Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (3): 569-577. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.03.022
Previous Articles Next Articles
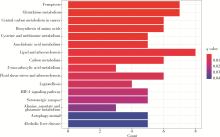
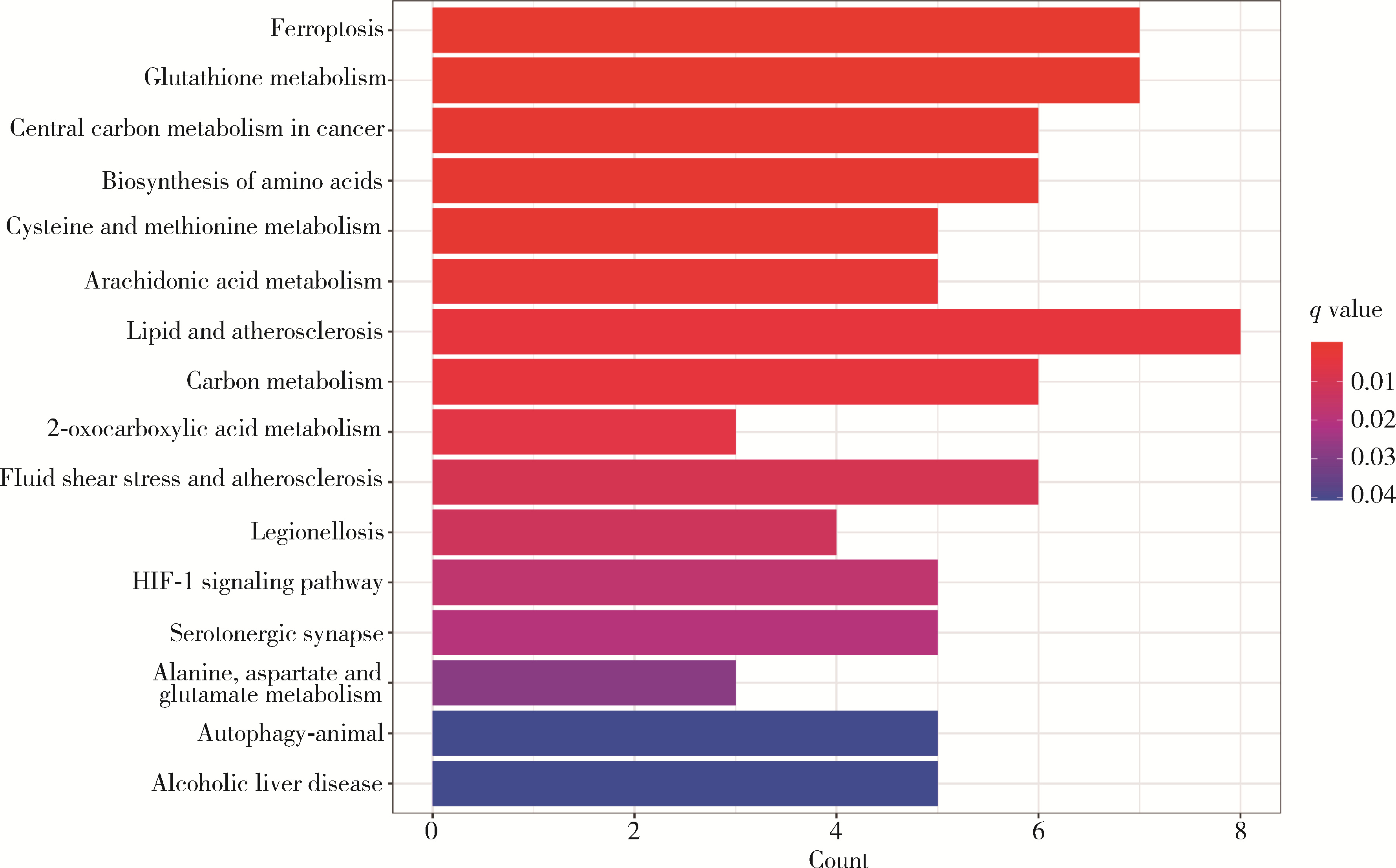
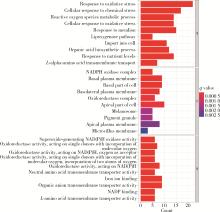
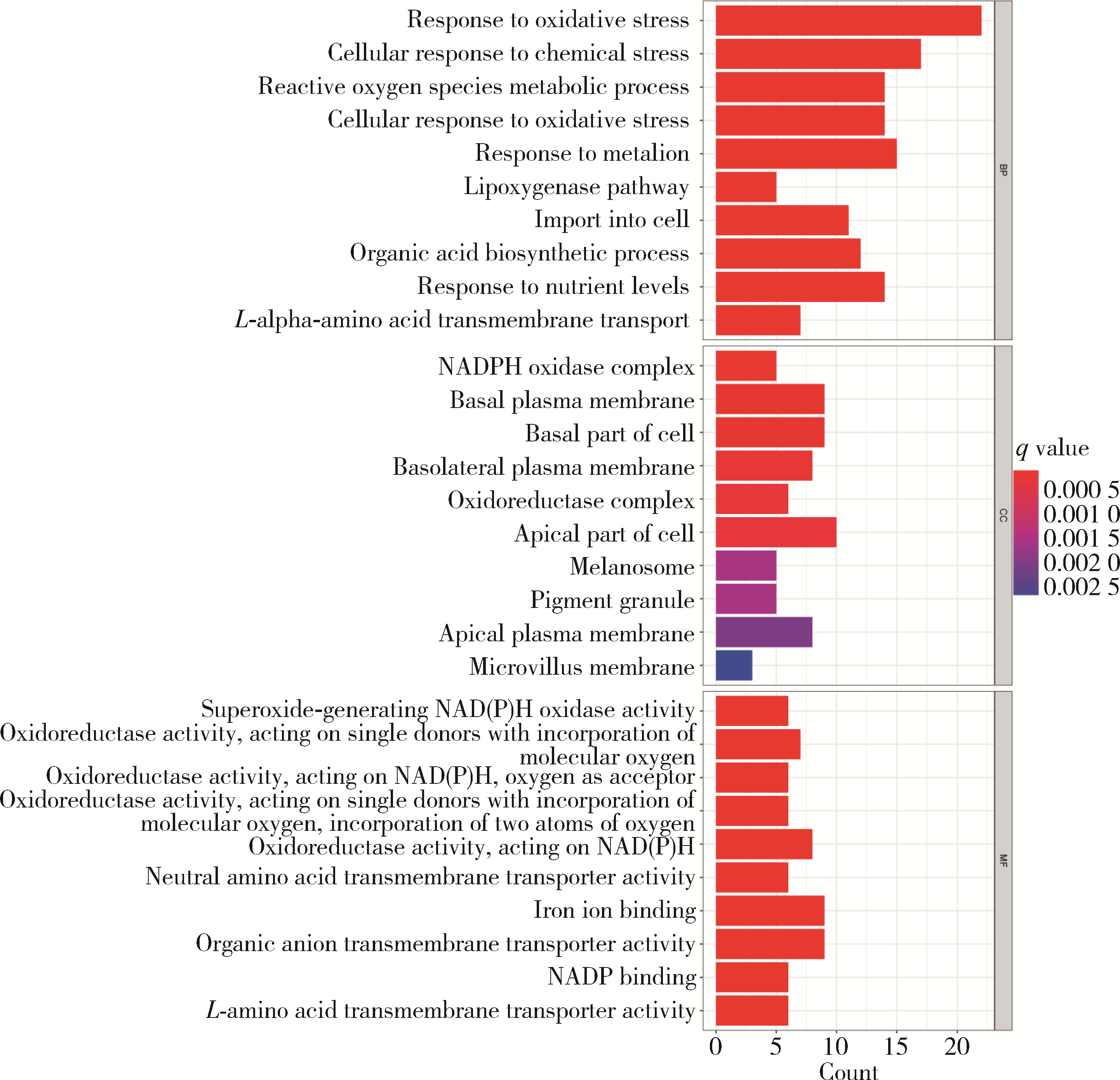
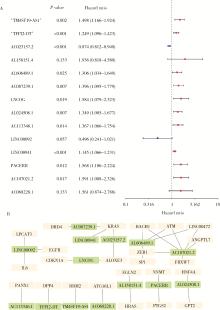
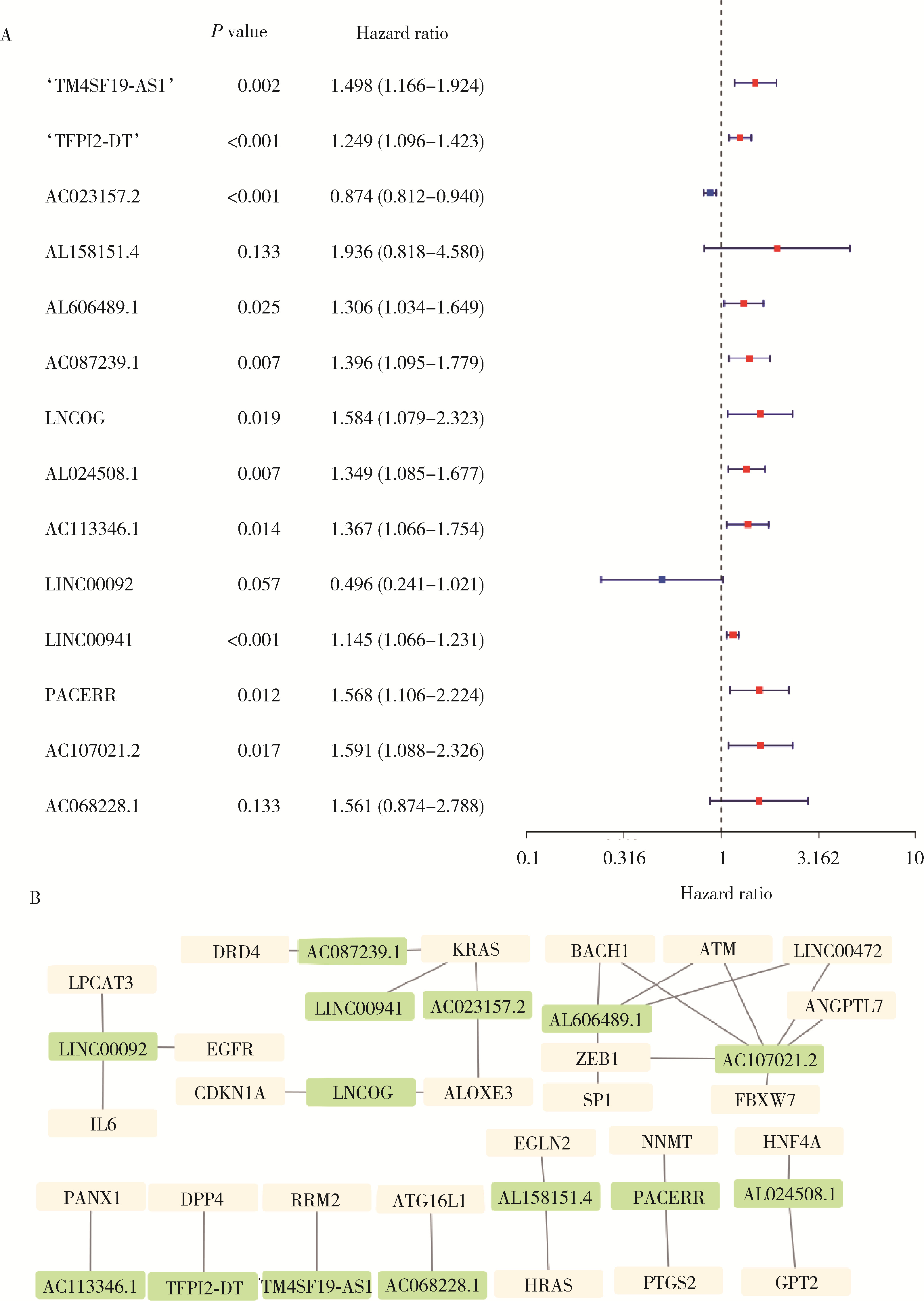
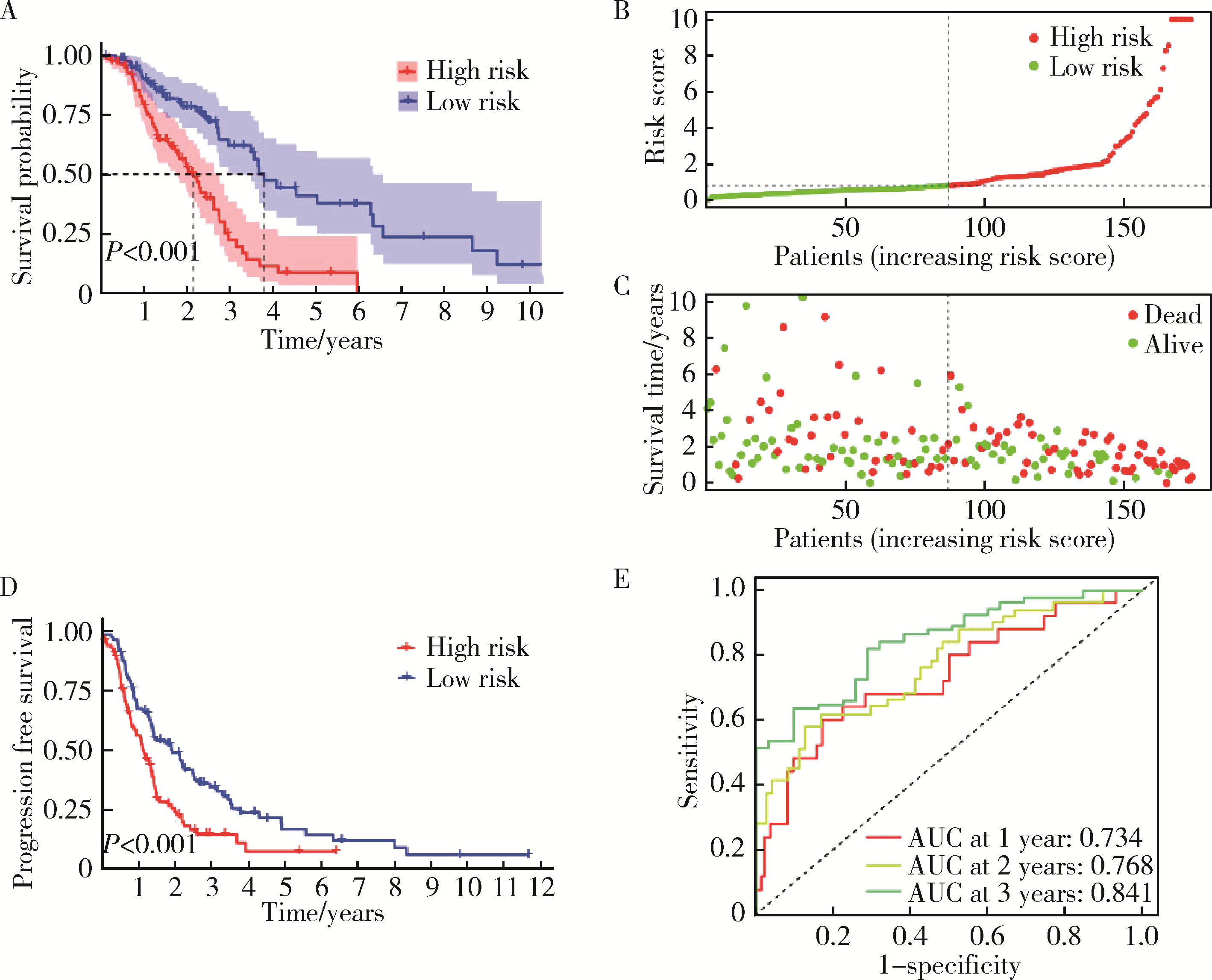
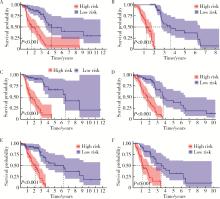
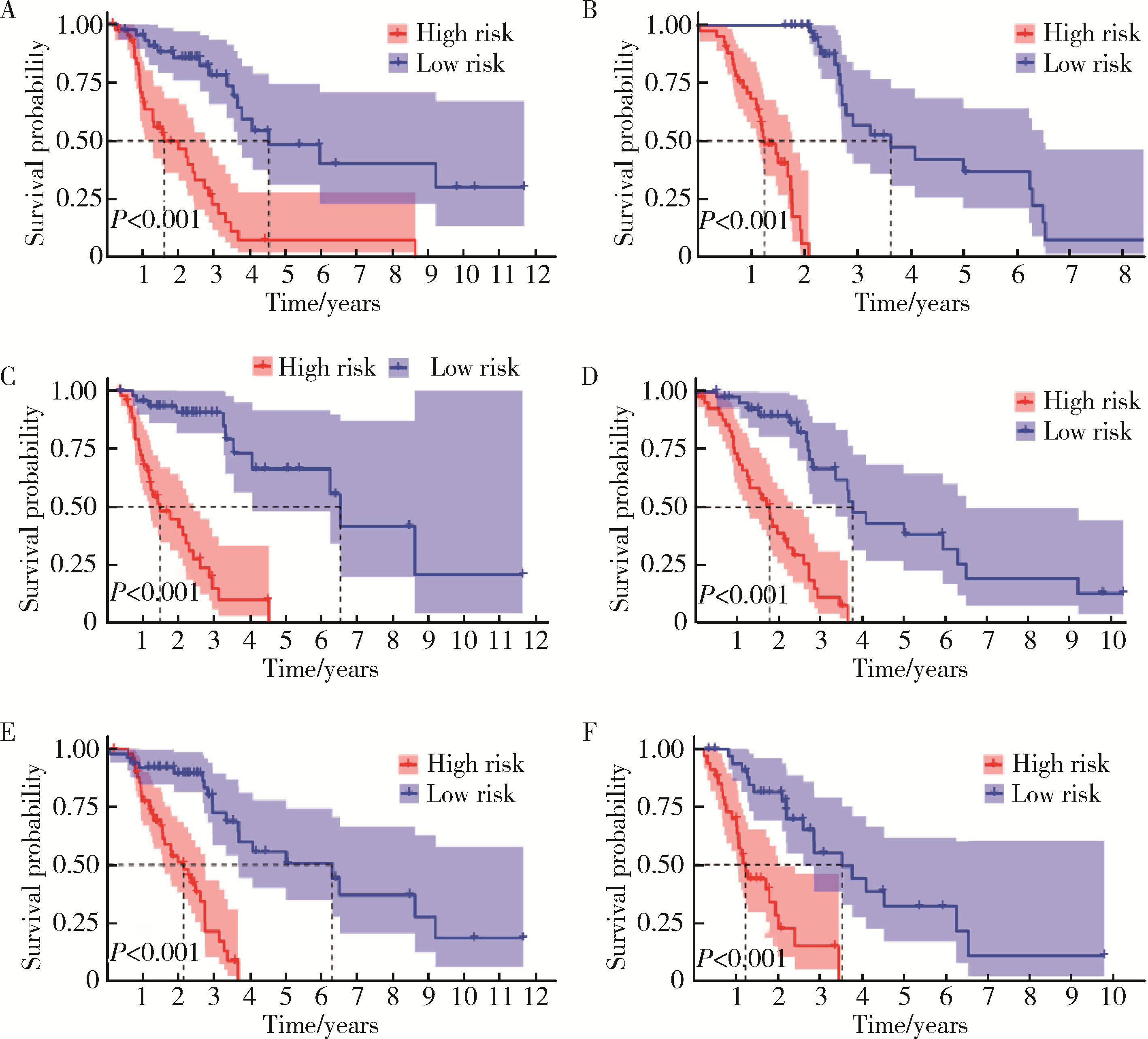
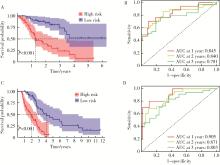
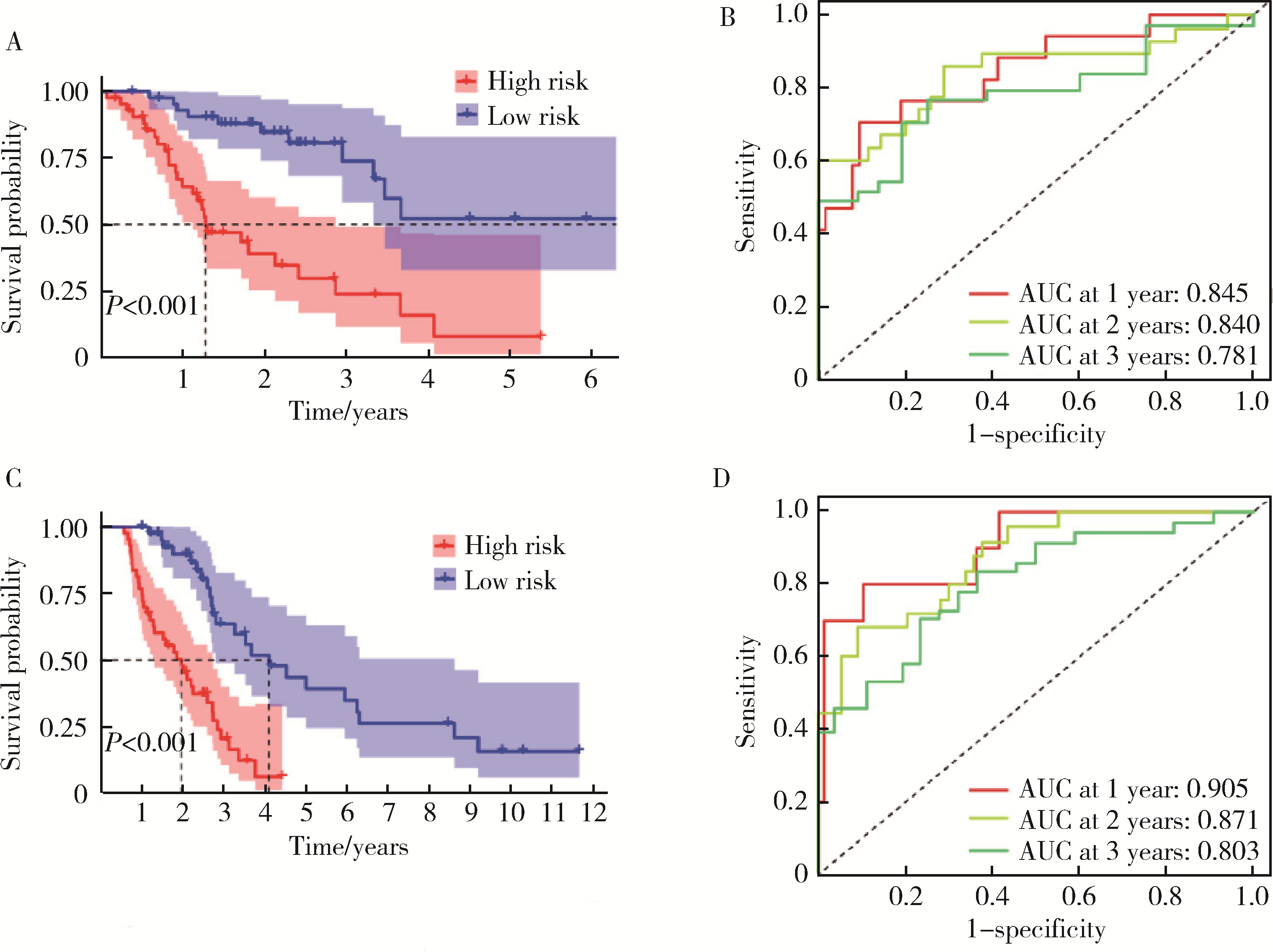
Ferroptosis-related long non-coding RNA to predict the clinical outcome of non-small cell lung cancer after radiotherapy
Qiushi XU1, Tong LIU2, Junjie WANG3,*( )
)
- 1. Institute of Medical Technology, Peking University Health Science Center, Beijing 100191, China
2. Center of Basic Medical Research, Institute of Medical Innovation and Research, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
3. Department of Radiation Oncology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
CLC Number:
- R34
| 1 |
doi: 10.3322/caac.21590 |
| 2 |
doi: 10.3390/ijms22168661 |
| 3 |
doi: 10.1097/CCO.0000000000000703 |
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1608986 |
| 6 |
doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-0298 |
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.042 |
| 9 |
doi: 10.1038/s41422-019-0164-5 |
| 10 |
doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.586578 |
| 11 |
doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2015.10.014 |
| 12 |
doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-19-0338 |
| 13 |
doi: 10.1038/s41422-019-0263-3 |
| 14 |
doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.621 |
| 15 |
doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2013.05.030 |
| 16 |
doi: 10.1186/s12967-015-0556-3 |
| 17 |
doi: 10.1038/cddis.2015.30 |
| 18 |
doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-14-0492 |
| 19 |
doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2013-305266 |
| 20 |
|
| 21 |
doi: 10.1039/D0NR08757B |
| 22 |
doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-3477 |
| 23 |
|
| 24 |
doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.675555 |
| 25 |
doi: 10.1021/acschembio.9b00939 |
| 26 |
doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-6-518 |
| 27 |
|
| 28 |
|
| 29 |
doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-83244-7 |
| 30 |
doi: 10.1038/nature08975 |
| 31 |
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000845 |
| 32 |
|
| 33 |
doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2022.101356 |
| 34 |
doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.03.021 |
| 35 |
doi: 10.1186/s13045-019-0773-y |
| 36 |
doi: 10.1136/jitc-2019-000110 |
| 37 |
doi: 10.1038/s41418-019-0304-y |
| 38 |
doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-02027-2 |
| [1] | Wanwei HUANG, Xianshen SHA, Yibao ZHANG, Guohao WU, Feng LUO, Zhihui CHEN, Dongming YE, Xuesong LI, Caiyong LAI. Total 3D laparoscopic ileal ureters replacement for bilateral ureters combined with bladder augmentation in the management of post-radiotherapy bilateral ureteral strictures and contracted bladder [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2025, 57(4): 789-795. |
| [2] | Kelin ZHAO, Xue XIA, Naixu SHI, Han ZHOU, Jingwen GAI, Ping LI. Expression and significance of ferroptosis marker 4-HNE in in vitro model of systemic sclerosis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(6): 950-955. |
| [3] | Shengjia PENG,Yu QI,Lijie SUN,Dan LI,Xinyu WANG,Jiangli HAN,Baoxia CHEN,Yuan ZHANG. Afferent baroreflex failure with hyponatremia: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 357-361. |
| [4] | Hai-hong JIANG,Xiao-fan LI,Jian-liu WANG. Relationship between chronic radiation enteritis of cervical cancer and gut microbiota [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 619-624. |
| [5] | SHUAI Ting,LIU Juan,GUO Yan-yan,JIN Chan-yuan. Knockdown of long non-coding RNA MIR4697 host gene inhibits adipogenic differentiation in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(2): 320-326. |
| [6] | Qiao ZHU,Cui REN,Yan ZHANG,Mei-jiao LI,Xiao-hua WANG. Comparative imaging study of mediastinal lymph node from pre-surgery dual energy CT versus post-surgeron verifications in non-small cell lung cancer patients [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(4): 730-737. |
| [7] | Hao WANG,Shu-kun JIANG,Ran PENG,Yi HUANG,Ming-qing WANG,Jun-jie WANG,Cheng LIU,Fan ZHANG,Lu-lin MA. Individual control of urine volume to improve stability of bladder volume in radiotherapy of urinary tumor [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(4): 688-691. |
| [8] | Yu-qing OUYANG,Lian-fang NI,Xin-min LIU. Prognosis factors analysis of patients with malignant solitary pulmonary nodules [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2020, 52(1): 158-162. |
| [9] | Fei-long YANG,Kai HONG,Guo-jiang ZHAO,Cheng LIU,Yi-meng SONG,Lu-lin MA. Construction of prognostic model and identification of prognostic biomarkers based on the expression of long non-coding RNA in bladder cancer via bioinformatics [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(4): 615-622. |
| [10] | SUN Hai-tao, YANG Rui-jie, JIANG Ping, JIANG Wei-juan, LI Jin-na, MENG Na, WANG Jun-jie. Dosimetric analysis of volumetric modulated arc therapy and intensity modulated radiotherapy for patients undergone breast-conserving operation [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(1): 188-192. |
| [11] | GUO Fu-xin, JIANG Yu-liang, JI Zhe, PENG Ran, SUN Hai-tao, WANG Jun-jie. 3D printed template-assisted and computed tomography image-guided 125-iodine seed implantation for supraclavicular metastatic tumor: a dosimetric study [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(3): 506-511. |
| [12] | LIU Xing-hua, JIANG Xie-yuan, GONG Mao-qi, ZHA Ye-jun. Effect of radiotherapy and indomethacin together in the prevention of recurrence of ectopic ossification around the elbow after resection [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2016, 48(2): 230-233. |
| [13] | JIANG Ping, ZHOU Shun,WANG Jun-jie, YANG Rui-jie, LIU Zi-yi, JIANG Shu-kun, WANG Wei. Errors in six degree-of-freedom pose estimation of spine tumors assessed by image guided radiotherapy [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2015, 47(6): 952-956. |
| [14] | WANG Qing-guo, LI Xiao-mei, ZHANG Min, LI Hang, WEN Bing, LI Hong-zhen, GAO Xian-shu. Effect of two dose fractionations on postoperative radiotherapy of keloid: an analysis of 107 patients [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2014, 46(1): 169-172. |
|
||