Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (3): 562-568. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.03.021
Previous Articles Next Articles
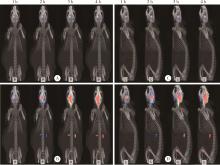
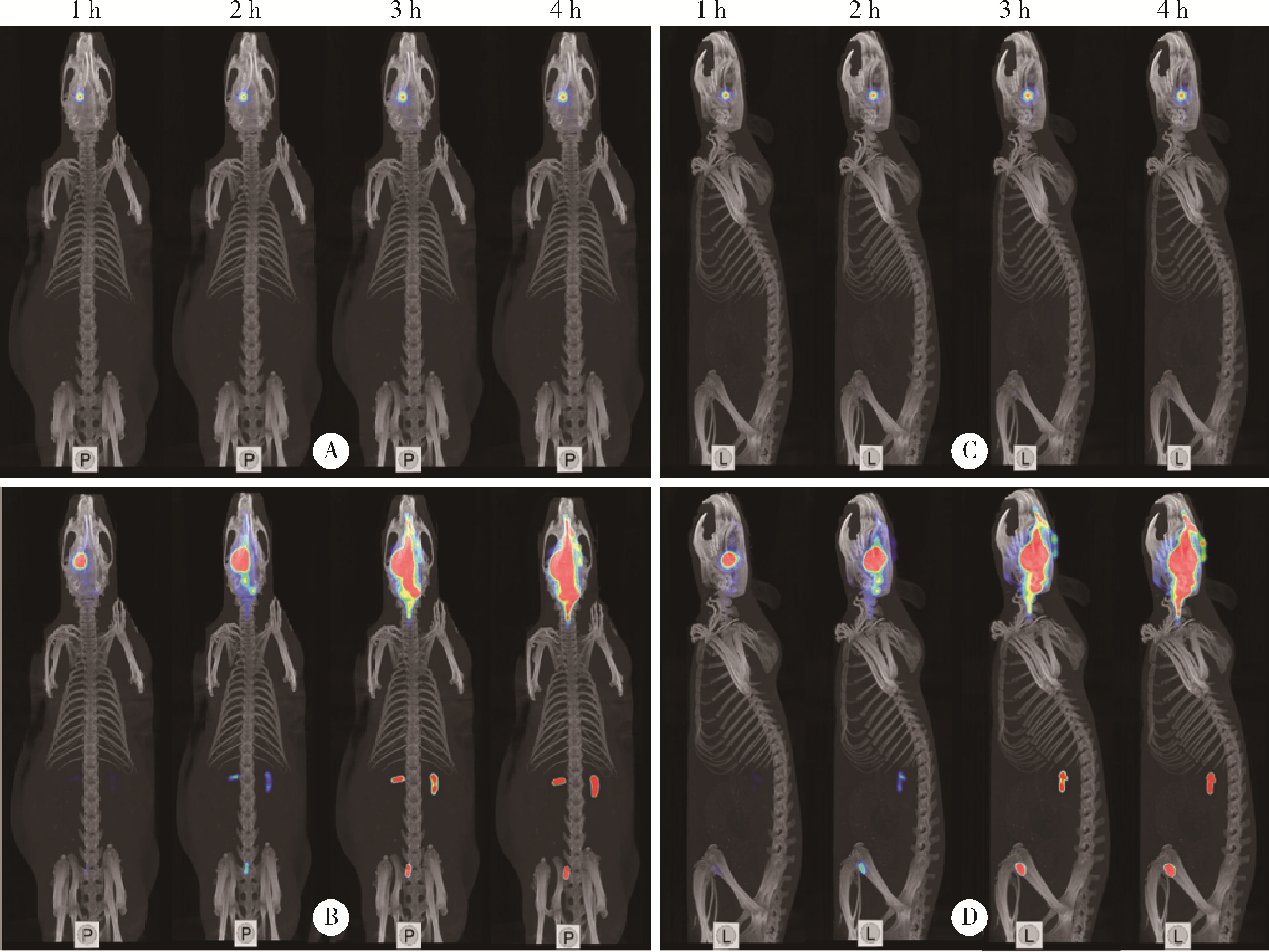
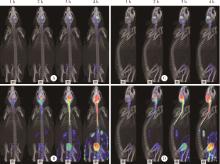
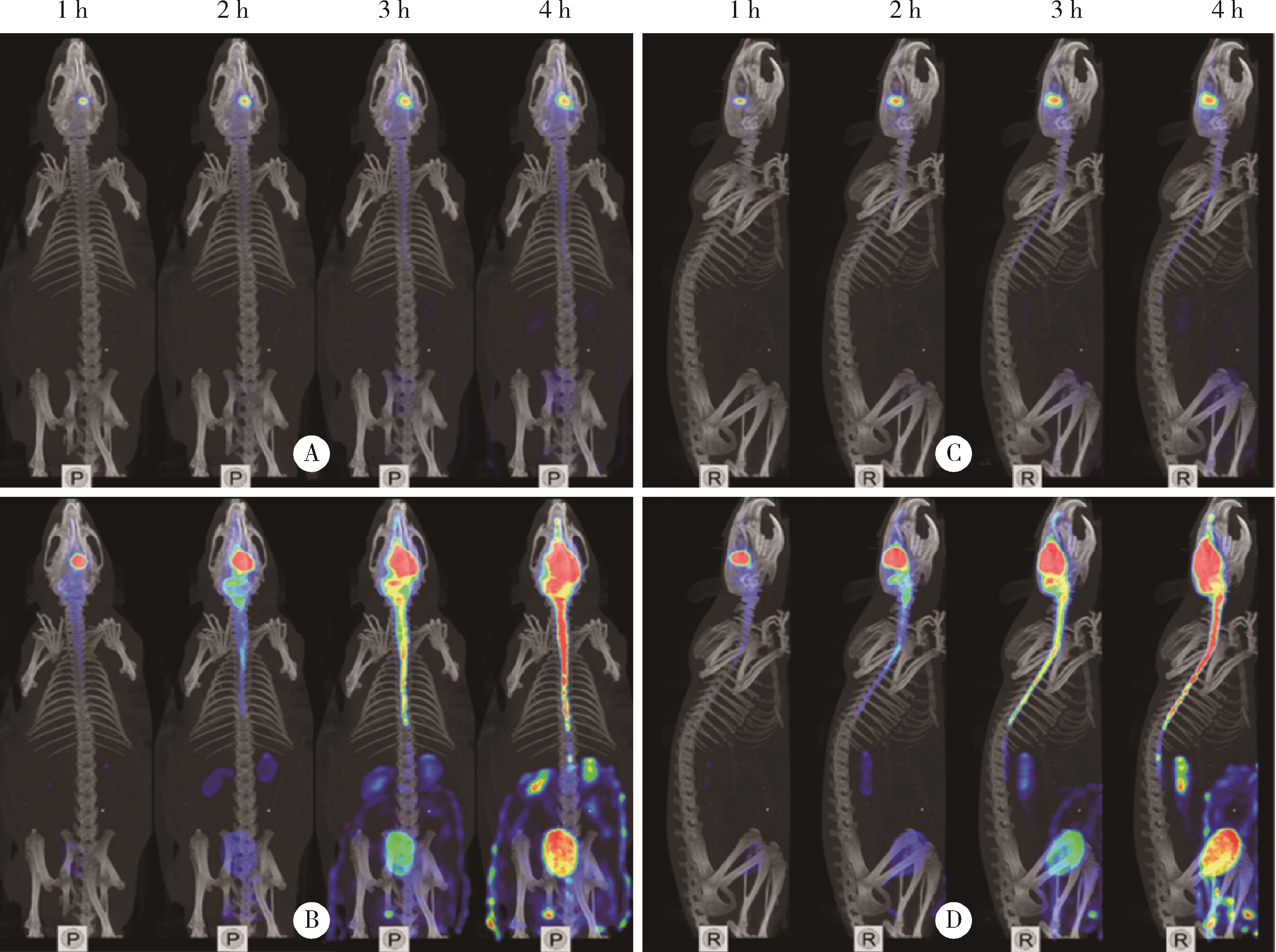
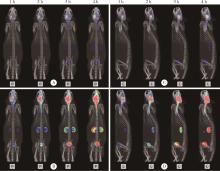
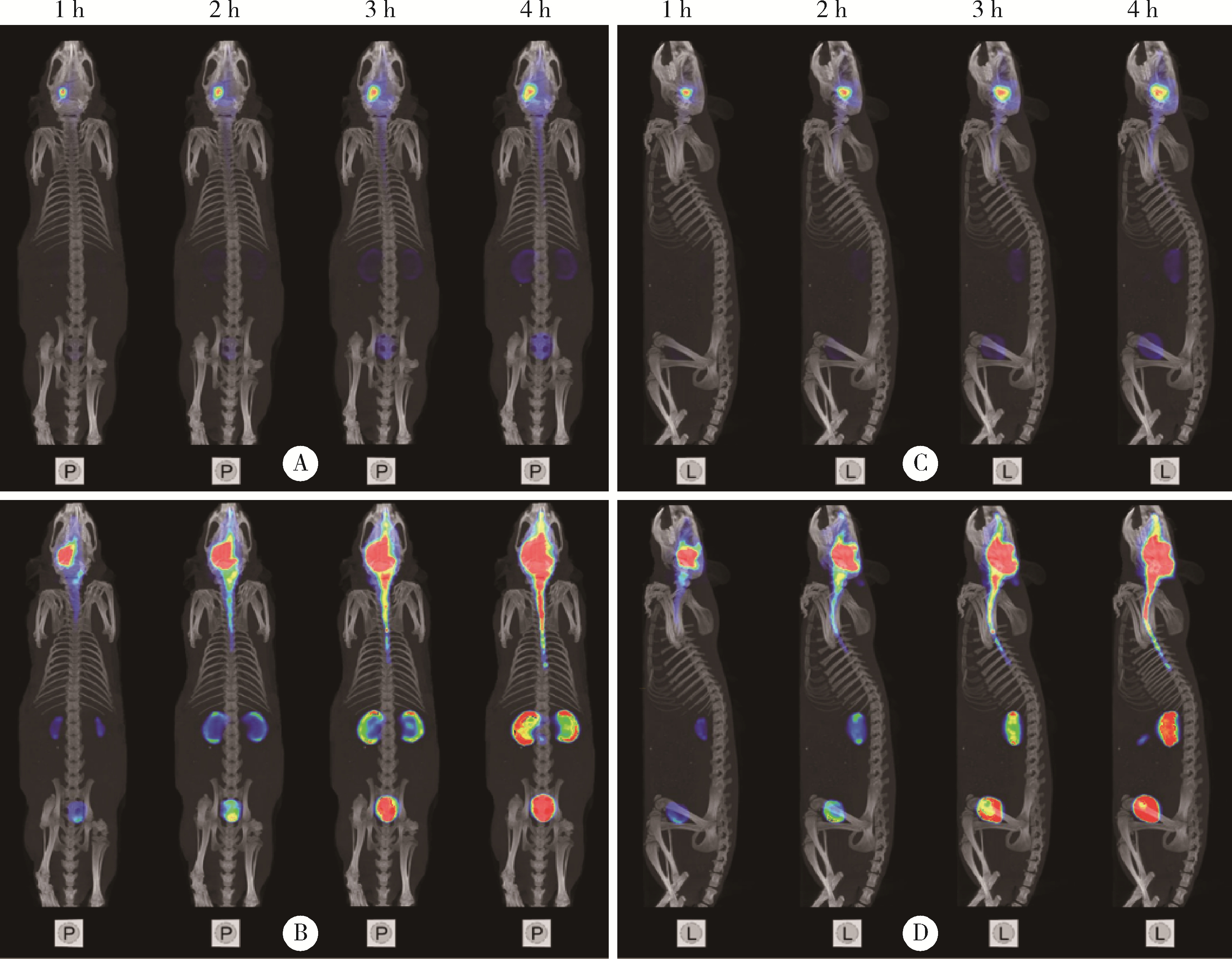
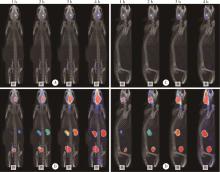
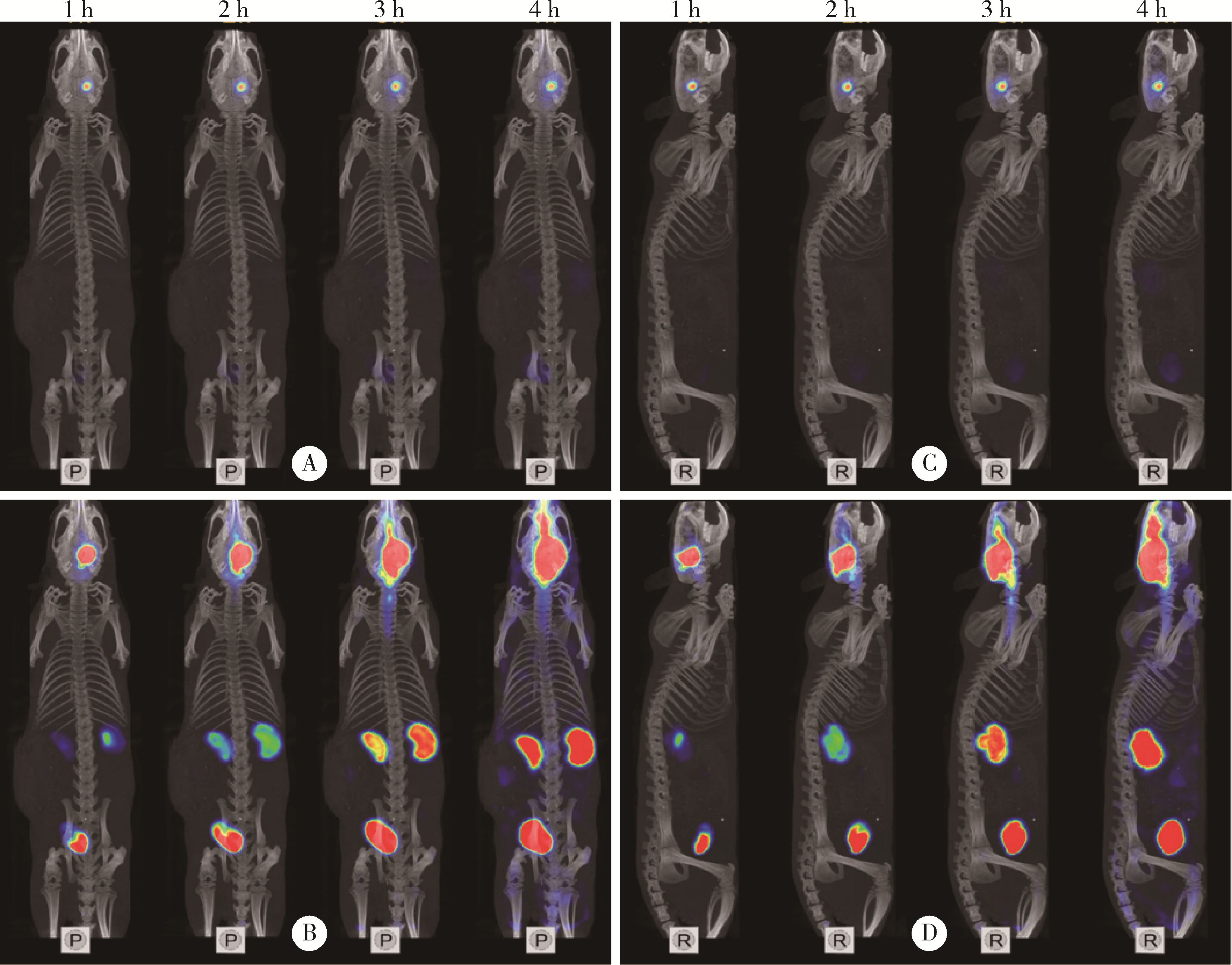
Dynamic distribution and clearance of 99mTc-DTPA in brain extracellular space
Jing ZOU1,2,3, Tianzi GAO1,3, Yang WANG1,3, Mengmeng REN1,2,3, Dongyang LIU4, Ren LONG1,2,3, Yumeng CHENG1,3,5, Meng LIU6, Zhengren XU7, Zhaoheng XIE1,3, Pengyu LV8, Lan YUAN1,2,3,*( ), Hongbin HAN1,3,5,*(
), Hongbin HAN1,3,5,*( )
)
- 1. Institute of Medical Technology, Peking University Health Science Center, Beijing 100191, China
2. Department of Chemical Biology, Peking University School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Beijing 100191, China
3. Beijing Key Lab of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Device and Technique, Beijing 100191, China
4. Peking University Third Hospital Drug Clinical Trial Institute, Beijing 100191, China
5. Department of Radiology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
6. Department of Nuclear Medicine, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
7. Department of Natural Medicines, Peking University School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Beijing 100191, China
8. Department of Mechanics and Engineering Science, Peking University School of Engineering, Beijing 100871, China
CLC Number:
- R817.4
| 1 |
doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2009.07.030 |
| 2 |
doi: 10.1016/j.nec.2017.05.012 |
| 3 |
doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2018.07.013 |
| 4 |
doi: 10.1007/s13311-017-0520-4 |
| 5 |
doi: 10.2176/nmc.ra.2016-0071 |
| 6 |
doi: 10.1097/00001756-200212200-00005 |
| 7 |
doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2015.12.007 |
| 8 |
赵越, 李昀倩, 李怀业, 等. 荧光及磁示踪法观测脑组织液的引流分区特征[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49 (2): 303- 309.
|
| 9 |
doi: 10.1007/s00723-015-0670-7 |
| 10 |
doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(95)00039-9 |
| 11 |
doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2009.10.012 |
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
doi: 10.14336/AD.2018.1206 |
| 14 |
doi: 10.12659/MSM.903010 |
| 15 |
doi: 10.14336/AD.2017.1115 |
| 16 |
doi: 10.14336/AD.2017.0415 |
| 17 |
李艳玲, 彭本君. 99mTc-DTPA肾动态显像对多囊肾病患者诊断价值分析[J]. 泰山医学院学报, 2019, 40 (10): 752- 753.
|
| [1] | Peng ZHONG, Xiaodan HU, Zhenzhou WANG. Optical coherence tomography angiography and microvessel density quantification in penumbra after traumatic brain injury in rats [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2025, 57(2): 262-266. |
| [2] | Jinna LI,Li' na XU,Min LI,Yi SONG,Jing ZHANG,Longbin JIA. Correlations between serum BDNF, IL-18 and hs-CRP levels in patients with acute cerebral infarction and vascular cognitive impairment [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 708-714. |
| [3] | Ren LONG, Xin MAO, Tianzi GAO, Qian XIE, Hanbo TAN, Ziyin LI, Hongbin HAN, Lan YUAN. Ursolic acid improved demyelination and interstitial fluid drainage disorders in schizophrenia mice [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 487-494. |
| [4] | HAN Song-chen,HUANG Zi-xiong,LIU Hui-xin,XU Tao. Renal functional compensation after unilateral radical nephrectomy of renal cell carcinoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(4): 680-685. |
| [5] | Yu SONG,Hong-bin HAN,Jun YANG,Ai-bo WANG,Qing-yuan HE,Yuan-yuan LI,Guo-mei ZHAO,Ya-juan GAO,Rui WANG,Yi-xing HAN,Ai-lian LIU,Qing-wei SONG. Effect of convection enhanced delivery on the microstructure of brain extracellular space in aged rats [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(2): 362-367. |
| [6] | Hong-bin HAN. Discovery of a new division system in brain and the regionalized drainage route of brain interstitial fluid [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(3): 397-401. |
| [7] | Wei WANG,Jin HOU,Wen-qiang HUANG. Temporary acceleration of interstitial fluid drainage in excited brain region induced by movement [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(2): 206-209. |
| [8] | LI Yun-qian1,2,3, SHENG Hui, LIANG Lei, ZHAO Yue, LI Huai-ye, BAI Ning, WAN Tong, YUAN Lan, HAN Hong-bin. Application of anoptomagnetic probe Gd-DO3A-EA-FITC in imaging and analyzing the brain interstitial space [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(2): 221-225. |
| [9] | LIU E, ZHANG Yi-xuan, SUN Lin-lin,TENG Ze, WANG Ai-bo, HAN Hong-bin, YAN Jun-hao. Role of aquaporin-4 in the change of interstitial fluid drainage in Alzheimer’s disease [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(2): 203-206. |
| [10] | WANG Hui, YE Jin-tang, YAO Hong-xin, LI Dong, DONG Ying. Clinicopathologic features of infant dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor: a case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(5): 904-909. |
| [11] | ZHAO Yue, LI Yun-qian, LI Huai-ye, LI Yu-liang, LIU Lan-xiang, YUAN Lan, ZHANG Shu-jia, . Drainage characteristic of the brain interstitial fluid detected by using fluorescence and magnetic tracer method [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(2): 303-309. |
| [12] | YANG Dan, QIAO Lin, ZHAO Li-dan. Cerebral infarction in a patient with primary Sj-gren’s syndrome: a case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2016, 48(6): 1077-1080. |
| [13] | XIAO Tian-yi, LIU Yan, LI Ji-lai, WANG Rui-tong, DU Ji-chen. Diagnostic value of carotid atherosclerosis score for ischemic stroke [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2016, 48(6): 1000-1005. |
| [14] | YANG Cheng, ZHANG Yu-qi, TANG Xun, GAO Pei, WEI Chen-lu, HU Yong-hua. Retrospective cohort study for the impact on readmission of patients with ischemic stroke after treatment of aspirin plus clopidogrel or aspirin mono-therapy [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2016, 48(3): 442-447. |
| [15] | TU Jing-yi, ZHU Ying, SHANG Shu-ling, ZHANG Xi, TANG Hui, WANG Rui-min. Keap1-tat peptide attenuates oxidative stress damage in hippocampal CA1 region and learning and memory deficits following global cerebral ischemia [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2016, 48(1): 154-159. |
|
||