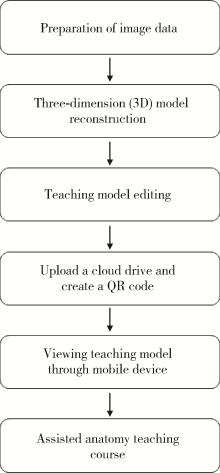
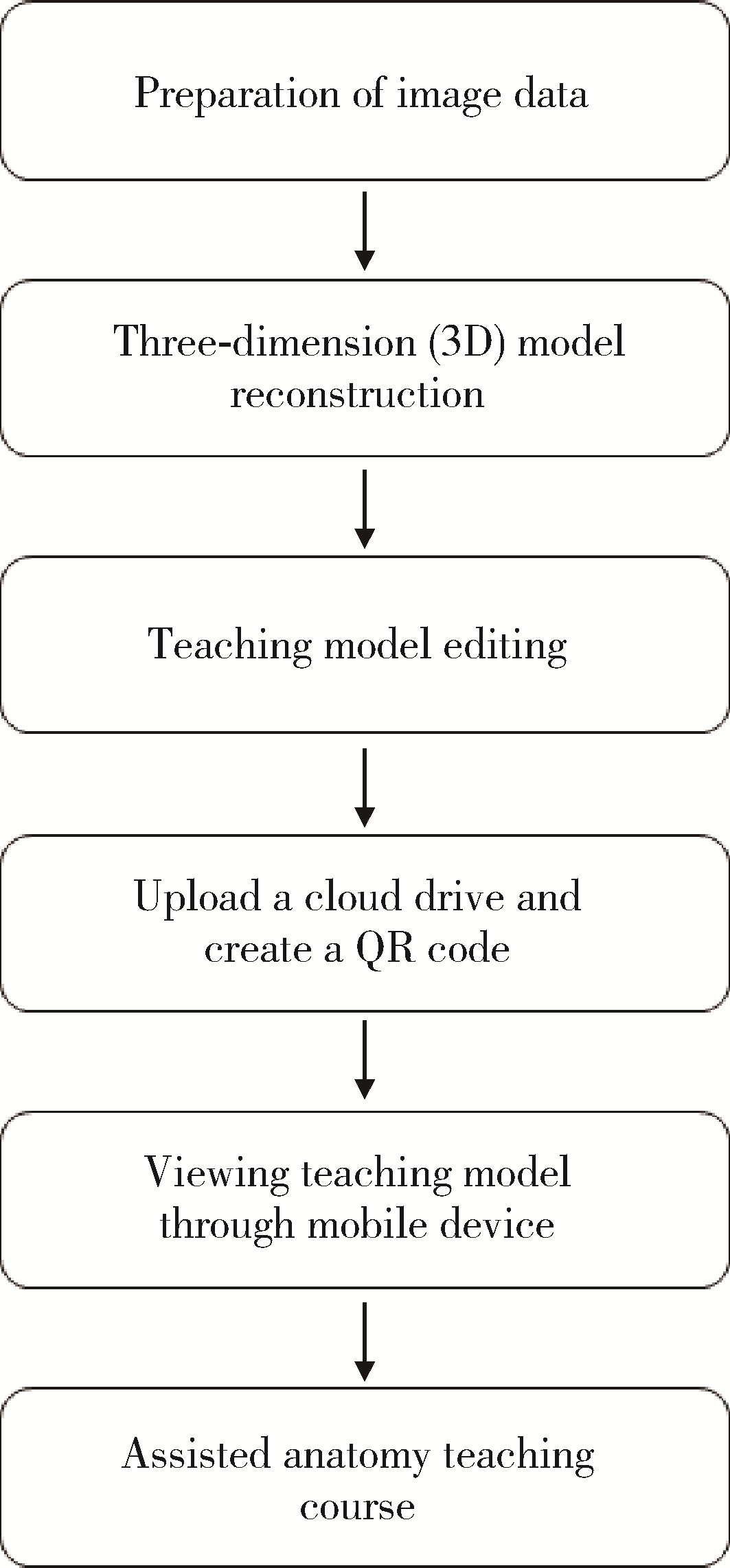
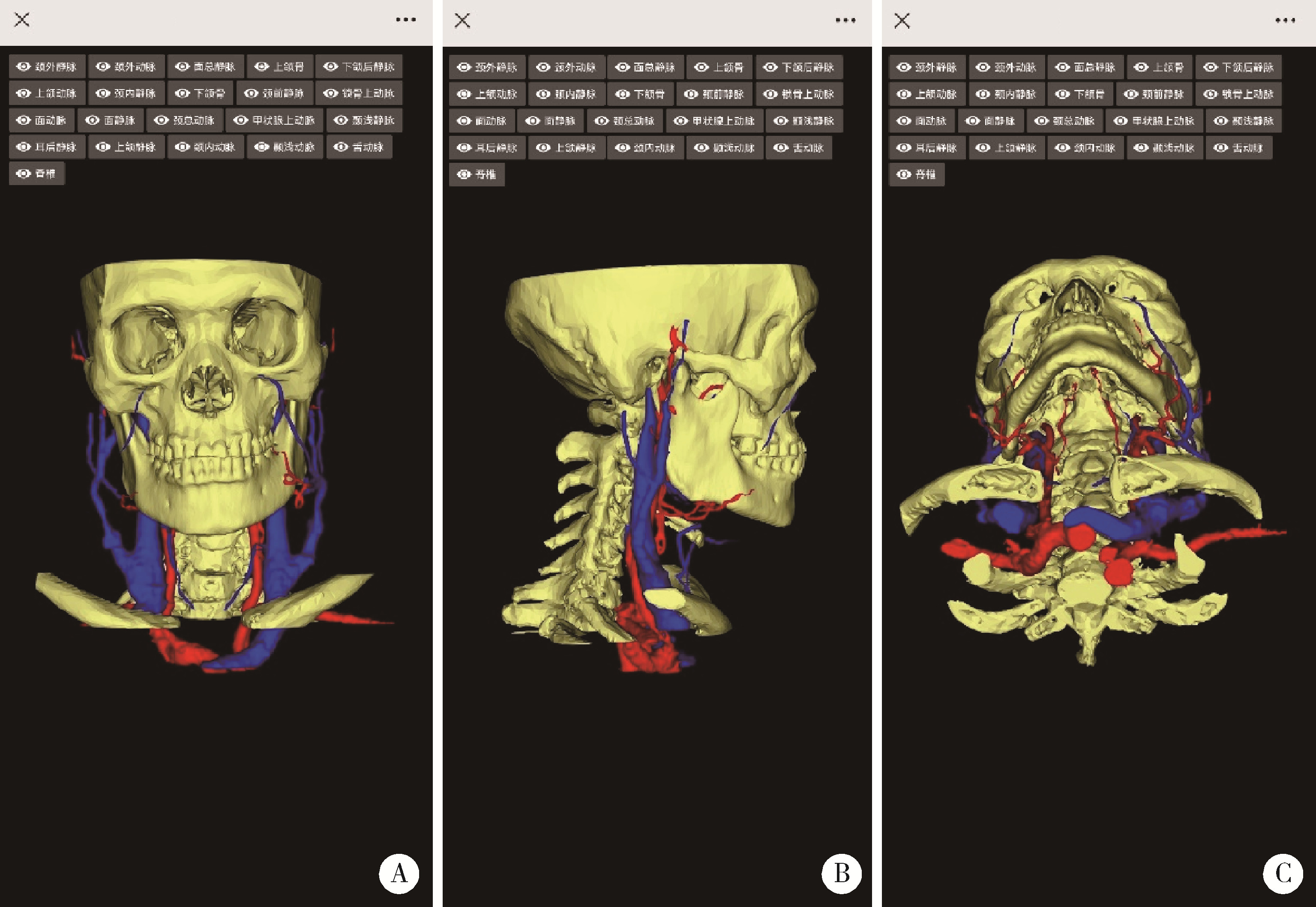
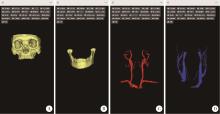
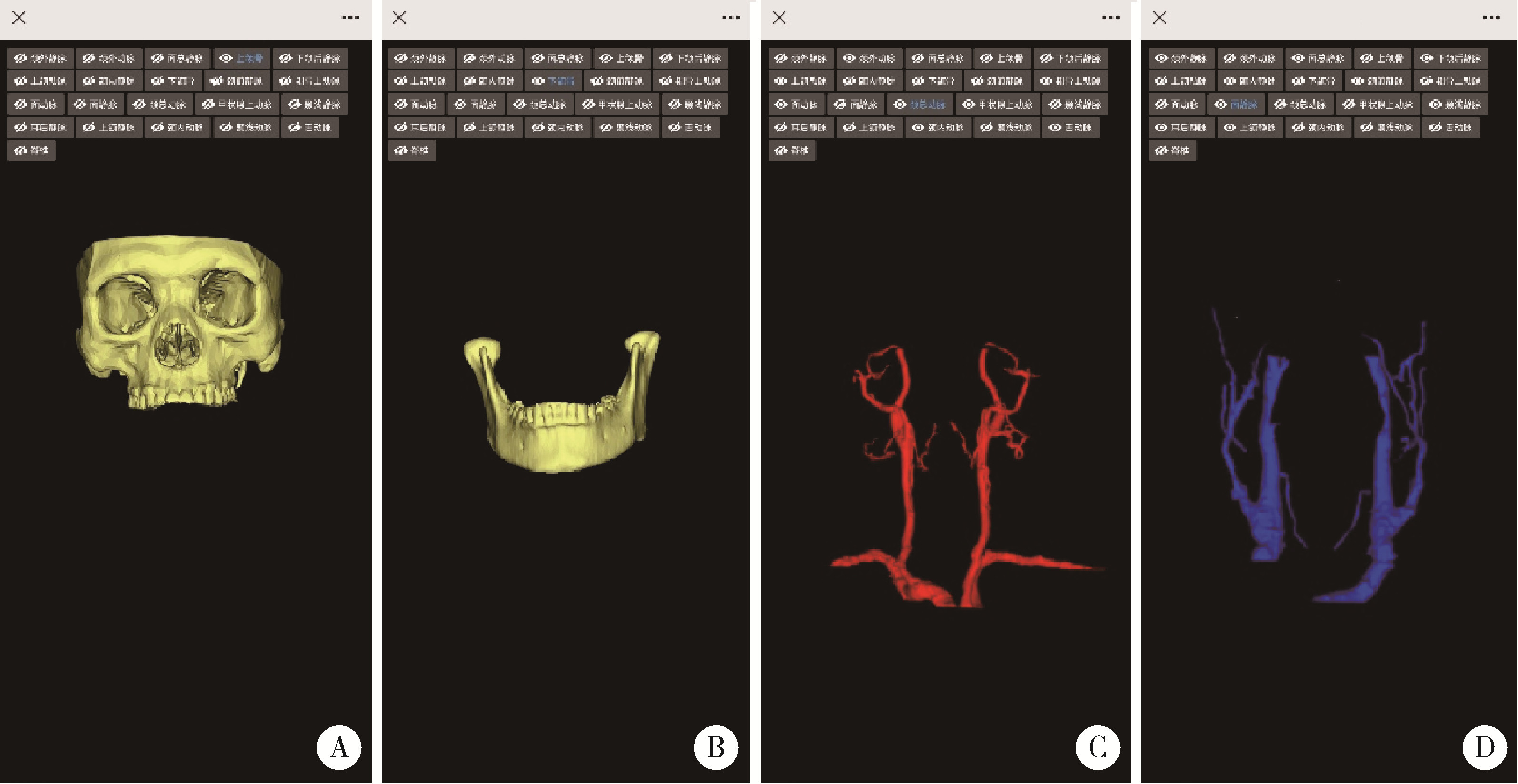
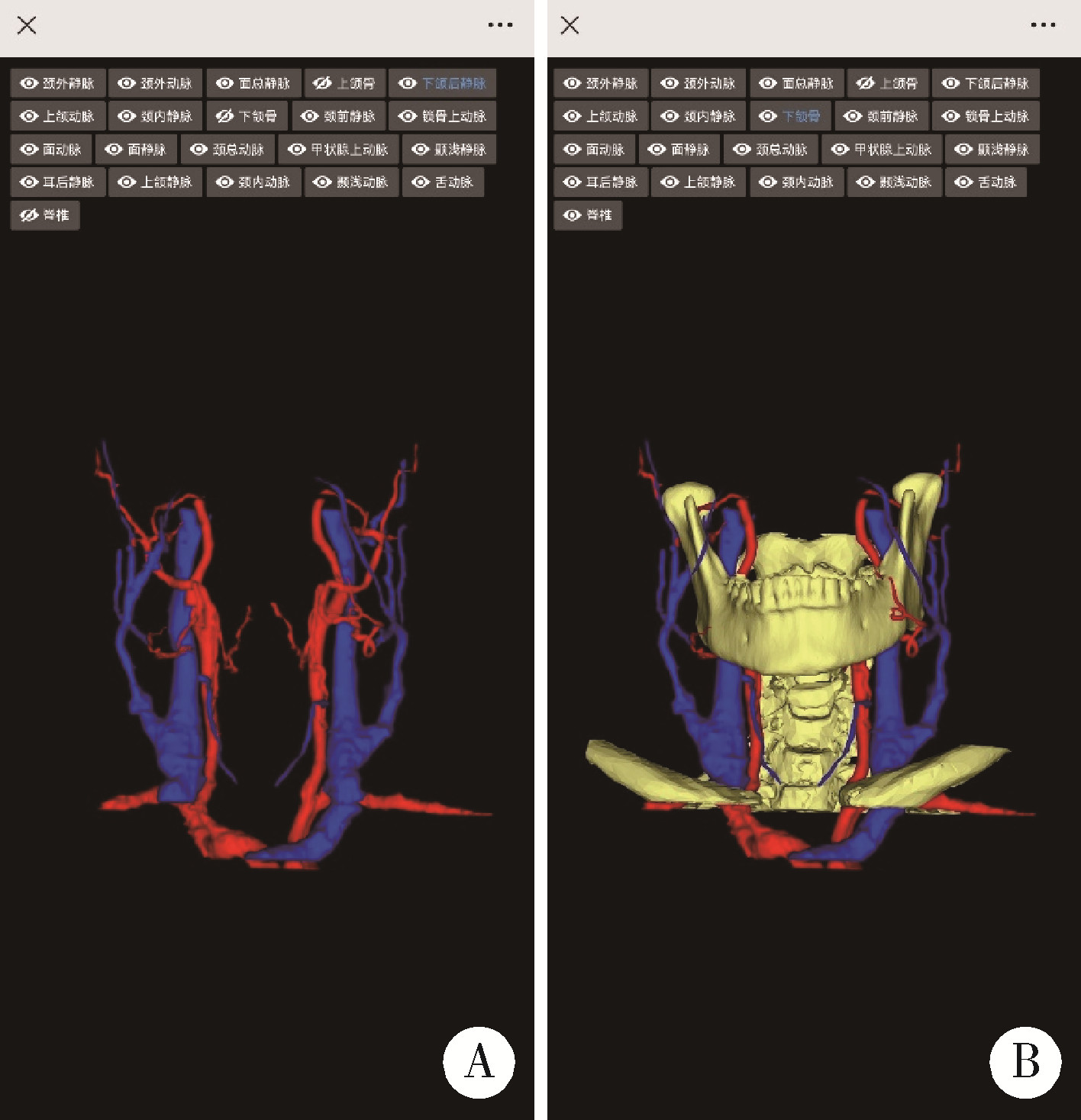
Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (3): 541-545. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.03.023
Previous Articles Next Articles
Evaluation of augmented reality technology in the recognizing of oral and maxillofacial anatomy
Zunan TANG,Leihao HU,Zhen CHEN,Yao YU,Wenbo ZHANG,Xin PENG*( )
)
- Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology & NHC Research Center of Engineering and Technology for Computerized Dentistry & NMPA Key Laboratory for Dental Materials, Beijing 100081, China
CLC Number:
- G642
| 1 | 夏青青, 王莉, 胡兵, 等. 基于数字人解剖系统进行人体解剖学微课开发的优势分析[J]. 解剖科学进展, 2018, 24 (4): 444-445, 448. |
| 2 | 刘克, 刘伟, 李文婷, 等. 人体解剖教学与临床结合初探[J]. 基础医学与临床, 2013, 33 (8): 1075- 1078. |
| 3 | 刘阳名, 李兵. 3D-Body人体解剖学虚拟软件在解剖学教学中的实践[J]. 中国组织化学与细胞化学杂志, 2018, 27 (4): 401- 404. |
| 4 |
Kwon HB , Park YS , Han JS . Augmented reality in dentistry: A current perspective[J]. Acta Odontol Scand, 2018, 76 (7): 497- 503.
doi: 10.1080/00016357.2018.1441437 |
| 5 |
Berryman DR . Augmented reality: A review[J]. Med Ref Serv Q, 2012, 31 (2): 212- 218.
doi: 10.1080/02763869.2012.670604 |
| 6 |
Moro C , Štromberga Z , Raikos A , et al. The effectiveness of virtual and augmented reality in health sciences and medical anatomy[J]. Anat Sci Educ, 2017, 10 (6): 549- 559.
doi: 10.1002/ase.1696 |
| 7 | 叶哲伟, 吴星火. 增强现实技术在骨科的最新应用进展[J]. 临床外科杂志, 2018, 26 (1): 13- 14. |
| 8 | 李嘉, 袁娜. 虚拟现实技术在骨科临床教学中的应用[J]. 中国医学教育技术, 2017, 31 (4): 392- 395. |
| 9 | 陈勃江, 李为民. 新冠肺炎疫情下临床医学本科教学方式的思考与探索[J]. 中国医学教育技术, 2020, 34 (3): 261-263, 266. |
| 10 | 王同聚. 虚拟和增强现实(VR/AR)技术在教学中的应用与前景展望[J]. 数字教育, 2017, 3 (1): 1- 10. |
| No related articles found! |
|
||