Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (4): 632-636. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.04.006
Previous Articles Next Articles
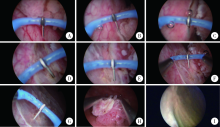
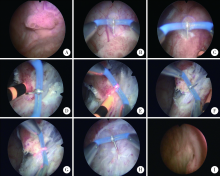
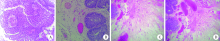
Clinical application of the needle electrode in transurethral plasmakinetic resection of bladder tumor around ureteral orifice: A report of 16 cases
Tian WANG,Xin HONG,Xiao-feng WANG( )
)
- Department of Urology, Peking University International Hospital, Beijing 102206, China
CLC Number:
- R737.14
| [1] | van den Bosch S, Alfred Witjes J. Long-term cancer-specific survival in patients with high-risk, non-muscle-invasive bladder can-cer and tumour progression: A systematic review[J]. Ero Urol, 2011,60(3):493-500. |
| [2] | 那彦群, 叶章群, 孙颖浩, 等. 2014版中国泌尿外科疾病诊断治疗指南[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2014: 36-39. |
| [3] |
Sharma D, Singh VP, Agarwal N, et al. Obturator nerve block in transurethral resection of bladder tumor: A comparative study by two techniques[J]. Anesth Essays Res, 2017,11(1):101-104.
pmid: 28298765 |
| [4] |
Engilbertsson H, Aaltonen KE, Björnsson S, et al. Transurethral bladder tumor resection can cause seeding of cancer cells into the bloodstream[J]. J Urol, 2015,193(1):53-57.
doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2014.06.083 |
| [5] |
Brauers A, Buettner R, Jakse G. Second resection and prognosis of primary high risk superficial bladder cancer: Is cystectomy often too early?[J]. J Urol, 2001,165(3):808-810.
pmid: 11176474 |
| [6] |
He D, Fan J, Wu K, et al. Novel green-light KTP laser en bloc encleation for nonmuscle-invasive bladder cancer: Technique and initial clinical experience[J]. J Endourol, 2014,28(8):975-979.
doi: 10.1089/end.2013.0740 pmid: 24735433 |
| [7] | 张翼飞, 梁朝朝, 施浩强, 等. 整块剜除术治疗非肌层浸润性膀胱肿瘤[J]. 中华腔镜泌尿外科杂志: 电子版, 2016,10(6):11-14. |
| [8] | Yang H, Shi L, Chen G, et a1. Transurethral needle electrode resection of bladder tumor: a technique obtaining en bloc resection and obviating obturator nerve stimulation[J]. World J Nephrol Urol, 2015,4(3):232-236. |
| [9] | 梅骅, 陈凌武, 高新, 等. 泌尿外科手术学[M]. 第3版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2008: 201-205. |
| [10] |
Chou E, Lin A, Chen K, et al. Superficial transitional cell carcinoma of the ureteral orifice: Higher risk of developing subsequent upper urinary tract tumors[J]. Int J Urol, 2006,13(6):682-685.
doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2042.2006.01385.x pmid: 16834642 |
| [1] | Shuang REN, Huijuan SHI, Zixuan LIANG, Si ZHANG, Xiaoqing HU, Hongshi HUANG, Yingfang AO. Biomechanics during cutting movement in individuals after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 868-873. |
| [2] | Mingrui WANG, Qi WANG, Hao HU, Jinhui LAI, Xinwei TANG, Chunyan WAN, Kexin XU, Tao XU. Efficacy of coated metal ureteral stent in the treatment of pelvic lipomatosis induced hydronephrosis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 919-922. |
| [3] | Junyong OU,Kunming NI,Lulin MA,Guoliang WANG,Ye YAN,Bin YANG,Gengwu LI,Haodong SONG,Min LU,Jianfei YE,Shudong ZHANG. Prognostic factors of patients with muscle invasive bladder cancer with intermediate-to-high risk prostate cancer [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 582-588. |
| [4] | Mingrui WANG,Jun LIU,Liulin XIONG,Luping YU,Hao HU,Kexin XU,Tao XU. Efficacy and safety of mini-track, mini-nephroscopy and mini-ultrasonic probe percutaneous nephrolithotomy for the treatment of 1.5-2.5 cm kidney stones [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 605-609. |
| [5] | Yicen YING,Yicong DU,Zhihua LI,Yiming ZHANG,Xinfei LI,Bing WANG,Peng ZHANG,Hongjian ZHU,Liqun ZHOU,Kunlin YANG,Xuesong LI. Robot-assisted laparoscopic ureteroplasty with buccal mucosa graft for complex ureteral stricture [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 640-645. |
| [6] | Wenbo YANG,Lei YU,Weiyu ZHANG,Tao XU,Qiang WANG. Effect and safety of self-draining ureteral stent with thread in kidney transplant reci-pients [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 656-660. |
| [7] | Kewei CHEN,Shaohui DENG,Zhuo LIU,Hongxian ZHANG,Lulin MA,Shudong ZHANG. Discussion on the surgical timing of rupture and hemorrhage of renal angiomyolipoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 326-331. |
| [8] | Xinyu XU,Ling WU,Fengqi SONG,Zili LI,Yi ZHANG,Xiaojing LIU. Mandibular condyle localization in orthognathic surgery based on mandibular movement trajectory and its preliminary accuracy verification [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 57-65. |
| [9] | Andong CAI,Xiaoxia WANG,Wenjuan ZHOU,Zhonghao LIU. Comparison of the virtual surgical planning position of maxilla and condyle with the postoperative real position in patients with mandibular protrusion [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 74-80. |
| [10] | Hui-li LIU,Yan-han LV,Xiao-xiao WANG,Min LI. Factors influencing the chronic post-surgical pain after laparoscopic surgery for elderly patients with urinary tract tumors [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 851-856. |
| [11] | Jin-hui LAI,Qi WANG,Jia-xiang JI,Ming-rui WANG,Xin-wei TANG,Ke-xin XU,Tao XU,Hao HU. Effects of delayed ureteral stents removal during the COVID-19 pandemic on the quality of life and psychological status of postoperative patients with urinary calculi [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 857-864. |
| [12] | Cai-peng QIN,Fei WANG,Yi-qing DU,Xiao-wei ZHANG,Qing LI,Shi-jun LIU,Tao XU. Diagnosis and treatment of four cases of asymptomatic and non-hydrous ureteral calculi [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 939-942. |
| [13] | Jian-xun MA,You-chen XIA,Bi LI,Hong-mei ZHAO,Yu-tao LEI,Xi BU. Choice of immediate breast reconstructive methods after modified radical mastectomy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 612-618. |
| [14] | Su-huan XU,Bei-bei WANG,Qiu-ying PANG,Li-jun ZHONG,Yan-ming DING,Yan-bo HUANG,Xin-yan CHE. Effect of equal temperature bladder irrigation in patients with transurethral resection of prostate: A meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 676-683. |
| [15] | Wen ZHANG,Xiao-jing LIU,Zi-li LI,Yi ZHANG. Effect of alar base cinch suture based on anatomic landmarks on the morphology of nasolabial region in patients after orthognathic surgery [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 736-742. |
|
||