2014: based on the national blood pressure reference for Chinese children and adolescents [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(3): 422-428. |
| [14] | ZHAO Yun, SU Bai-ge, XIAO Hui-jie, ZHANG Hong-wen, LIU Xiao-yu, WANG Fang, DING Jie. Clinical characteristics of glucocorticoid-induced eye adverse reactions in children with primary nephrotic syndrome [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(5): 794-797. |
| [15] | LIU Xue-qin, YAN Hui, QIU Jian-xing, ZHANG Chun-yu, QI Jian-guang, ZHANG Xin, XIAO Hui-jie, YANG Yan-ling, CHEN Yong-hong, DU Jun-bao. Pulmonary arterial hypertension as leading manifestation of methylmalonic aciduria: clinical characteristics and gene testing in 15 cases [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(5): 768-777. |
|
||