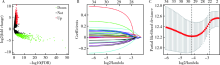
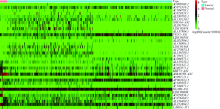
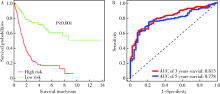
Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (4): 615-622. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.04.003
Previous Articles Next Articles
Construction of prognostic model and identification of prognostic biomarkers based on the expression of long non-coding RNA in bladder cancer via bioinformatics
Fei-long YANG,Kai HONG,Guo-jiang ZHAO,Cheng LIU,Yi-meng SONG( ),Lu-lin MA(
),Lu-lin MA( )
)
- Department of Urology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
CLC Number:
- R737.11
| [1] | Bellmunt J, Orsola A, Leow JJ , et al. Bladder cancer: ESMO practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up[J]. Ann Oncol, 2014,25(Suppl 3):40-48. |
| [2] | Welty CJ, Sanford TH, Wright JL , et al. Thecancer of the bladder risk assessment (COBRA) score: estimating mortality after radical cystectomy[J]. Cancer, 2017,123(23):4574-4582. |
| [3] | 李吉, 刘裔道, 蚌凌青 . 肌层浸润性膀胱癌患者膀胱部分切除术结合放化疗的临床疗效及预后分析[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2017,32(10):767-770. |
| [4] | Esteller M . Non-coding RNAs in human disease[J]. Nat Rev Genet, 2011,12(12):861-874. |
| [5] | Martens-Uzunova ES, Bottcher R, Croce CM , et al. Long nonco-ding RNA in prostate, bladder, and kidney cancer[J]. Eur Urol, 2014,65(6):1140-1151. |
| [6] | Jin Y, Feng SJ, Qiu S , et al. LncRNA MALAT1 promotes proliferation and metastasis in epithelial ovarian cancer via the PI3K-AKT pathway[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2017,21(14):3176-3184. |
| [7] | Gupta RA, Shah N, Wang KC , et al. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer metastasis[J]. Nature, 2010,464(7291):1071-1076. |
| [8] | Quinn JJ, Chang HY . Unique features of long non-coding RNA biogenesis and function[J]. Nat Rev Genet, 2016,17(1):47-62. |
| [9] | Djebali S, Davis CA, Merkel A , et al. Landscape of transcription in human cells[J]. Nature, 2012,489(7414):101-108. |
| [10] | Lee JT . Epigenetic regulation by long noncoding RNAs[J]. Science, 2012,338(6113):1435-1439. |
| [11] | Wang KC, Chang HY . Molecular mechanisms of long noncoding RNAs[J]. Mol Cell, 2011,43(6):904-914. |
| [12] | Liu D, Li Y, Luo G , et al. LncRNA SPRY4-IT1 sponges miR-101-3p to promote proliferation and metastasis of bladder cancer cells through up-regulating EZH2[J]. Cancer Lett, 2017,388:281-291. |
| [13] | Schmitt AM, Chang HY . Longnoncoding RNAs in cancer pathways[J]. Cancer Cell, 2016,29(4):452-463. |
| [14] | Yue B, Qiu S, Zhao S , et al. LncRNA-ATB mediated E-cadherin repression promotes the progression of colon cancer and predicts poor prognosis[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2016,31(3):595-603. |
| [15] | Zhang S, Zhong G, He W , et al. lncRNA up-regulated in non-muscle invasive bladder cancer facilitates tumor growth and acts as a negative prognostic factor of recurrence[J]. J Urol, 2016,196(4):1270-1278. |
| [16] | Berrondo C, Flax J, Kucherov V , et al. Expression of the long non-coding RNA HOTAIR correlates with disease progression in bladder cancer and is contained in bladder cancer patient urinary exosomes[J]. PLoS One, 2016,11(1):e0147236. |
| [17] | Huang HW, Xie H, Ma X , et al. Upregulation of lncRNA PANDAR predicts poor prognosis and promotes cell proliferation in cervical cancer[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2017,21(20):4529-4535. |
| [18] | Cao X, Xu J, Yue D . LncRNA-SNHG16 predicts poor prognosis and promotes tumor proliferation through epigenetically silencing p21 in bladder cancer[J]. Cancer Gene Ther, 2018,25(1/2):10-17. |
| [19] | Tuo Z, Zhang J, Xue W . LncRNA TP73-AS1 predicts the prognosis of bladder cancer patients and functions as a suppressor for bladder cancer by EMT pathway[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2018,499(4):875-881. |
| [20] | Li HJ, Sun XM, Li ZK , et al. LncRNA UCA1promotes mitochondrial function of bladder cancer via the miR-195/ARL2 signaling pathway[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2017,43(6):2548-2561. |
| [1] | Huan-rui LIU,Xiang PENG,Sen-lin LI,Xin GOU. Risk modeling based on HER-2 related genes for bladder cancer survival prognosis assessment [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 793-801. |
| [2] | Fei WANG,Cai-peng QIN,Yi-qing DU,Shi-jun LIU,Qing LI,Tao XU. Optimal surveillance intensity of cystoscopy in intermediate-risk non-muscle invasive bladder cancer [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(4): 669-673. |
| [3] | SHUAI Ting,LIU Juan,GUO Yan-yan,JIN Chan-yuan. Knockdown of long non-coding RNA MIR4697 host gene inhibits adipogenic differentiation in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(2): 320-326. |
| [4] | Hong-quan QIN,You ZHENG,Man-na WANG,Zheng-rong ZHANG,Zu-biao NIU,Li MA,Qiang SUN,Hong-yan Huang,Xiao-ning WANG. Subcellular localization of GTPase of immunity-associated protein 2 [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(2): 221-226. |
| [5] | ZHU Shi-wei, LIU Zuo-jing, LI Mo, ZHU Huai-qiu, DUAN Li-ping. Comparison of gut microbiotal compositional analysis of patients with irritable bowel syndrome through different bioinformatics pipelines [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(2): 231-238. |
| [6] | ZHANG Ming-ming, ZHENG Ying-dong, LIANG Yu-hong. A prognostic model for assessment of outcome of root canal treatment in teeth with pulpitis or apical periodontitis#br# [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(1): 123-130. |
| [7] | SHEN Qi, HU Shuai, LI Jun, WANG Jing-Hua, HE Qun. Incidence and clinicopathological characteristics of incidental prostatic adenocarcinoma in radical cystoprostatectomy specimens [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2014, 46(4): 515-518. |
|
||