Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (4): 789-795. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.04.026
Previous Articles Next Articles
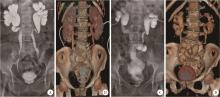
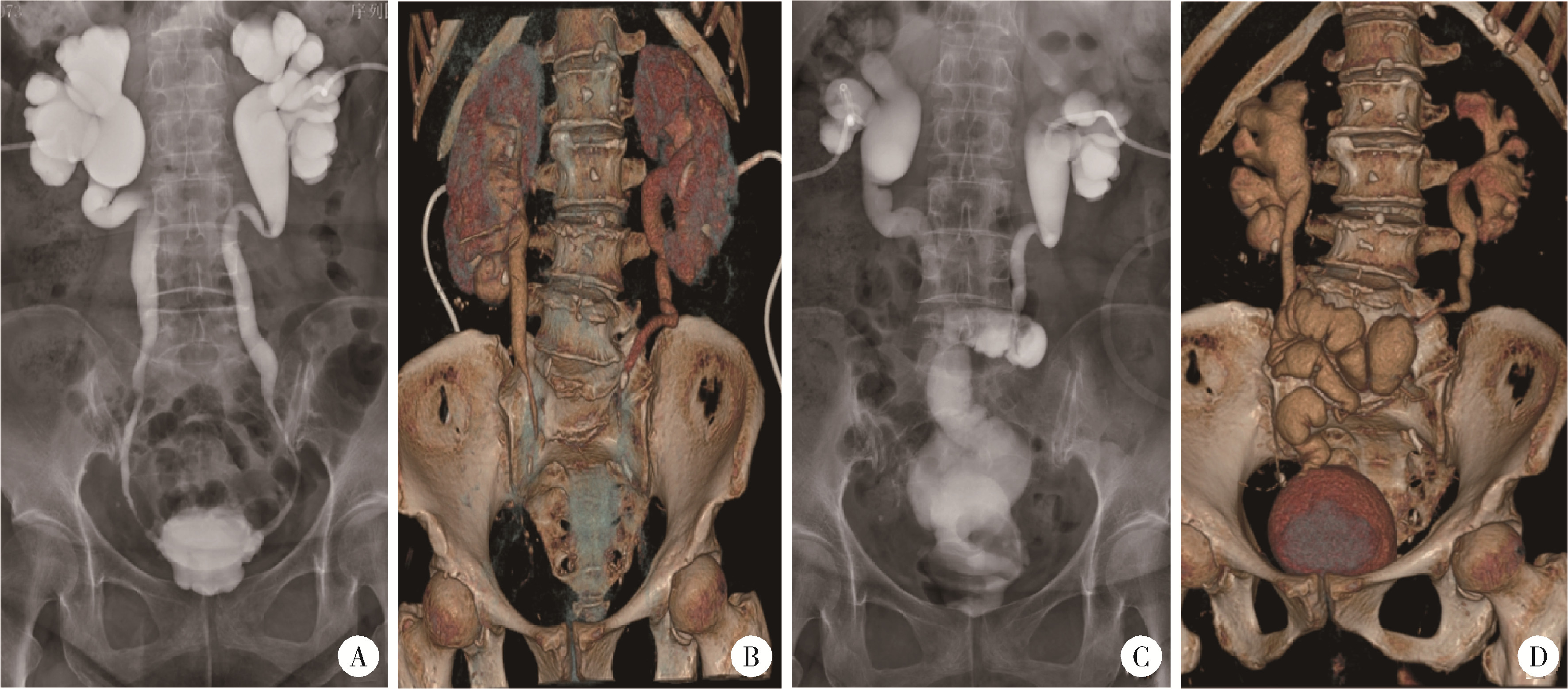
Total 3D laparoscopic ileal ureters replacement for bilateral ureters combined with bladder augmentation in the management of post-radiotherapy bilateral ureteral strictures and contracted bladder
Wanwei HUANG1, Xianshen SHA1, Yibao ZHANG1, Guohao WU2, Feng LUO2, Zhihui CHEN2, Dongming YE2, Xuesong LI3,*( ), Caiyong LAI1,2,*(
), Caiyong LAI1,2,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Urology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Jinan University, Guangzhou 510630, China
2. Department of Urology, The Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Jinan University, Dongguan 523570, Guangdong, China
3. Department of Urology, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
CLC Number:
- R699
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
杨昆霖, 吴昱晔, 丁光璞, 等. 回肠代输尿管联合膀胱扩大术治疗输尿管狭窄合并膀胱挛缩的初步研究[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2019, 40 (6): 416- 421.
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
李兵, 梁超启. 输尿管狭窄修复重建策略[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2019, 34 (5): 335- 339.
|
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
祁小龙, 徐智慧, 刘锋, 等. 腹腔镜下回肠膀胱扩大术治疗低顺应性膀胱的初步临床结果[J]. 中华外科杂志, 2015, 53 (8): 594- 598.
|
| 14 |
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
|
| 17 |
|
| 18 |
|
| [1] | Qiushi XU, Tong LIU, Junjie WANG. Ferroptosis-related long non-coding RNA to predict the clinical outcome of non-small cell lung cancer after radiotherapy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2025, 57(3): 569-577. |
| [2] | Junyong OU,Kunming NI,Lulin MA,Guoliang WANG,Ye YAN,Bin YANG,Gengwu LI,Haodong SONG,Min LU,Jianfei YE,Shudong ZHANG. Prognostic factors of patients with muscle invasive bladder cancer with intermediate-to-high risk prostate cancer [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 582-588. |
| [3] | Wenbo YANG,Lei YU,Weiyu ZHANG,Tao XU,Qiang WANG. Effect and safety of self-draining ureteral stent with thread in kidney transplant reci-pients [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 656-660. |
| [4] | Shengjia PENG,Yu QI,Lijie SUN,Dan LI,Xinyu WANG,Jiangli HAN,Baoxia CHEN,Yuan ZHANG. Afferent baroreflex failure with hyponatremia: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 357-361. |
| [5] | Hai-hong JIANG,Xiao-fan LI,Jian-liu WANG. Relationship between chronic radiation enteritis of cervical cancer and gut microbiota [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 619-624. |
| [6] | Su-huan XU,Bei-bei WANG,Qiu-ying PANG,Li-jun ZHONG,Yan-ming DING,Yan-bo HUANG,Xin-yan CHE. Effect of equal temperature bladder irrigation in patients with transurethral resection of prostate: A meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 676-683. |
| [7] | WANG Jia-wen,LIU Jing-chao,MENG Ling-feng,ZHANG Wei,LIU Xiao-dong,ZHANG Yao-guang. Quality of life and related factors in patients with interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(4): 653-658. |
| [8] | Tian WANG,Xin HONG,Xiao-feng WANG. Clinical application of the needle electrode in transurethral plasmakinetic resection of bladder tumor around ureteral orifice: A report of 16 cases [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(4): 632-636. |
| [9] | Wen-min DONG,Ming-rui WANG,Hao HU,Qi WANG,Ke-xin XU,Tao XU. Initial clinical experience and follow-up outcomes of treatment for ureteroileal anastomotic stricture with Allium coated metal ureteral stent [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(4): 637-641. |
| [10] | Hao WANG,Shu-kun JIANG,Ran PENG,Yi HUANG,Ming-qing WANG,Jun-jie WANG,Cheng LIU,Fan ZHANG,Lu-lin MA. Individual control of urine volume to improve stability of bladder volume in radiotherapy of urinary tumor [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(4): 688-691. |
| [11] | Shi-ming ZHAO,Tie-jun YANG,Chun-miao XU,Xiao-feng GUO,Yong-kang MA,Xue-jun CHEN,Xiang LI,Chao-hong HE. Bladder cancer local staging about muscle invasion: 3.0T MRI performance following transurethral resection [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(4): 701-704. |
| [12] | Kai MA,Xing-ke QU,Qing-quan XU,Liu-lin XIONG,Xiong-jun YE,Li-zhe AN,Wei-nan CHEN,Xiao-bo HUANG. Endoscopic treatment for ureterovesical junction stenosis in patients with kidney transplantation: 13 cases report [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(6): 1155-1158. |
| [13] | Wei-yu ZHANG,Qiu-xiang XIA,Hao HU,Jing-wen CHEN,Yi-ran SUN,Ke-xin XU,Xiao-peng ZHANG. Analysis of urodynamic study of female outpatients with lower urinary tract symptoms and follow-up of the patients with detrusor underactive [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(5): 856-862. |
| [14] | Hai-wen HUANG,Bing YAN,Mei-xia SHANG,Li-bo LIU,Han HAO,Zhi-jun XI. Propensity-matched comparison of laparoscopic and open radical cystectomy for female patients with bladder cancer [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(4): 698-705. |
| [15] | Chen LIANG,Wei-yu ZHANG,Hao HU,Qi WANG,Zhi-wei FANG,Ke-xin XU. Comparison of effectiveness and complications between two different methods of augmentation cystoplasty [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(2): 293-297. |
|
||