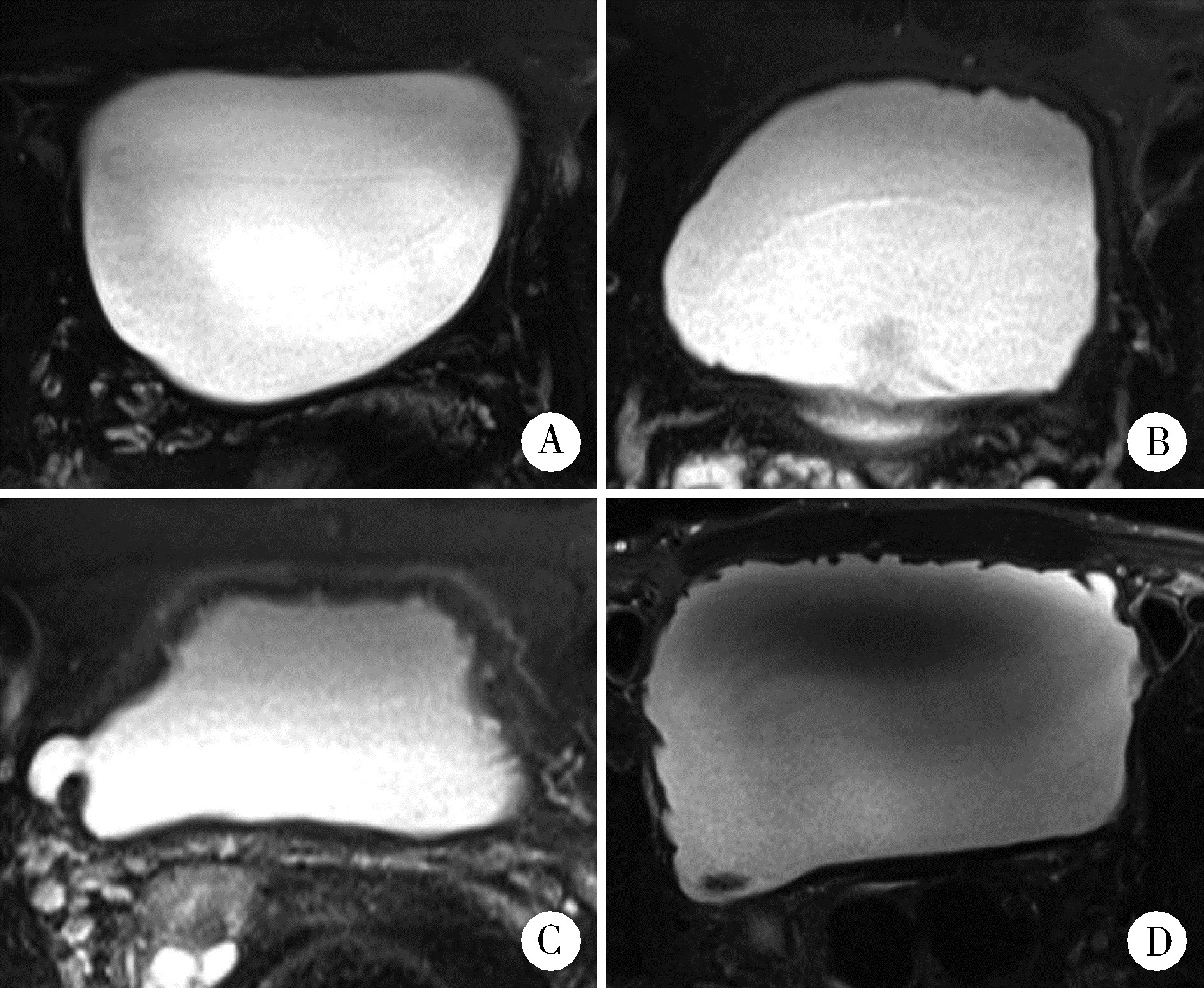
Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (4): 589-593. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.04.007
Previous Articles Next Articles
Analysis of risk factors for long-term overactive bladder after radical prostatectomy
Ye YAN,Xiaolong LI,Haizhui XIA,Xuehua ZHU,Yuting ZHANG,Fan ZHANG,Ke LIU,Cheng LIU*( ),Lulin MA*(
),Lulin MA*( )
)
- Department of Urology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
CLC Number:
- R737.25
| 1 |
Abrams P , Cardozo L , Fall M , et al. The standardisation of terminology of lower urinary tract function: Report from the standardisation sub-committee of the international continence society[J]. Neurourol Urodyn, 2002, 21 (2): 167- 178.
doi: 10.1002/nau.10052 |
| 2 |
Porena M , Mearini E , Mearini L , et al. Voiding dysfunction after radical retropubic prostatectomy: More than external urethral sphincter deficiency[J]. Eur Urol, 2007, 52 (1): 38- 45.
doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2007.03.051 |
| 3 |
Matsukawa Y , Yoshino Y , Ishida S , et al. De novo overactive bladder after robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy[J]. Neurourol Urodyn, 2018, 37 (6): 2008- 2014.
doi: 10.1002/nau.23556 |
| 4 |
Hosier GW , Tennankore KK , Himmelman JG , et al. Overactive bladder and storage lower urinary tract symptoms following radical prostatectomy[J]. Urology, 2016, 94, 193- 197.
doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2016.05.007 |
| 5 |
Thiruchelvam N , Cruz F , Kirby M , et al. A review of detrusor overactivity and the overactive bladder after radical prostate cancer treatment[J]. BJU Int, 2015, 116 (6): 853- 861.
doi: 10.1111/bju.13078 |
| 6 |
Ventimiglia B , Sigona M , Di Dio A , et al. Urinary incontinence and neuropathy after radical prostatectomy: Diagnosis and treatment[J]. Urologia, 2015, 82 (1): 42- 45.
doi: 10.5301/uro.5000064 |
| 7 | Chung DE , Dillon B , Kurta J , et al. Detrusor underactivity is prevalent after radical prostatectomy: A urodynamic study including risk factors[J]. Can Urol Assoc J, 2013, 7 (1/2): E33- E37. |
| 8 |
Giannantoni A , Mearini E , Zucchi A , et al. Bladder and urethral sphincter function after radical retropubic prostatectomy: A prospective long-term study[J]. Eur Urol, 2008, 54 (3): 657- 664.
doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2007.10.054 |
| 9 |
Leach GE , Trockman B , Wong A , et al. Post-prostatectomy incontinence: Urodynamic findings and treatment outcomes[J]. J Urol, 1996, 155 (4): 1256- 1259.
doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(01)66235-9 |
| 10 |
Haga N , Ogawa S , Yabe M , et al. Association between postoperative pelvic anatomic features on magnetic resonance imaging and lower tract urinary symptoms after radical prostatectomy[J]. Urology, 2014, 84 (3): 642- 649.
doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2014.04.044 |
| 11 |
Dubbelman Y , Groen J , Wildhagen M , et al. Quantification of changes in detrusor function and pressure-flow parameters after radical prostatectomy: Relation to postoperative continence status and the impact of intensity of pelvic floor muscle exercises[J]. Neurourol Urodyn, 2012, 31 (5): 637- 641.
doi: 10.1002/nau.21199 |
| 12 |
Groutz A , Blaivas JG , Chaikin DC , et al. The pathophysiology of post-radical prostatectomy incontinence: A clinical and video urodynamic study[J]. J Urol, 2000, 163 (6): 1767- 1770.
doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(05)67538-6 |
| [1] | Zhicun LI, Tianyu WU, Lei LIANG, Yu FAN, Yisen MENG, Qian ZHANG. Risk factors analysis and nomogram model construction of postoperative pathological upgrade of prostate cancer patients with single core positive biopsy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 896-901. |
| [2] | Shuhui YU,Jianing HAN,Lijun ZHONG,Congyu CHEN,Yunxiang XIAO,Yanbo HUANG,Yang YANG,Xinyan CHE. Predictive value of preoperative pelvic floor electrophysiological parameters on early urinary incontinence following radical prostatectomy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 594-599. |
| [3] | Yan CHEN,Kuangmeng LI,Kai HONG,Shudong ZHANG,Jianxing CHENG,Zhongjie ZHENG,Wenhao TANG,Lianming ZHAO,Haitao ZHANG,Hui JIANG,Haocheng LIN. Retrospective study on the impact of penile corpus cavernosum injection test on penile vascular function [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 680-686. |
| [4] | Bo PANG,Tongjun GUO,Xi CHEN,Huaqi GUO,Jiazhang SHI,Juan CHEN,Xinmei WANG,Yaoyan LI,Anqi SHAN,Hengyi YU,Jing HUANG,Naijun TANG,Yan WANG,Xinbiao GUO,Guoxing LI,Shaowei WU. Personal nitrogen oxides exposure levels and related influencing factors in adults over 35 years old in Tianjin and Shanghai [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 700-707. |
| [5] | Jing HE,Zhongze FANG,Ying YANG,Jing LIU,Wenyao MA,Yong HUO,Wei GAO,Yangfeng WU,Gaoqiang XIE. Relationship between lipid metabolism molecules in plasma and carotid atheroscle-rotic plaques, traditional cardiovascular risk factors, and dietary factors [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 722-728. |
| [6] | Shan CAI,Yihang ZHANG,Ziyue CHEN,Yunfe LIU,Jiajia DANG,Di SHI,Jiaxin LI,Tianyu HUANG,Jun MA,Yi SONG. Status and pathways of factors influencing physical activity time among elementary and junior high school students in Beijing [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 403-410. |
| [7] | Zuhong ZHANG,Tianjiao CHEN,Jun MA. Associations between puberty timing and cardiovascular metabolic risk factors among primary and secondary students [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 418-423. |
| [8] | Yuting LIN,Huali WANG,Yu TIAN,Litong GONG,Chun CHANG. Factors influencing cognitive function among the older adults in Beijing [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 456-461. |
| [9] | Jinrong ZHU,Yana ZHAO,Wei HUANG,Weiwei ZHAO,Yue WANG,Song WANG,Chunyan SU. Clinical characteristics of COVID-19 infection in patients undergoing hemodialysis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 267-272. |
| [10] | Zhanhong LAI,Jiachen LI,Zelin YUN,Yonggang ZHANG,Hao ZHANG,Xiaoyan XING,Miao SHAO,Yuebo JIN,Naidi WANG,Yimin LI,Yuhui LI,Zhanguo LI. A unicenter real-world study of the correlation factors for complete clinical response in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 284-292. |
| [11] | Xiaoqian SI,Xiujuan ZHAO,Fengxue ZHU,Tianbing WANG. Risk factors for acute respiratory distress syndrome in patients with traumatic hemorrhagic shock [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 307-312. |
| [12] | Junqi SU,Xiaoying WANG,Zhiqiang SUN. Establishment and verification of a prognostic nomogram for survival of tongue squamous cell carcinoma patients who underwent cervical dissection [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 120-130. |
| [13] | Yangyang LI,Lin HOU,Zijun MA,Shanyamei HUANG,Jie LIU,Chaomei ZENG,Jiong QIN. Association of pregnancy factors with cow's milk protein allergy in infants [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 144-149. |
| [14] | Xiaoqiang LIU,Yin ZHOU. Risk factors of perioperative hypertension in dental implant surgeries with bone augmentation [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 93-98. |
| [15] | Liang LUO,Yun LI,Hong-yan WANG,Xiao-hong XIANG,Jing ZHAO,Feng SUN,Xiao-ying ZHANG,Ru-lin JIA,Chun LI. Anti-endothelial cell antibodies in predicting early miscarriage [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1039-1044. |
|
||