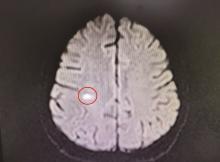
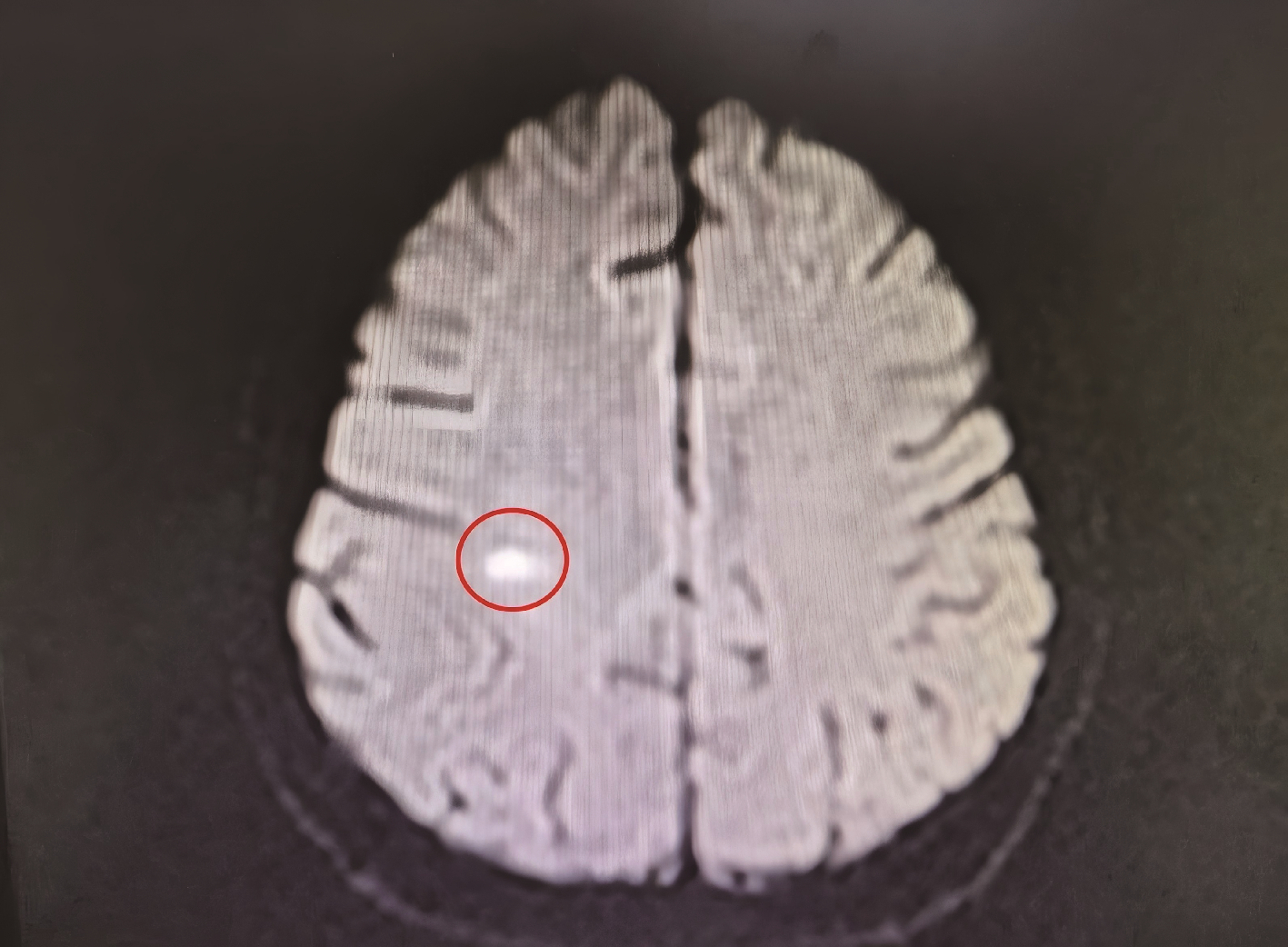
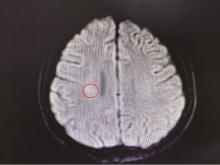
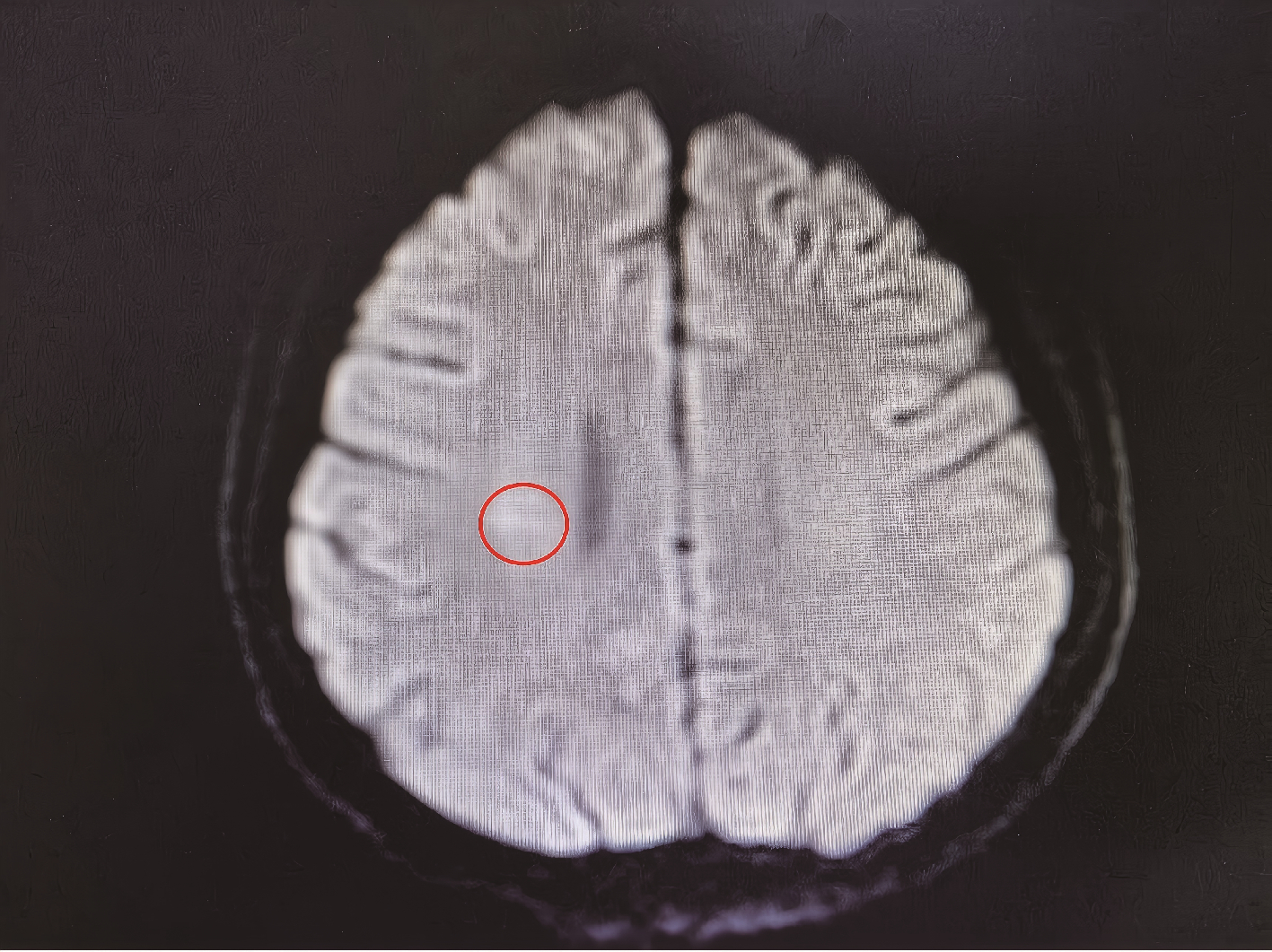
Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (6): 1188-1192. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.06.026
Previous Articles Next Articles
Central nervous system infection mimicking neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus: A case report
Kai ZHAO, Fu'ai LU, Yongfu WANG*( )
)
- Department of Rheumatism and Immunology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Baotou Medical College, Inner Mongolia University of Science and Technology; Inner Mongolia Autoimmunology Key Laboratory, Baotou 014010, Inner Mongolia, China
CLC Number:
- R593.24
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
doi: 10.1097/BOR.0000000000000682 |
| 3 |
doi: 10.1038/s41584-018-0156-8 |
| 4 |
国家皮肤与免疫疾病临床医学研究中心, 中华医学会风湿病学分会, 风湿免疫病学教育部重点实验室, 等. 中国成人中枢神经精神狼疮临床实践专家共识(2024版)[J]. 中华风湿病学杂志, 2024, 28 (9): 613- 625.
|
| 5 |
doi: 10.1186/s12879-020-05327-6 |
| 6 |
doi: 10.1080/1040841X.2021.1911930 |
| 7 |
蒋钟吉, 许智坤, 吴劲松, 等. 深圳单核细胞增生李斯特菌感染10例临床分析[J]. 中国抗生素杂志, 2022, 47 (11): 1202- 1206.
|
| 8 |
doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2018.11.007 |
| 9 |
年李想, 葛沈瑞, 帅垠琦. 系统性红斑狼疮合并李斯特菌脓毒症1例[J]. 临床医学进展, 2024, 14 (4): 718- 723.
|
| 10 |
doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102592 |
| 11 |
罗芷筠, 吴佳佳, 宋优, 等. 伴神经精神系统病变的系统性红斑狼疮相关巨噬细胞活化综合征2例[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55 (6): 1111- 1117.
doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.06.024 |
| [1] | Xinyi LI, Jinxia ZHAO, Rong MU. Impact of aspirin use on pregnancy outcomes in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2025, 57(6): 1074-1080. |
| [2] | Xiaolin WANG, Shaoyi GUO, Dazhao CHEN, Xijie WEN, Yong HUA, Liang ZHANG, Qin ZHANG. A follow-up study on total hip arthroplasty in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus combined with osteonecrosis of femoral head [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2025, 57(6): 1081-1088. |
| [3] | Chun WEI, Yue YANG, Xinju ZHAO, Xu LIU, Yuan JIA. Systemic lupus erythematosus complicated by autoimmune nodopathy: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2025, 57(6): 1174-1179. |
| [4] | Wenqiong WANG, Yuke HOU, Chun LI, Xuewu ZHANG. Predictors of adverse pregnancy outcomes in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2025, 57(3): 599-603. |
| [5] | Hongyan WANG, Xinming LI, Kechi FANG, Huaqun ZHU, Rulin JIA, Jing WANG. Analysis of characteristics related to the disease activity of systemic lupus erythematosus and construction of an evaluation model [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(6): 1017-1022. |
| [6] | Dandan CHEN, Yun LI, Qingyi LU, Xiaohong XIANG, Feng SUN, Yingni LI, Jing ZHAO, Hongyan WANG, Chun LI. Ovarian function in patients of childbearing age with systemic lupus erythematosus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(6): 1023-1028. |
| [7] | Li WANG, Chao GAO, Huanhuan REN, Yanping SHEN, Xiaowei HUANG, Hong YAO, Dandan HAN. Current status and influential factors of self-management ability in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(6): 1029-1035. |
| [8] | Jing CHAI, Yue WANG, Rong MU, Jinxia ZHAO. Systemic lupus erythematosus involving the fornix column leading to hyponatremia: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(6): 1115-1118. |
| [9] | Mingxia WANG, Ling DING, Min WANG, Chanjuan ZOU, Siyu YAN, Yingwen LIANG, Weijia WANG, Shanzhi HE. Safe pregnancy and delivery in a female patient with systemic lupus erythematosus after discontinuation of dual-target chimeric antigen receptor T cells therapy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(6): 1119-1125. |
| [10] | Zhihui WU, Mingzhi HU, Qiaoying ZHAO, Fengfeng LV, Jingying ZHANG, Wei ZHANG, Yongfu WANG, Xiaolin SUN, Hui WANG. Immunomodulatory mechanism of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells modified by miR-125b-5p in systemic lupus erythematosus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 860-867. |
| [11] | Limin REN,Chuchu ZHAO,Yi ZHAO,Huiqiong ZHOU,Liyun ZHANG,Youlian WANG,Lingxun SHEN,Wenqiang FAN,Yang LI,Xiaomei LI,Jibo WANG,Yongjing CHENG,Jiajing PENG,Xiaozhen ZHAO,Miao SHAO,Ru Li. Low disease activity and remission status of systemic lupus erythematosus in a real-world study [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 273-278. |
| [12] | Zhi-jun LUO,Jia-jia WU,You SONG,Chun-li MEI,Rong DU. Systemic lupus erythematosus associated macrophage activation syndrome with neuropsychiatric symptoms: A report of 2 cases [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1111-1117. |
| [13] | Hai-hong YAO,Fan YANG,Su-mei TANG,Xia ZHANG,Jing HE,Yuan JIA. Clinical characteristics and diagnostic indicators of macrophage activation syndrome in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and adult-onset Still's disease [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 966-974. |
| [14] | Xiang-ge ZHAO,Jia-qing LIU,Hui-na HUANG,Zhi-min LU,Zi-ran BAI,Xia LI,Jing-jing QI. Interferon-α mediating the functional damage of CD56dimCD57+natural killer cells in peripheral blood of systemic lupus erythematosuss [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 975-981. |
| [15] | Miao SHAO,Hui-fang GUO,Ling-yan LEI,Qing ZHAO,Yan-jie DING,Jin LIN,Rui WU,Feng YU,Yu-cui LI,Hua-li MIAO,Li-yun ZHANG,Yan DU,Rui-ying JIAO,Li-xia PANG,Li LONG,Zhan-guo LI,Ru LI. A multicenter study on the tolerance of intravenous low-dose cyclophosphamide in systemic lupus erythematosus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1112-1116. |
|
||