Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (6): 1184-1187. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.06.025
Previous Articles Next Articles
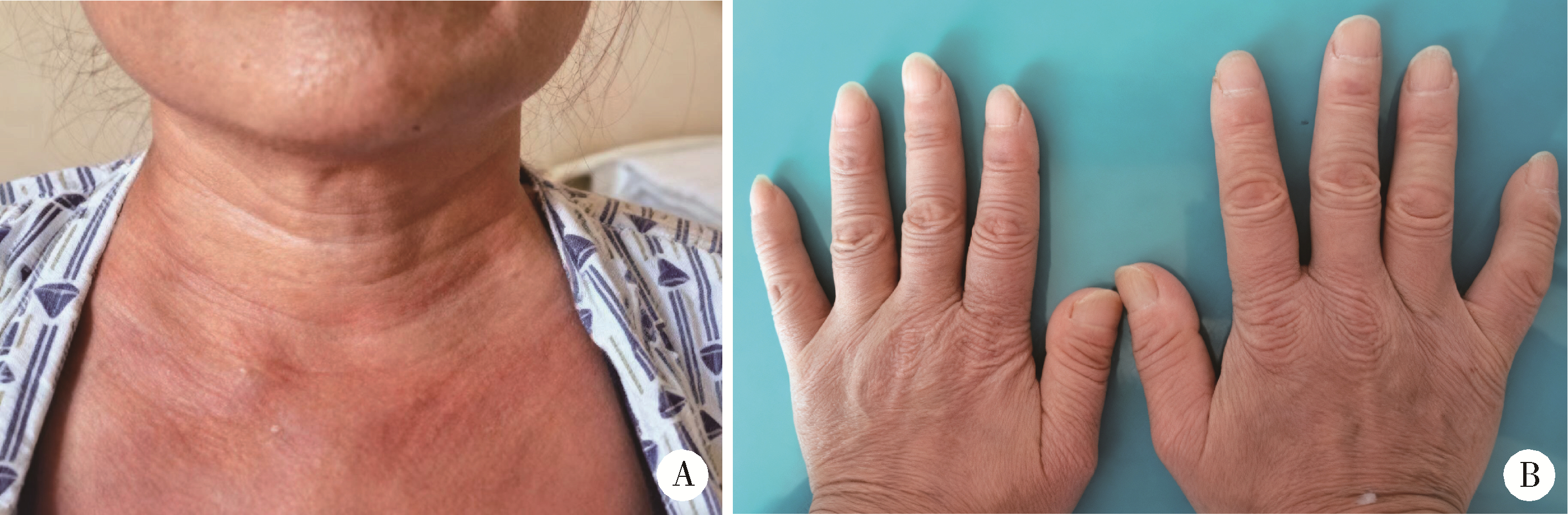
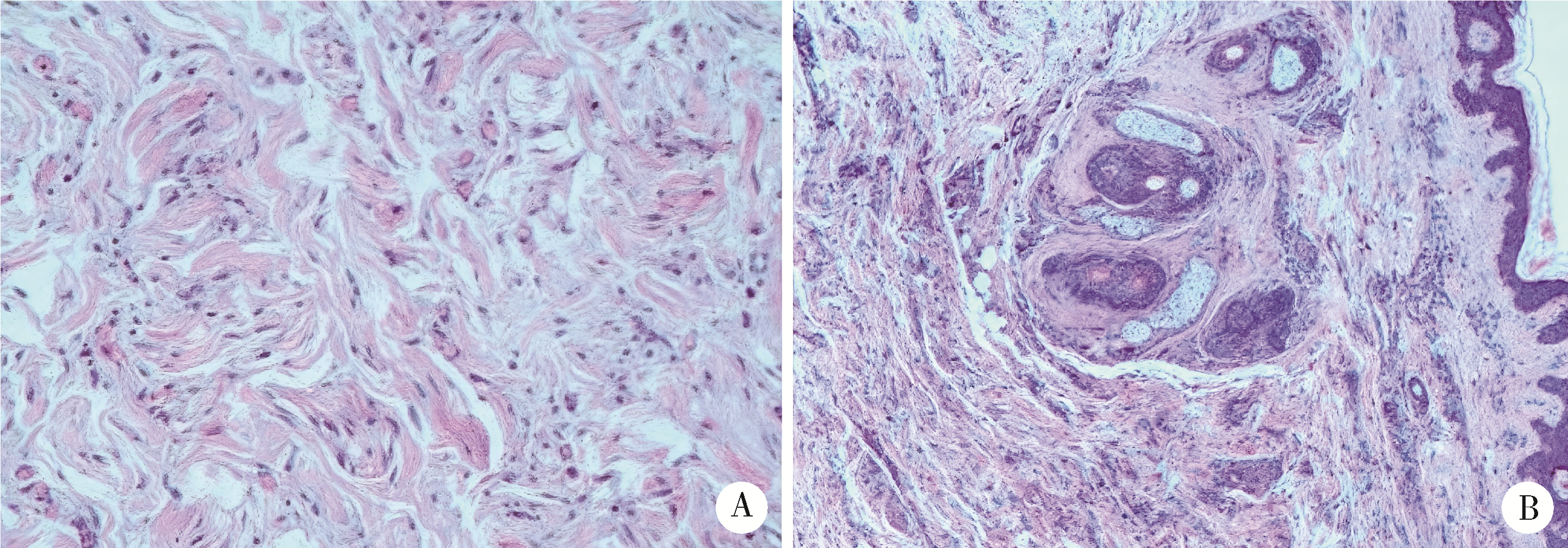
POEMS syndrome misdiagnosed as systemic sclerosis: A case report
Jingyuan LIANG1,2, Xia ZHANG1,*( ), Haihong YAO1
), Haihong YAO1
- 1. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Peking University People's Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
2. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, North China University of Science and Technology Affiliated Hospital, Tang-shan 063000, Hebei, China
CLC Number:
- R733
| 1 |
中华医学会神经病学分会, 中华医学会神经病学分会周围神经病协作组, 中华医学会神经病学分会肌电图与临床神经电生理学组, 等. 中国POEMS综合征周围神经病变诊治专家共识[J]. 中华神经科杂志, 2019, 52 (11): 893- 897.
|
| 2 |
李剑. 我如何诊断和治疗POEMS综合征[J]. 中华血液学杂志, 2019, 40 (5): 368- 371.
|
| 3 |
中国POEMS综合征诊疗专家共识组. POEMS综合征诊疗中国专家共识(2025年)[J]. 中华血液学杂志, 2025, 46 (3): 177- 184.
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
张超, 王先令, 陈予龙, 等. 136例POEMS综合征患者内分泌代谢异常的临床特点回顾性分析[J]. 国际内分泌代谢杂志, 2021, 41 (1): 38- 43.
|
| 6 |
樊慧守, 严文强, 刘佳慧, 等. POEMS综合征患者就诊行为特征及临床误诊漏诊分析[J]. 中国肿瘤临床, 2021, 48 (21): 1120- 1124.
|
| 7 |
doi: 10.1002/ajh.26240 |
| 8 |
邹和建, 朱小霞, 戴生明, 等. 系统性硬化病诊疗规范[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2022, 61 (8): 874- 882.
|
| 9 |
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01692-0 |
| 10 |
doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2013.05.002 |
| 11 |
doi: 10.1111/j.1346-8138.2012.01609.x |
| [1] | Xiandun YUAN, Zhaohua LI, Dan XU, Ting LI, Dan FANG, Rong MU. Pathogenesis and mechanism of serine protease 23 in skin fibrosis of systemic sclerosis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2025, 57(5): 903-910. |
| [2] | Kelin ZHAO, Xue XIA, Naixu SHI, Han ZHOU, Jingwen GAI, Ping LI. Expression and significance of ferroptosis marker 4-HNE in in vitro model of systemic sclerosis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(6): 950-955. |
| [3] | Wei PAN, Yun LI, Junjia LUO, Chun LI, Hua YE, Xue LI, Yuan JIA. COVID-19 vaccines efficacy and infection features in patients with systemic sclerosis: A single-center cohort study [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(6): 1041-1046. |
| [4] | Wen-gen LI,Xiao-dong GU,Rui-qiang WENG,Su-dong LIU,Chao CHEN. Expression and clinical significance of plasma exosomal miR-34-5p and miR-142-3p in systemic sclerosis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1022-1027. |
| [5] | Zhuo-hua LIN,Ru-yi CAI,Yang SUN,Rong MU,Li-gang CUI. Methodology and clinical use of superb microvascular imaging in assessing micro-circulation changes of fingertips in systemic sclerosis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 636-640. |
| [6] | MA Xiang-bo,ZHANG Xue-wu,JIA Ru-lin,GAO Ying,LIU Hong-jiang,LIU Yu-fang,LI Ying-ni. Application of lymphocytes test in peripheral blood of patients with systemic sclerosis during the treatment [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(4): 721-727. |
| [7] | Jing ZHAO,Feng SUN,Yun LI,Xiao-zhen ZHAO,Dan XU,Ying-ni LI,Yu-hui LI,Xiao-lin SUN. Significance of anti-tubulin-α-1C autoantibody in systemic sclerosis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(6): 1009-1013. |
| [8] | Hong-lin ZHU,Qian DU,Wei-lin CHEN,Xiao-xia ZUO,Quan-zhen LI,Si-jia LIU. Altered serum cytokine expression profile in systemic sclerosis and its regulatory mechanisms [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(4): 716-722. |
| [9] | HU Ping, LUO Ying-ying, WU Jing, GAO Lei-li. Analysis of clinical features of 23 patients with POEMS syndrome [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(6): 985-989. |
|
||