Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (3): 546-550. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.03.024
Previous Articles Next Articles
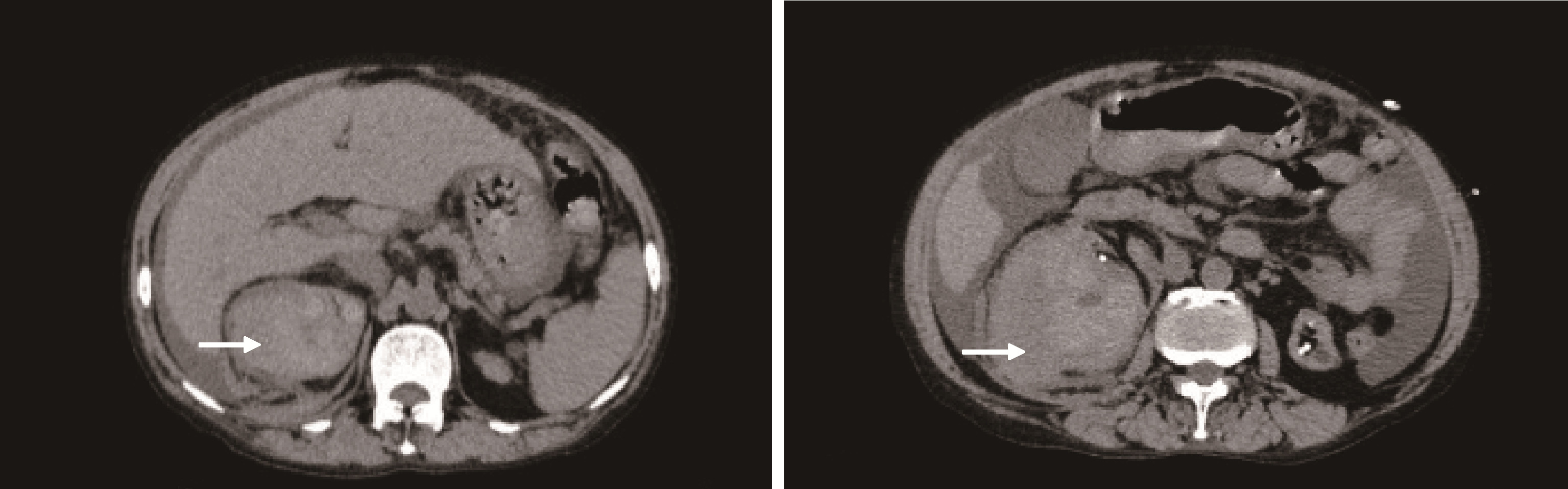
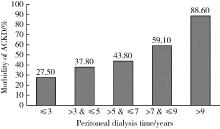
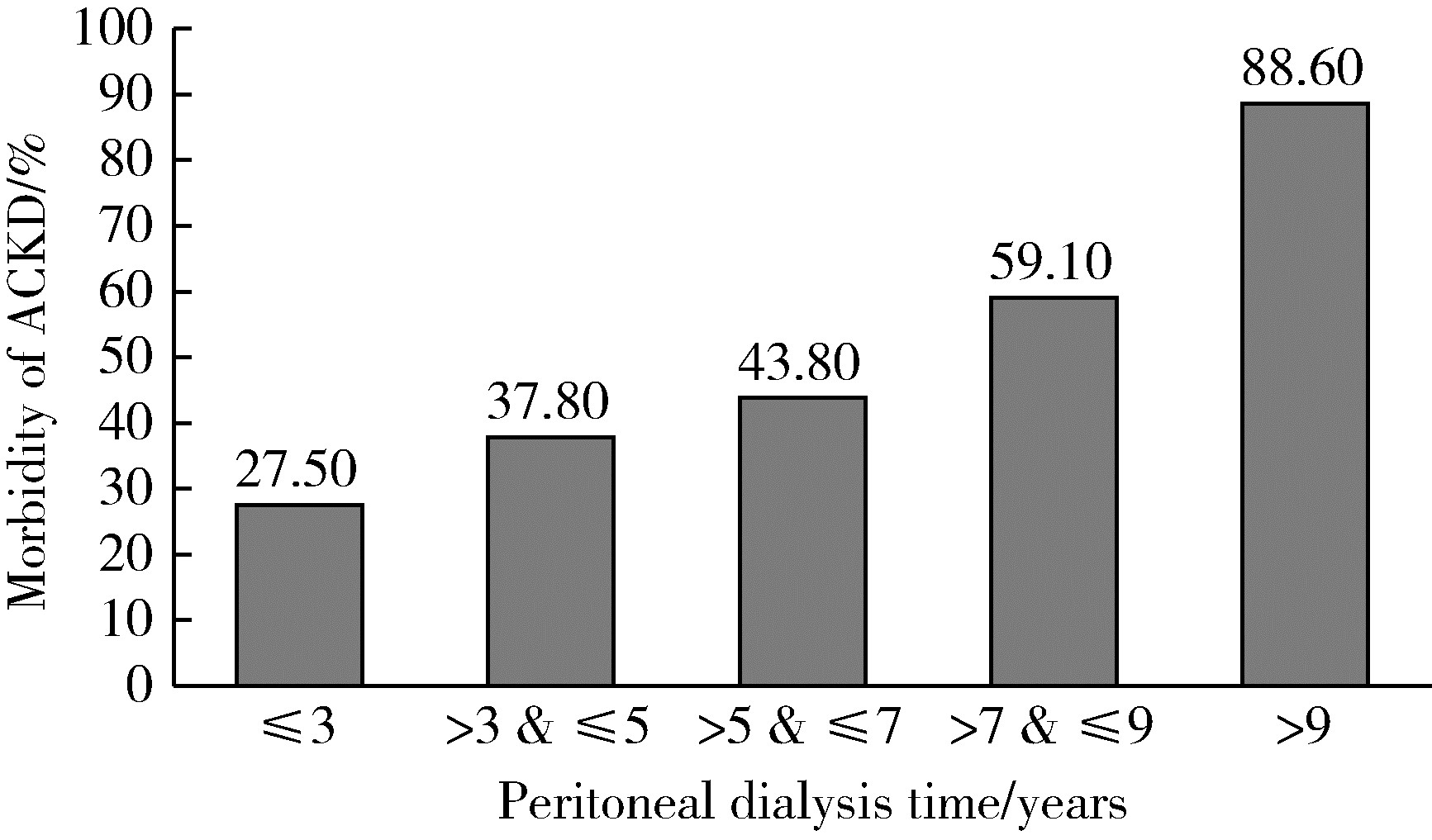
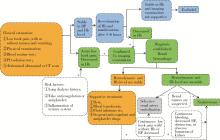
Acquired cystic kidney hemorrhage in peritoneal dialysis patients: A report of three cases
- Department of Nephrology, Peking University First Hospital; Institute of Nephrology, Peking University; Key Lab of Renal Disease, Ministry of Health of China; Key Laboratory of CKD Prevention and Treatment, Ministry of Education of China, Beijing 100034, China
CLC Number:
- R459.5
| 1 |
Li PK , Chow KM , Van de Luijtgaarden MW , et al. Changes in the worldwide epidemiology of peritoneal dialysis[J]. Nat Rev Nephrol, 2017, 13 (2): 90- 103.
doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2016.181 |
| 2 |
Yang C , Gao B , Zhao X , et al. Executive summary for China kidney disease network (CK-NET) 2016 annual data report[J]. Kidney Int, 2020, 98 (6): 1419- 1423.
doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.09.003 |
| 3 |
Zhang JQ , Fielding JR , Zou KH . Etiology of spontaneous perirenal hemorrhage: A meta-analysis[J]. J Urol, 2002, 167 (4): 1593- 1596.
doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(05)65160-9 |
| 4 |
Cinman AC , Farrer J , Kaufman JJ , et al. Spontaneous perinephric hemorrhage in a 65-year-old man[J]. J Urol, 1985, 133 (5): 829- 832.
doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(17)49243-3 |
| 5 | Chapman AB, Rahbari-Oskoui FF, Bennett WM, et al. Acquired cystic disease of the kidney in adults [DB/OL]. Uptodate. [2022-03-19]. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/acquired-cystic-disease-of-the-kidney-in-adults?search=Acquired%20cystic%20disease%20of%20the%20kidney%20in%20adults&source=Out%20of%20date%20-%20zh-Hans&selectedTitle=1%7E32. |
| 6 |
Rahbari-Oskoui F , O'Neill WC . Diagnosis and management of acquired cystic kidney disease and renal tumors in ESRD patients[J]. Semin Dial, 2017, 30 (4): 373- 379.
doi: 10.1111/sdi.12605 |
| 7 |
Narasimhan N , Golper TA , Wolfson M , et al. Clinical characte-ristics and diagnostic considerations in acquired renal cystic di-sease[J]. Kidney Int, 1986, 30 (5): 748- 752.
doi: 10.1038/ki.1986.251 |
| 8 |
Ferda J , Hora M , Hes O , et al. Computed tomography of renal cell carcinoma in patients with terminal renal impairment[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2007, 63 (2): 295- 301.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2007.01.027 |
| 9 |
Liu JS , Ishikawa I , Horiguchi T . Incidence of acquired renal cysts in biopsy specimens[J]. Nephron, 2000, 84 (2): 142- 147.
doi: 10.1159/000045562 |
| 10 |
Choyke PL . Acquired cystic kidney disease[J]. Eur Radiol, 2000, 10 (11): 1716- 1721.
doi: 10.1007/s003300000601 |
| 11 | Ishikawa I . Acquired cystic disease: Mechanisms and manifestations[J]. Semin Nephrol, 1991, 11 (6): 671- 684. |
| 12 |
Sun Y , Argani P , Tickoo SK , et al. Acquired cystic disease-associated renal cell carcinoma (ACKD-RCC)-like cysts[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2018, 42 (10): 1396- 1401.
doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000001124 |
| 13 |
Rainio J , De Giorgio F , Carbone A . Death from renal cyst: Spontaneous or traumatic rupture?[J]. Am J Forensic Med Pathol, 2006, 27 (2): 193- 195.
doi: 10.1097/01.paf.0000220918.46766.f8 |
| 14 |
Sarasin FP , Wong JB , Leve AS , et al. Screening for acquired cystic kidney disease: A decision analytic perspective[J]. Kidney Int, 1995, 48 (1): 207- 219.
doi: 10.1038/ki.1995.286 |
| 15 |
Levine E , Slusher SL , Grantham JJ , et al. Natural history of acquired renal cystic disease in dialysis patients: A prospective longitudinal CT study[J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 1991, 156 (3): 501- 506.
doi: 10.2214/ajr.156.3.1899744 |
| 16 |
Zhou C , Gu Y , Mei C , et al. Dialysis modality and mortality in polycystic kidney disease[J]. Hemodial Int, 2018, 22 (4): 515- 523.
doi: 10.1111/hdi.12673 |
| 17 |
Xie Y , Yang B , Jiang G , et al. Spontaneous perirenal hemorrhage in hemodialysis patient treated with selective embolization: A case series and review of the literature[J]. Hemodial Int, 2018, 22 (2): 222- 227.
doi: 10.1111/hdi.12607 |
| 18 |
Brennan JF , Stilmant MM , Babayan RK , et al. Acquired renal cystic disease: Implications for the urologist[J]. Br J Urol, 1991, 67 (4): 342- 348.
doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.1991.tb15158.x |
| 19 |
Levine E . Acquired cystic kidney disease[J]. Radiol Clin North Am, 1996, 34 (5): 947- 964.
doi: 10.1016/S0033-8389(22)00680-7 |
| 20 |
Gulanikar AC , Daily PP , Kilambi NK , et al. Prospective pretransplant ultrasound screening in 206 patients for acquired renal cysts and renal cell carcinoma[J]. Transplantation, 1998, 66 (12): 1669- 1672.
doi: 10.1097/00007890-199812270-00017 |
| 21 | Mallofré C , Almirall J , Campistol JM , et al. Acquired renal cystic disease in HD: A study of 82 nephrectomies in young patients[J]. Clin Nephrol, 1992, 37 (6): 297- 302. |
| 22 |
Truong LD , Krishnan B , Cao JT , et al. Renal neoplasm in acquired cystic kidney disease[J]. Am J Kidney Dis, 1995, 26 (1): 1- 12.
doi: 10.1016/0272-6386(95)90146-9 |
| 23 |
Grantham JJ . Acquired cystic kidney disease[J]. Kidney Int, 1991, 40 (1): 143- 152.
doi: 10.1038/ki.1991.192 |
| 24 |
Scandling JD . Acquired cystic kidney disease and renal cell cancer after transplantation: Time to rethink screening?[J]. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol, 2007, 2 (4): 621- 622.
doi: 10.2215/CJN.02000507 |
| [1] | Jiajun LIU, Guokang LIU, Yuhu ZHU. Immune-related severe pneumonia: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 932-937. |
| [2] | Kewei CHEN,Shaohui DENG,Zhuo LIU,Hongxian ZHANG,Lulin MA,Shudong ZHANG. Discussion on the surgical timing of rupture and hemorrhage of renal angiomyolipoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 326-331. |
| [3] | Shengjia PENG,Yu QI,Lijie SUN,Dan LI,Xinyu WANG,Jiangli HAN,Baoxia CHEN,Yuan ZHANG. Afferent baroreflex failure with hyponatremia: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 357-361. |
| [4] | Chen CHEN,Yuhong LIANG. Root canal therapy of maxillary molars with atypical canals: A report of three cases [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 190-195. |
| [5] | Han ZHANG,Yixuan QIN,Diyuan WEI,Jie HAN. A preliminary study on compliance of supportive treatment of patients with periodontitis after implant restoration therapy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 39-44. |
| [6] | Min FENG,Zhe CHEN,Yong-jing CHENG. A case of duodenal ulcer as prominent manifestation of IgG4-related disease [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1125-1129. |
| [7] | Dong LAN,Zhuo LIU,Yu-xuan LI,Guo-liang WANG,Xiao-jun TIAN,Lu-lin MA,Shu-dong ZHANG,Hong-xian ZHANG. Risk factors for massive hemorrhage after radical nephrectomy and removal of venous tumor thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 825-832. |
| [8] | Hai-hong JIANG,Xiao-fan LI,Jian-liu WANG. Relationship between chronic radiation enteritis of cervical cancer and gut microbiota [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 619-624. |
| [9] | Jie QIAO,Li-xia LU,Yu-ting HE,Chun-cui MEN,Xin-xin CHU,Bei WU,Hui-ping ZHAO,Mei WANG. Fungal peritoneal dialysis catheter-related exit-site infection combined with tunnel infection: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 748-754. |
| [10] | Yan XIONG,Bo ZHANG,Li-gong NIE,Shi-kai WU,Hu ZHAO,Dong LI,Ji-ting DI. Thoracic SMARCA4-deficient undifferentiated tumor-pathological diagnosis and combined immune checkpoint inhibitor treatment [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 351-356. |
| [11] | Zi WANG,Jun-jun ZHANG,Li ZUO,Yue WANG,Wen-ge LI,Hong CHENG,Guang-yan CAI,Hua-ying PEI,Li-hua WANG,Xu-jie ZHOU,Su-fang SHI,Li-jun LIU,Ji-cheng LV,Hong ZHANG. Efficacy of plasma exchange in severe crescentic IgA nephropathy: A multicentered, cohort study [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(5): 1038-1046. |
| [12] | Jing LIU,Ai-dong LU,Ying-xi ZUO,Jun WU,Zhi-zhuo HUANG,Yue-ping JIA,Ming-ming DING,Le-ping ZHANG,Jiong QIN. Clinical characteristics and prognosis of seizures in 75 children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(5): 948-953. |
| [13] | Sheng-jie LIU,Hui-min HOU,Zheng-tong LV,Xin DING,Lu WANG,Lei ZHANG,Ming LIU. Bipolar androgen therapy followed by immune checkpoint inhibitors in metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer: A report of 4 cases [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(4): 766-769. |
| [14] | Bo YU,Yang-yu ZHAO,Zhe ZHANG,Yong-qing WANG. Infective endocarditis in pregnancy: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(3): 578-580. |
| [15] | Shuang HU,Li-ping YANG. Expression pattern of different serotypes of adeno-associated viral vectors in mouse retina [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(5): 845-850. |
|
||