Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (5): 820-827. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.05.011
Previous Articles Next Articles
Impact of fine particulate matter exposure on non-accidental mortality under different apparent temperature levels
Yuxin WANG1, Ru CAO1, Jing HUANG1, Ponsawansong Pitakchon2, Tawatsupa Benjawan3, Xiaochuan PAN1, Prapamontol Tippawan2, Guoxing LI1,*( )
)
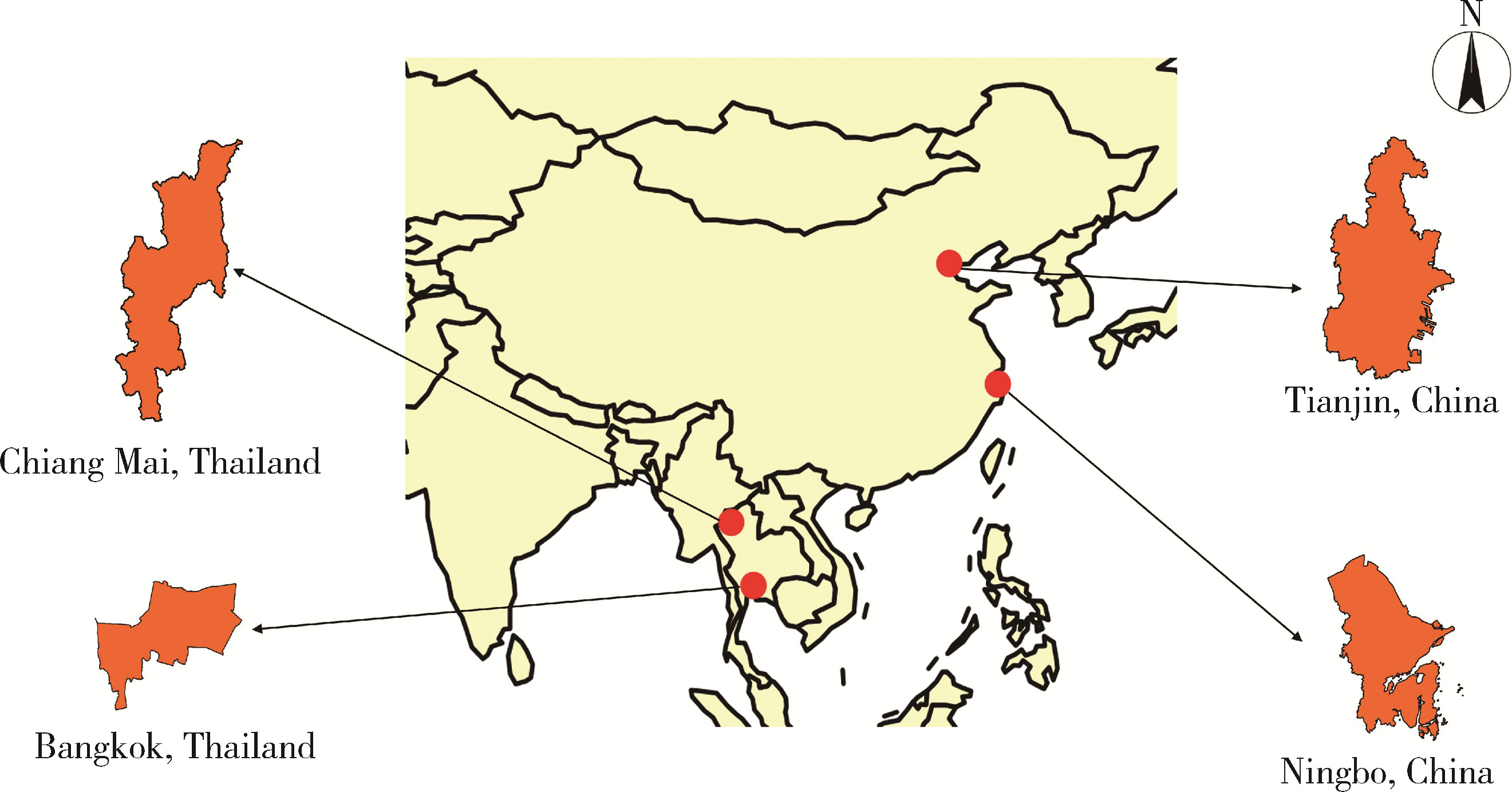
- 1. Department of Occupational and Environmental Health Sciences, Peking University School of Public Health, Beijing 100191, China
2. Environment and Health Research Unit, Research Institute for Health Sciences, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai 50200, Thailand
3. Health Impact Assessment Division, Department of Health, Ministry of Public Health, Bangkok 11000, Thailand
CLC Number:
- R122.26
| 1 | WHO. Ten threats to global health in 2019 [EB/OL]. (2019-03-21) [2021-01-18]. www.who.int/vietnam/news/feature-stories/detail/ten-threats-to-global-health-in-2019. |
| 2 | 李勇. 中国空气污染相关疾病负担的动态评估及其减排响应[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2020. |
| 3 | Zeng Q , Ni Y , Jiang G , et al. The short term burden of ambient particulate matters on non-accidental mortality and years of life lost: A ten-year multi-district study in Tianjin, China[J]. Environ Pollut, 2017, 220 (Pt A): 713- 719. |
| 4 | Chen R , Yin P , Wang L , et al. Association between ambient temperature and mortality risk and burden: time series study in 272 main Chinese cities[J]. BMJ, 2018, 363, k4306. |
| 5 | Gasparrini A , Guo Y , Hashizume M , et al. Mortality risk attri-butable to high and low ambient temperature: A multicountry observational study[J]. Lancet, 2015, 386 (9991): 369- 375. |
| 6 | Burkart K , Canário P , Breitner S , et al. Interactive short-term effects of equivalent temperature and air pollution on human mortality in Berlin and Lisbon[J]. Environ Pollut, 2013, 183, 54- 63. |
| 7 | Kioumourtzoglou MA , Schwartz J , James P , et al. PM2.5 and mortality in 207 US cities: Modification by temperature and city characteristics[J]. Epidemiology, 2016, 27 (2): 221- 227. |
| 8 | Meng X , Zhang Y , Zhao Z , et al. Temperature modifies the acute effect of particulate air pollution on mortality in eight Chinese cities[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2012, 435/436, 215- 221. |
| 9 | Li P , Xin J , Wang Y , et al. The acute effects of fine particles on respiratory mortality and morbidity in Beijing, 2004-2009[J]. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int, 2013, 20 (9): 6433- 6444. |
| 10 | Hsu WH , Hwang SA , Kinney PL , et al. Seasonal and temperature modifications of the association between fine particulate air pollution and cardiovascular hospitalization in New York state[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2017, 578, 626- 632. |
| 11 | Zhang J , Feng L , Hou C , et al. Interactive effect between tempe-rature and fine particulate matter on chronic disease hospital admissions in the urban area of Tianjin, China[J]. Int J Environ Health Res, 2021, 31 (1): 75- 84. |
| 12 | Sun S , Cao P , Chan KP , et al. Temperature as a modifier of the effects of fine particulate matter on acute mortality in Hong Kong[J]. Environ Pollut, 2015, 205, 357- 364. |
| 13 | Li Y , Ma Z , Zheng C , et al. Ambient temperature enhanced acute cardiovascular-respiratory mortality effects of PM2.5 in Beijing, China[J]. Int J Biometeorol, 2015, 59 (12): 1761- 1770. |
| 14 | Wang Y , Kloog I , Coull BA , et al. Estimating causal effects of long-term PM2.5 exposure on mortality in New Jersey[J]. Environ Health Perspect, 2016, 124 (8): 1182- 1188. |
| 15 | Vanos JK , Baldwin JW , Jay O , et al. Simplicity lacks robustness when projecting heat-health outcomes in a changing climate[J]. Nat Commun, 2020, 11 (1): 6079. |
| 16 | Puza B , Roberts S . A Bayesian approach to modeling the interaction between air pollution and temperature[J]. Ann Epidemiol, 2013, 23 (4): 198- 203. |
| 17 | Shaposhnikov D , Revich B , Bellander T , et al. Mortality related to air pollution with the Moscow heat wave and wildfire of 2010[J]. Epidemiology, 2014, 25 (3): 359- 364. |
| 18 | Ma Z , Hu X , Sayer AM , et al. Satellite-based spatiotemporal trends in PM2.5 concentrations: China, 2004-2013[J]. Environ Health Perspect, 2016, 124 (2): 184- 192. |
| 19 | Kovats RS , Hajat S . Heat stress and public health: A critical review[J]. Annu Rev Public Health, 2008, 29, 41- 55. |
| 20 | Ho HC , Knudby A , Xu Y , et al. A comparison of urban heat islands mapped using skin temperature, air temperature, and apparent temperature (Humidex), for the greater Vancouver area[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2016, 544, 929- 938. |
| 21 | Zeng Q , Li G , Zhao L , et al. Characteristics of the exposure-response relationship of particulate matter and mortality: A time series analysis of 7 cities in China[J]. J Occup Environ Med, 2015, 57 (10): e93- e100. |
| 22 | Macdonald RW , Harner T , Fyfe J . Recent climate change in the Arctic and its impact on contaminant pathways and interpretation of temporal trend data[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2004, 342 (1/2/3): 5- 86. |
| 23 | Li G , Zhou M , Cai Y , et al. Does temperature enhance acute mortality effects of ambient particle pollution in Tianjin city, China[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2011, 409 (10): 1811- 1817. |
| 24 | Chung Y , Lim YH , Honda Y , et al. Mortality related to extreme temperature for 15 cities in Northeast Asia[J]. Epidemiology, 2015, 26 (2): 255- 262. |
| 25 | Gao J , Sun Y , Liu Q , et al. Impact of extreme high temperature on mortality and regional level definition of heat wave: A multi-city study in China[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2015, 505, 535- 544. |
| 26 | Chen K , Bi J , Chen J , et al. Influence of heat wave definitions to the added effect of heat waves on daily mortality in Nanjing, China[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2015, 506/507, 18- 25. |
| 27 | Williams R , Rankin N , Smith T , et al. Relationship between the humidity and temperature of inspired gas and the function of the airway mucosa[J]. Crit Care Med, 1996, 24 (11): 1920- 1929. |
| 28 | Krall JR , Anderson GB , Dominici F , et al. Short-term exposure to particulate matter constituents and mortality in a national study of U.S. urban communities[J]. Environ Health Perspect, 2013, 121 (10): 1148- 1153. |
| 29 | Chen C , Zhao B , Weschler CJ . Indoor exposure to "Outdoor PM10": Assessing its influence on the relationship between PM10 and short-term mortality in U.S. cities[J]. Epidemiology, 2012, 23 (6): 870- 878. |
| 30 | Keatinge WR , Coleshaw SR , Easton JC , et al. Increased platelet and red cell counts, blood viscosity, and plasma cholesterol levels during heat stress, and mortality from coronary and cerebral thrombosis[J]. Am J Med, 1986, 81 (5): 795- 800. |
| 31 | Gordon CJ , Leon LR . Thermal stress and the physiological response to environmental toxicants[J]. Rev Environ Health, 2005, 20 (4): 235- 263. |
| 32 | Leon LR . Thermoregulatory responses to environmental toxicants: The interaction of thermal stress and toxicant exposure[J]. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol, 2008, 233 (1): 146- 161. |
| 33 | Li J , Woodward A , Hou XY , et al. Modification of the effects of air pollutants on mortality by temperature: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2017, 575, 1556- 1570. |
| 34 | Stafoggia M , Schwartz J , Forastiere F , et al. Does temperature modify the association between air pollution and mortality? A multicity case-crossover analysis in Italy[J]. Am J Epidemiol, 2008, 167 (12): 1476- 1485. |
| 35 | Qian Z , He Q , Lin HM , et al. High temperatures enhanced acute mortality effects of ambient particle pollution in the "oven" city of Wuhan, China[J]. Environ Health Perspect, 2008, 116 (9): 1172- 1178. |
| 36 | Li G , Jiang L , Zhang Y , et al. The impact of ambient particle pollution during extreme-temperature days in Guangzhou city, China[J]. Asia Pac J Public Health, 2014, 26 (6): 614- 621. |
| 37 | Li J , Wang Y , Yin P , et al. The burden of sulfur dioxide pollution on years of life lost from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A nationwide analysis in China[J]. Environ Res, 2021, 194, 110503. |
| [1] | Ya-nan ZHAO,Hui-yun FAN,Xiang-yu WANG,Ya-nan LUO,Rong ZHANG,Xiao-ying ZHENG. Early death and causes of death of patients with autism spectrum disorders: A systematic review [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 375-383. |
| [2] | Lin MA,Jing-yi WU,Shuang-cheng LI,Peng-fei LI,Lu-xia ZHANG. Effect of modification of antihypertensive medications on the association of nitrogen dioxide long-term exposure and chronic kidney disease [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(5): 1047-1055. |
| [3] | Yun-fei LIU,Jia-jia DANG,Pan-liang ZHONG,Ning MA,Di SHI,Yi SONG. Injury mortality among Chinese aged 5 to 24 years from 1990 to 2019 [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(3): 498-504. |
| [4] | LIU Jie,GUO Chao. A prospective cohort study of the influence of positive/negative effectivity on the mortality risk of the Chinese elderly [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(2): 255-260. |
| [5] | Wen TANG,Jun-yi GAO,Xin-yu MA,Chao-he ZHANG,Lian-tao MA,Ya-sha WANG. Application of recurrent neural network in prognosis of peritoneal dialysis [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(3): 602-608. |
| [6] | YANG Chao, WANG Jin-wei, YANG Yao-zheng, BAI Kun-hao, GAO Bi-xia, ZHAO Ming-hui, ZHANG Lu-xia, WU Shou-ling, WANG Fang. Impact of anemia and chronic kidney disease on the risk of cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality among diabetic patients [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(3): 495-500. |
| [7] | LIN Ke, XIE Jun-qing, HU Yong-hua, KONG Gui-lan. Application of support vector machine in predicting in-hospital mortality risk of patients with acute kidney injury in ICU [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(2): 239-244. |
|
||