Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (5): 989-995. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.05.026
Previous Articles Next Articles
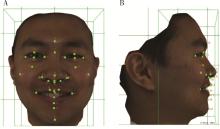
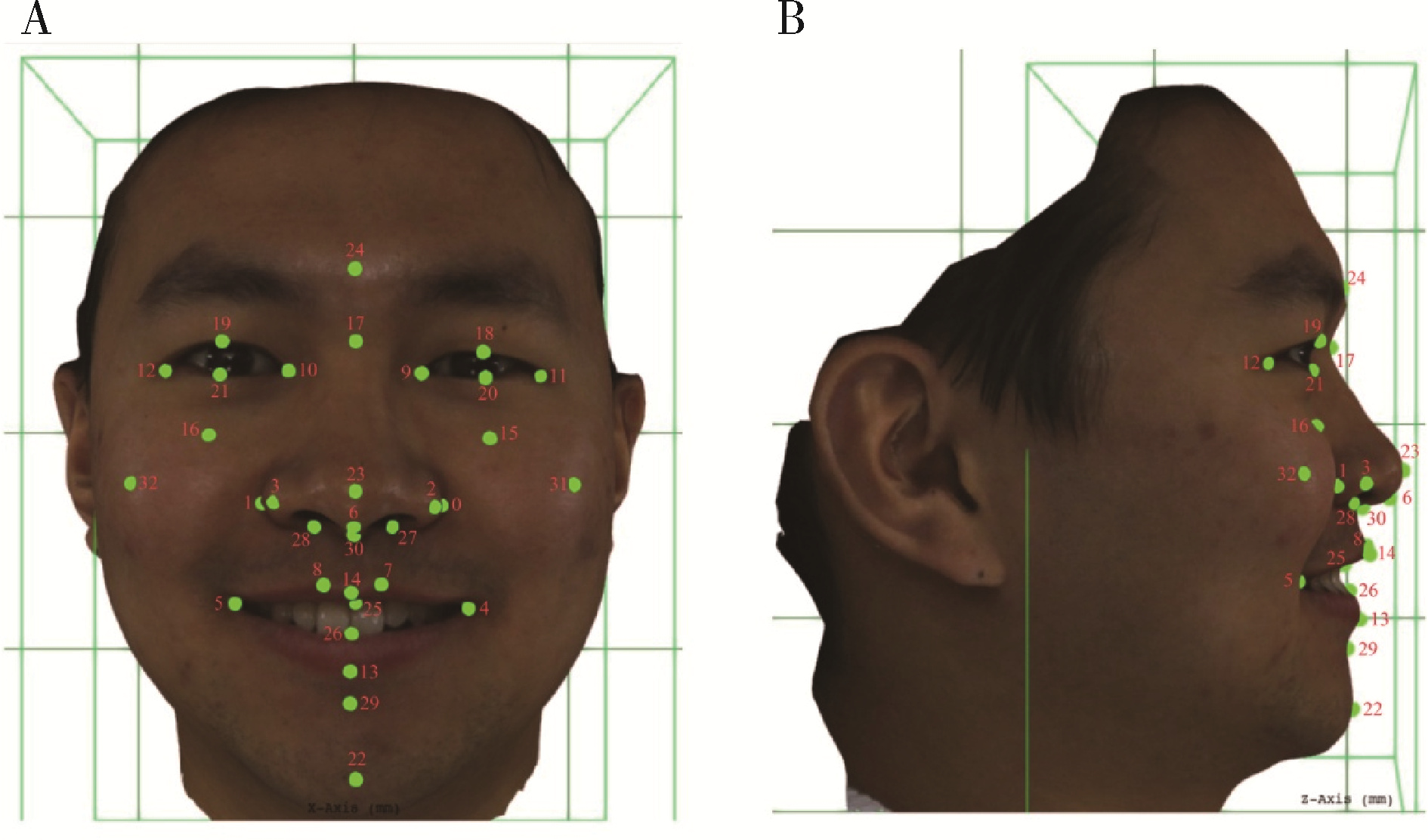
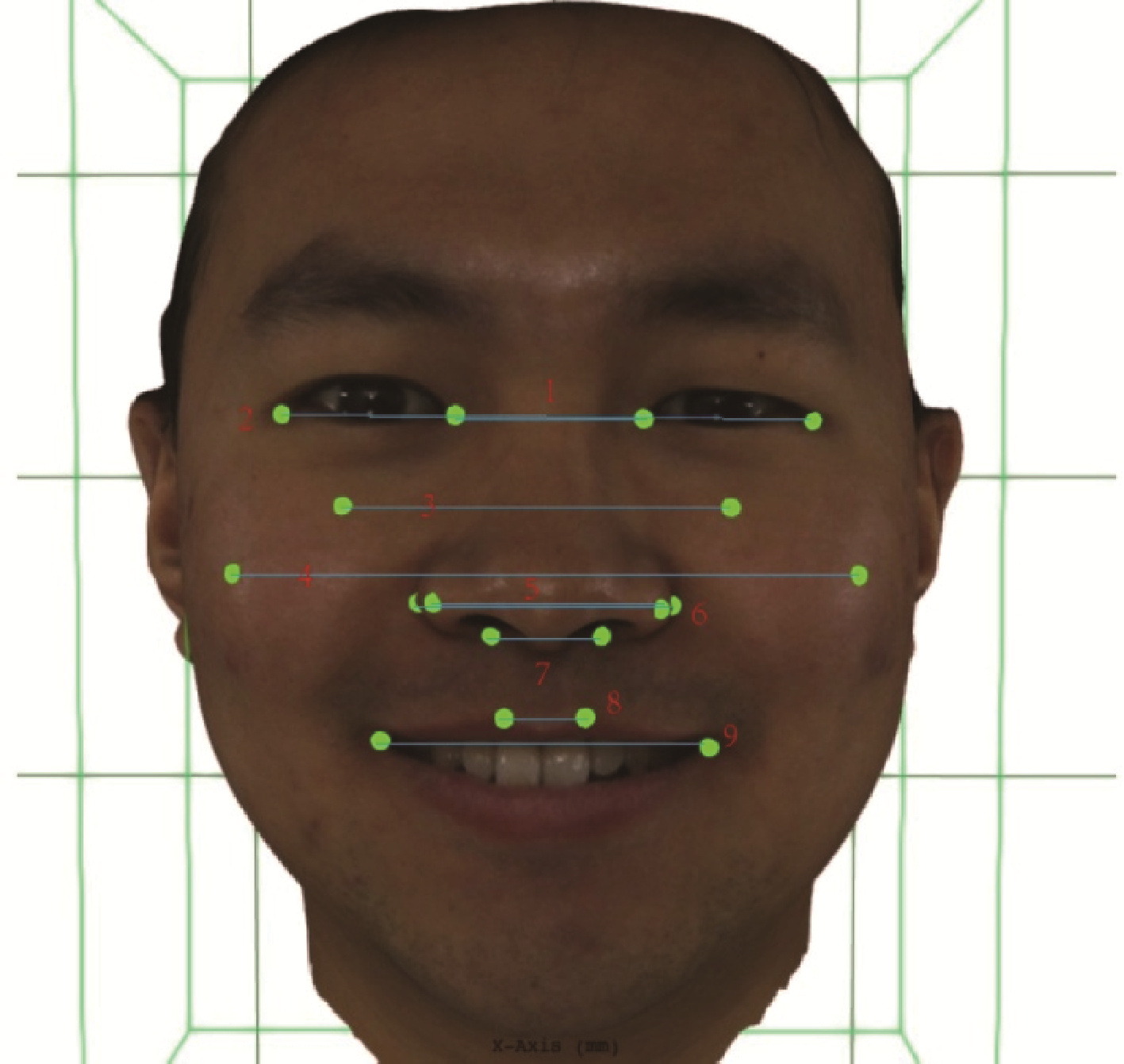
Three-dimensional morphological analysis of posed smile
Yujia XIAO, Bochun MAO, Yanheng ZHOU*( )
)
- Department of Orthodontics, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology & NHC Research Center of Engineering and Technology for Computerized Dentistry & NMPA Key Laboratory for Dental Materials, Beijing 100081, China
CLC Number:
- R782
| 1 |
doi: 10.1111/ocr.1998.1.1.2 |
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2017.04.002 |
| 4 |
doi: 10.1186/s12903-018-0673-5 |
| 5 |
doi: 10.1016/j.cden.2019.12.003 |
| 6 |
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2017.08.005 |
| 7 |
doi: 10.1007/s00266-017-1028-3 |
| 8 |
doi: 10.1016/j.jobcr.2021.01.001 |
| 9 |
doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2012.01528.x |
| 10 |
邱淑婷, 朱玉佳, 王时敏, 等. 姿势微笑位口唇对称参考平面的数字化构建及初步应用验证[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54 (1): 193- 199.
doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.01.031 |
| 11 |
doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-42533-y |
| 12 |
doi: 10.1196/annals.1280.010 |
| 13 |
|
| 14 |
doi: 10.31729/jnma.7072 |
| 15 |
doi: 10.3390/s20247184 |
| 16 |
doi: 10.1007/s10919-005-0003-x |
| 17 |
doi: 10.3390/s20041199 |
| 18 |
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0244647 |
| 19 |
doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.00202 |
| 20 |
doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000005969 |
| 21 |
|
| 22 |
doi: 10.1007/s10919-012-0139-4 |
| 23 |
doi: 10.4067/S0717-95022019000100232 |
| 24 |
doi: 10.1097/00006534-198901000-00001 |
| 25 |
doi: 10.1093/asj/sjab152 |
| 26 |
|
| 27 |
doi: 10.2319/062617-425.1 |
| [1] | Yujia ZHU, Hua SHEN, Aonan WEN, Zixiang GAO, Qingzhao QIN, Shenyao SHAN, Wenbo LI, Xiangling FU, Yijiao ZHAO, Yong WANG. Deep learning algorithms for intelligent construction of a three-dimensional maxillofacial symmetry reference plane [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2025, 57(1): 113-120. |
| [2] | Shuangyun ZHAO, Siyu ZOU, Xueying LI, Lijuan SHEN, Hong ZHOU. Evaluation of reliability and validity of Chinese version of a short-form of Health Literacy Dental scale (HeLD-14) in the application among parents of preschool children [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 828-832. |
| [3] | QIU Shu-ting,ZHU Yu-jia,WANG Shi-min,WANG Fei-long,YE Hong-qiang,ZHAO Yi-jiao,LIU Yun-song,WANG Yong,ZHOU Yong-sheng. Preliminary clinical application verification of complete digital workflow of design lips symmetry reference plane based on posed smile [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(1): 193-199. |
| [4] | ZHU Yu-jia,ZHAO Yi-jiao,ZHENG Sheng-wen,WEN Ao-nan,FU Xiang-ling,WANG Yong. A method for constructing three-dimensional face symmetry reference plane based on weighted shape analysis algorithm [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(1): 220-226. |
| [5] | Tian-cheng QIU,Xiao-jing LIU,Zhu-lin XUE,Zi-li LI. Evaluation of the reproducibility of non-verbal facial expressions in normal persons using dynamic stereophotogrammetric system [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(6): 1107-1111. |
| [6] | Ning XIAO,Yu-chun SUN,Yi-jiao ZHAO,Yong WANG. A method to evaluate the trueness of reconstructed dental models made with photo-curing 3D printing technologies [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(1): 120-130. |
| [7] | ZHENG Bang, LI Man, WANG Kai-lu, LV Jun. Analysis of the reliability and validity of the Chinese version of Pittsburgh sleep qua-lity index among medical college students [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2016, 48(3): 424-428. |
| [8] | HE Ying, GUO Chuan-Bin, DENG Xu-Liang, WANG Xing, WANG Xiao-Xia. Three-dimensional measurement and facial symmetry analysis for the craniofacial structure of people in North China with normal occlusion [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2015, 47(4): 708-713. |
| [9] | XIONG Yu-Xue, Yang-Hui-Fang, Zhao-Yi-Jiao, WANG Yong. Comparison of two kinds of methods evaluating the degree of facial asymmetry by three-dimensional data [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2015, 47(2): 340-343. |
|
||