Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (4): 582-588. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.04.006
Previous Articles Next Articles
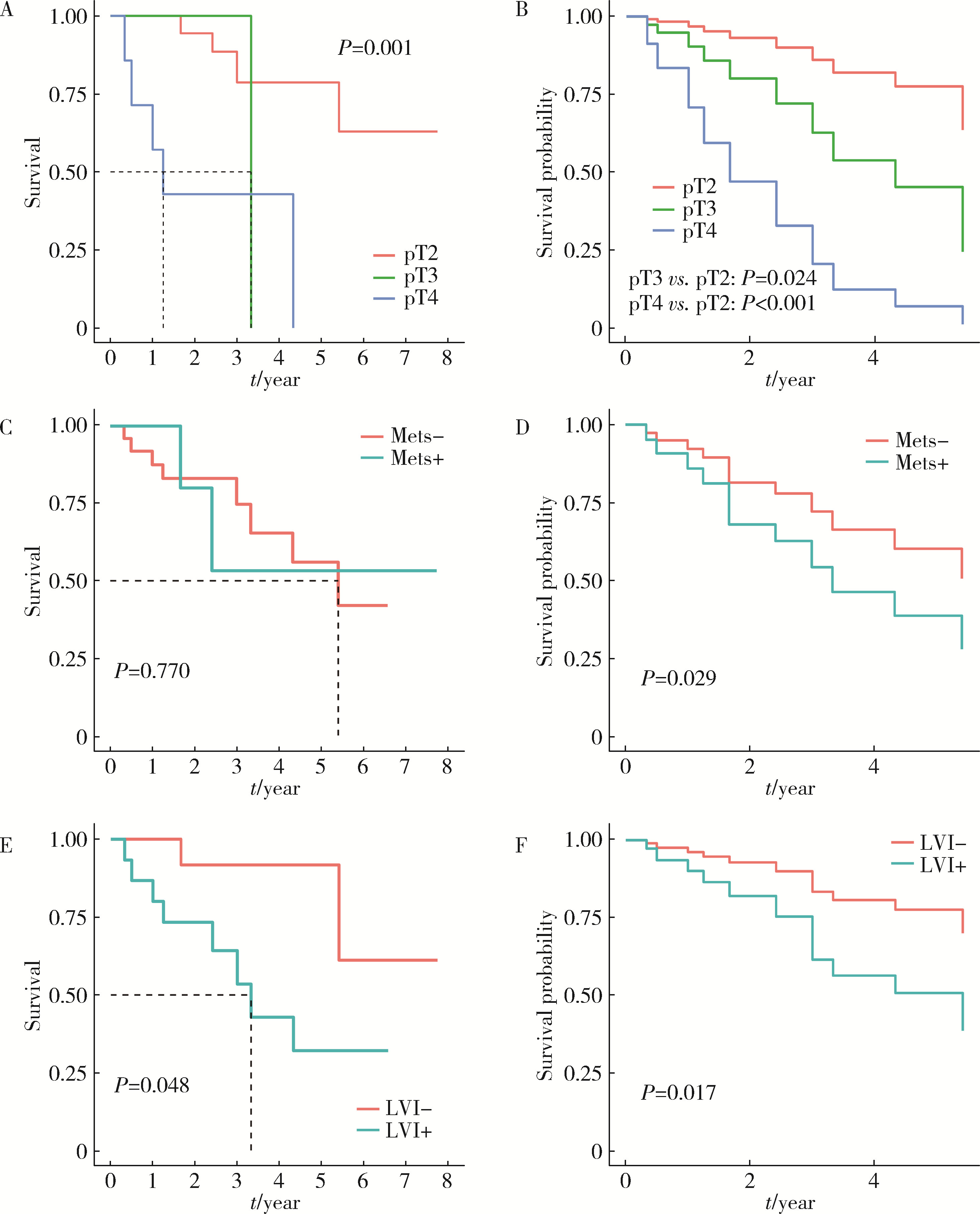
Prognostic factors of patients with muscle invasive bladder cancer with intermediate-to-high risk prostate cancer
Junyong OU1,Kunming NI2,Lulin MA1,Guoliang WANG1,Ye YAN1,Bin YANG1,Gengwu LI1,Haodong SONG1,Min LU2,Jianfei YE1,*( ),Shudong ZHANG1,*(
),Shudong ZHANG1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Urology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
2. Department of Pathology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
CLC Number:
- R737.1
| 1 |
Alfred Witjes J , Max Bruins H , Carrión A , et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on muscle-invasive and metastatic bladder cancer: Summary of the 2023 guidelines[J]. Eur Urol, 2024, 85 (1): 17- 31.
doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2023.08.016 |
| 2 |
Siegel RL , Giaquinto AN , Jemal A . Cancer statistics, 2024[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2024, 74 (1): 12- 49.
doi: 10.3322/caac.21820 |
| 3 |
Dyrskjøt L , Hansel DE , Efstathiou JA , et al. Bladder cancer[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2023, 9 (1): 58.
doi: 10.1038/s41572-023-00468-9 |
| 4 |
Compérat E , Amin MB , Cathomas R , et al. Current best practice for bladder cancer: A narrative review of diagnostics and treatments[J]. Lancet, 2022, 400 (10364): 1712- 1721.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01188-6 |
| 5 |
Lopez-Beltran A , Cheng L , Montorsi F , et al. Concomitant bladder cancer and prostate cancer: Challenges and controversies[J]. Nat Rev Urol, 2017, 14 (10): 620- 629.
doi: 10.1038/nrurol.2017.124 |
| 6 |
Jing Y , Zhang R , Ma P , et al. Prevalence and clonality of synchronous primary carcinomas in the bladder and prostate[J]. J Pathol, 2018, 244 (1): 5- 10.
doi: 10.1002/path.4997 |
| 7 |
Aljabery F , Liedberg F , Häggström C , et al. Treatment and prognosis of patients with urinary bladder cancer with other primary cancers: A nationwide population-based study in the bladder can-cer data base Sweden (BladderBaSe)[J]. BJU Int, 2020, 126 (5): 625- 632.
doi: 10.1111/bju.15198 |
| 8 | Claps F , Pavan N , Umari P , et al. Incidence, predictive factors and survival outcomes of incidental prostate cancer in patients who underwent radical cystectomy for bladder cancer[J]. Minerva Urol Nephrol, 2021, 73 (3): 349- 356. |
| 9 |
Malte R , Kluth LA , Kaushik D , et al. Frequency and prognostic significance of incidental prostate cancer at radical cystectomy: Results from an international retrospective study[J]. Eur J Surg Oncol, 2017, 43 (11): 2193- 2199.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2017.08.013 |
| 10 |
Fahmy O , Khairul-Asri MG , Schubert T , et al. Clinicopathological features and prognostic value of incidental prostatic adenocarcinoma in radical cystoprostatectomy specimens: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 13 140 patients[J]. J Urol, 2017, 197 (2): 385- 390.
doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2016.08.088 |
| 11 |
Kaelberer JB , O'donnell MA , Mitchell DL , et al. Incidental prostate cancer diagnosed at radical cystoprostatectomy for bladder cancer: Disease-specific outcomes and survival[J]. Prostate Int, 2016, 4 (3): 107- 112.
doi: 10.1016/j.prnil.2016.06.002 |
| 12 |
Wu S , Lin SX , Lu M , et al. Assessment of 5-year overall survival in bladder cancer patients with incidental prostate cancer identified at radical cystoprostatectomy[J]. Int Urol Nephrol, 2019, 51 (9): 1527- 1535.
doi: 10.1007/s11255-019-02181-7 |
| 13 |
Mazzucchelli R , Barbisan F , Scarpelli M , et al. Is incidentally detected prostate cancer in patients undergoing radical cystoprostatectomy clinically significant?[J]. Am J Clin Pathol, 2009, 131 (2): 279- 283.
doi: 10.1309/AJCP4OCYZBAN9TJU |
| 14 |
Moschini M , Shariat SF , Freschi M , et al. Impact of prostate involvement on outcomes in patients treated with radical cystoprostatectomy for bladder cancer[J]. Urol Int, 2017, 98 (3): 290- 297.
doi: 10.1159/000454736 |
| [1] | Zhicun LI, Tianyu WU, Lei LIANG, Yu FAN, Yisen MENG, Qian ZHANG. Risk factors analysis and nomogram model construction of postoperative pathological upgrade of prostate cancer patients with single core positive biopsy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 896-901. |
| [2] | Yuxuan TIAN,Mingjian RUAN,Yi LIU,Derun LI,Jingyun WU,Qi SHEN,Yu FAN,Jie JIN. Predictive effect of the dual-parametric MRI modified maximum diameter of the lesions with PI-RADS 4 and 5 on the clinically significant prostate cancer [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 567-574. |
| [3] | Kaifeng YAO,Mingjian RUAN,Derun LI,Yuxuan TIAN,Yuke CHEN,Yu FAN,Yi LIU. Diagnostic efficacy of targeted biopsy combined with regional systematic biopsy in prostate cancer in patients with PI-RADS 4-5 [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 575-581. |
| [4] | Shuai LIU,Lei LIU,Zhuo LIU,Fan ZHANG,Lulin MA,Xiaojun TIAN,Xiaofei HOU,Guoliang WANG,Lei ZHAO,Shudong ZHANG. Clinical treatment and prognosis of adrenocortical carcinoma with venous tumor thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 624-630. |
| [5] | Le YU,Shaohui DENG,Fan ZHANG,Ye YAN,Jianfei YE,Shudong ZHANG. Clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of multilocular cystic renal neoplasm of low malignant potential [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 661-666. |
| [6] | Zezhen ZHOU,Shaohui DENG,Ye YAN,Fan ZHANG,Yichang HAO,Liyuan GE,Hongxian ZHANG,Guoliang WANG,Shudong ZHANG. Predicting the 3-year tumor-specific survival in patients with T3a non-metastatic renal cell carcinoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 673-679. |
| [7] | Yangyi FANG,Qiang LI,Zhigao HUANG,Min LU,Kai HONG,Shudong ZHANG. Well-differentiated papillary mesothelial tumour of the tunica vaginalis: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 741-744. |
| [8] | Yuanyuan ZENG,Yun XIE,Daonan CHEN,Ruilan WANG. Related factors of euthyroid sick syndrome in patients with sepsis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 526-532. |
| [9] | Jian-bin LI,Meng-na LYU,Qiang CHI,Yi-lin PENG,Peng-cheng LIU,Rui WU. Early prediction of severe COVID-19 in patients with Sjögren’s syndrome [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1007-1012. |
| [10] | Huan-rui LIU,Xiang PENG,Sen-lin LI,Xin GOU. Risk modeling based on HER-2 related genes for bladder cancer survival prognosis assessment [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 793-801. |
| [11] | Zi-xuan XUE,Shi-ying TANG,Min QIU,Cheng LIU,Xiao-jun TIAN,Min LU,Jing-han DONG,Lu-lin MA,Shu-dong ZHANG. Clinicopathologic features and prognosis of young renal tumors with tumor thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 802-811. |
| [12] | Yi LIU,Chang-wei YUAN,Jing-yun WU,Qi SHEN,Jiang-xi XIAO,Zheng ZHAO,Xiao-ying WANG,Xue-song LI,Zhi-song HE,Li-qun ZHOU. Diagnostic efficacy of prostate cancer using targeted biopsy with 6-core systematic biopsy for patients with PI-RADS 5 [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 812-817. |
| [13] | Chang-wei YUAN,De-run LI,Zhi-hua LI,Yi LIU,Gang-zhi SHAN,Xue-song LI,Li-qun ZHOU. Application of dynamic contrast enhanced status in multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging for prostatic cancer with PI-RADS 4 lesion [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 838-842. |
| [14] | Han LU,Jian-yun ZHANG,Rong YANG,Le XU,Qing-xiang LI,Yu-xing GUO,Chuan-bin GUO. Clinical factors affecting the prognosis of lower gingival squamous cell carcinoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 702-707. |
| [15] | Yun-fei SHI,Hao-jie WANG,Wei-ping LIU,Lan MI,Meng-ping LONG,Yan-fei LIU,Yu-mei LAI,Li-xin ZHOU,Xin-ting DIAO,Xiang-hong LI. Analysis of clinicopathological and molecular abnormalities of angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(3): 521-529. |
|
||