Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (4): 637-641. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.04.007
Previous Articles Next Articles
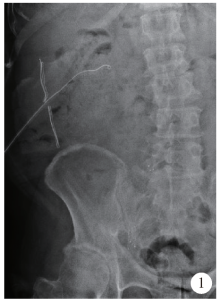
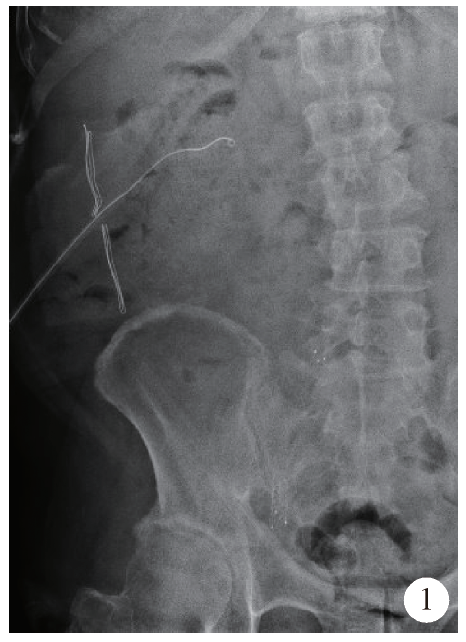
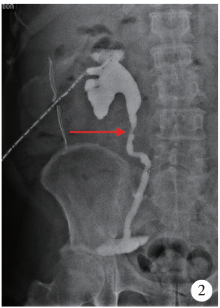
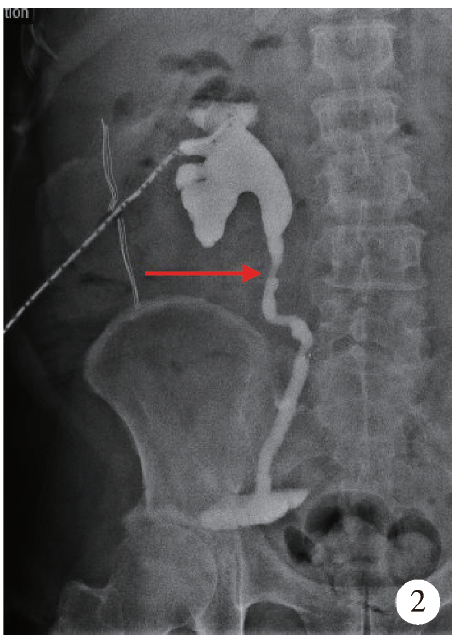
Initial clinical experience and follow-up outcomes of treatment for ureteroileal anastomotic stricture with Allium coated metal ureteral stent
Wen-min DONG1,2,Ming-rui WANG1,Hao HU1,△( ),Qi WANG1,Ke-xin XU1,Tao XU1
),Qi WANG1,Ke-xin XU1,Tao XU1
- 1. Department of Urology, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
2. Department of Urology, People’s Hospital of Daxing District, Beijing 102600, China
CLC Number:
- R693.2
| [1] |
Anderson CB, Morgan TM, Kappa S, et al. Ureteroenteric anastomotic strictures after radical cystectomy-does operative approach matter?[J]. J Urol, 2013,189(2):541-547.
doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2012.09.034 pmid: 23260561 |
| [2] | Richards KA, Cohn JA, Large MC, et al. The effect of length of ureteral resection on benign ureterointestinal stricture rate in ileal conduit or ileal neobladder urinary diversion following radical cystectomy[J]. Urol Oncol, 2015,33(2):61-65. |
| [3] |
Lobo N, Dupre S, Sahai A, et al. Getting out of a tight spot: an overview of ureteroenteric anastomotic strictures[J]. Nat Rev Urol, 2016,13(8):447-455.
doi: 10.1038/nrurol.2016.104 pmid: 27349367 |
| [4] | 林磊. 球囊扩张加双重双J管置入对良性输尿管狭窄的治疗效果观察[J]. 中国卫生标准管理, 2015,6(29):44-45. |
| [5] | 杨存让, 尹向东. 腔内三重双J管引流在输尿管狭窄治疗中的价值探讨[J]. 临床医药实践, 2008(S3):735-736. |
| [6] | 尹向军, 曹炳航, 崔文芳, 等. 双J管支架内置入应用于输尿管狭窄治疗效果分析[J]. 临床合理用药杂志, 2014,7(10):109-110. |
| [7] |
Lange D, Bidnur S, Hoag N, et al. Ureteral stent-associated complications: Where we are and where we are going[J]. Nat Rev Urol, 2015,12(1):17-25.
pmid: 25534997 |
| [8] | Bahouth Z, Moskovitz B, Halachmi S, et al. Allium stents: A novel solution for the management of upper and lower urinary tract strictures[J]. Rambam Maimonides Med J, 2017,8(4):e0043. |
| [9] | 那彦群, 叶章群, 孙颖浩. 中国泌尿外科疾病诊断治疗指南[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2014. |
| [10] | 易宏刚. 良性输尿管狭窄的诊治现状分析[D]. 重庆: 重庆医科大学, 2018. |
| [11] |
Baten E, Akand M, Floyd MJ, et al. Evaluation of conservative approach in the management of ureteroenteric strictures following radical cystectomy with Bricker ileal conduit: a single-center experience[J]. Scand J Urol, 2016,50(6):439-444.
pmid: 27686879 |
| [12] | 李涛, 肖亚军, 邢毅飞, 等. 膀胱全切原位回肠新膀胱术后输尿管肠吻合口良性狭窄的处理[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2013,28(11):850-852. |
| [13] |
Hu W, Su B, Xiao B, et al. Simultaneous antegrade and retrograde endoscopic treatment of non-malignant ureterointestinal anastomotic strictures following urinary diversion[J]. BMC Urol, 2017,17(1):61.
pmid: 28789635 |
| [14] | Shapiro MJ, Banner MP, Amendola MA, et al. Balloon catheter dilation of ureteroenteric strictures: long-term results[J]. Radio-logy, 1988,168(2):385-387. |
| [15] |
DiMarco DS, LeRoy AJ, Thieling S, et al. Long-term results of treatment for ureteroenteric strictures[J]. Urology, 2001,58(6):909-913.
doi: 10.1016/s0090-4295(01)01420-0 pmid: 11744456 |
| [16] |
Singal RK, Denstedt JD, Razvi HA, et al. Holmium YAG laser endoureterotomy for treatment of ureteral stricture[J]. Urology, 1997,50(6):875-880.
pmid: 9426717 |
| [17] |
Leonardo C, Salvitti M, Franco G, et al. Allium stent for treatment of ureteral stenosis[J]. Minerva Urol Nefrol, 2013,65(4):277-283.
pmid: 24091480 |
| [18] |
Bahouth Z, Meyer G, Halachmi S, et al. Multicenter experience with Allium ureteral stent for the treatment of ureteral stricture and fistula[J]. Harefuah, 2015,154(12):753-756.
pmid: 26897774 |
| [19] | Guandalino M, Droupy S, Ruffion A, et al. Stent Allium urétéral dans la prise en charge des sténoses urétérales. Étude rétrospective multicentrique[J]. Progrès en Urologie, 2017,27(1):26-32. |
| [20] | Moskovitz B, Halachmi S, Nativ O. A new self-expanding, large-caliber ureteral stent: Results of a multicenter experience[J]. J Endourol, 2012,26(11):1523-1527. |
| [1] | Mingrui WANG, Qi WANG, Hao HU, Jinhui LAI, Xinwei TANG, Chunyan WAN, Kexin XU, Tao XU. Efficacy of coated metal ureteral stent in the treatment of pelvic lipomatosis induced hydronephrosis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 919-922. |
| [2] | Mingrui WANG,Jun LIU,Liulin XIONG,Luping YU,Hao HU,Kexin XU,Tao XU. Efficacy and safety of mini-track, mini-nephroscopy and mini-ultrasonic probe percutaneous nephrolithotomy for the treatment of 1.5-2.5 cm kidney stones [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 605-609. |
| [3] | Yicen YING,Yicong DU,Zhihua LI,Yiming ZHANG,Xinfei LI,Bing WANG,Peng ZHANG,Hongjian ZHU,Liqun ZHOU,Kunlin YANG,Xuesong LI. Robot-assisted laparoscopic ureteroplasty with buccal mucosa graft for complex ureteral stricture [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 640-645. |
| [4] | Wenbo YANG,Lei YU,Weiyu ZHANG,Tao XU,Qiang WANG. Effect and safety of self-draining ureteral stent with thread in kidney transplant reci-pients [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 656-660. |
| [5] | Ying ZHOU,Ning ZHAO,Hongyuan HUANG,Qingxiang LI,Chuanbin GUO,Yuxing GUO. Application of double-layer soft tissue suture closure technique in the surgical treatment of patients with mandible medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw of early and medium stages [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 51-56. |
| [6] | Xinyu XU,Ling WU,Fengqi SONG,Zili LI,Yi ZHANG,Xiaojing LIU. Mandibular condyle localization in orthognathic surgery based on mandibular movement trajectory and its preliminary accuracy verification [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 57-65. |
| [7] | Andong CAI,Xiaoxia WANG,Wenjuan ZHOU,Zhonghao LIU. Comparison of the virtual surgical planning position of maxilla and condyle with the postoperative real position in patients with mandibular protrusion [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 74-80. |
| [8] | Jin-hui LAI,Qi WANG,Jia-xiang JI,Ming-rui WANG,Xin-wei TANG,Ke-xin XU,Tao XU,Hao HU. Effects of delayed ureteral stents removal during the COVID-19 pandemic on the quality of life and psychological status of postoperative patients with urinary calculi [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 857-864. |
| [9] | Jian-xun MA,You-chen XIA,Bi LI,Hong-mei ZHAO,Yu-tao LEI,Xi BU. Choice of immediate breast reconstructive methods after modified radical mastectomy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 612-618. |
| [10] | Bin CHEN,Chao WU,Bin LIU,Tao YU,Zhen-yu WANG. Prognosis of patients with spinal intramedullary cavernous hemangioma by different treatments [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 652-657. |
| [11] | Su-huan XU,Bei-bei WANG,Qiu-ying PANG,Li-jun ZHONG,Yan-ming DING,Yan-bo HUANG,Xin-yan CHE. Effect of equal temperature bladder irrigation in patients with transurethral resection of prostate: A meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 676-683. |
| [12] | Wen ZHANG,Xiao-jing LIU,Zi-li LI,Yi ZHANG. Effect of alar base cinch suture based on anatomic landmarks on the morphology of nasolabial region in patients after orthognathic surgery [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 736-742. |
| [13] | Yun-peng CUI,Xue-dong SHI,Jia LIU,Chuan MI,Bing WANG,Yuan-xing PAN,Yun-fei LIN. Percutaneous pedicle screw fixation combined expandable tubular retractor in the treatment of spinal metastases [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(3): 530-536. |
| [14] | Jin-tao HAN,Yu-xiang ZHANG,Zi-chang JIA,Chu-han JIANG,Lian LIU,Jing-yuan LUAN,Fei LIANG,Yan-qing ZHAO. Clinical application of Neuroform Atlas stent-assisted coiling in the treatment of unruptured wide-neck intracranial aneurysms [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(1): 139-143. |
| [15] | Hui LI,Yang-xu GAO,Shu-lei WANG,Hong-xin YAO. Surgical complications of totally implantable venous access port in children with malignant tumors [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1167-1171. |
|
||