1 材料与方法
1.1 材料与设备
1.2 试样分组与制作
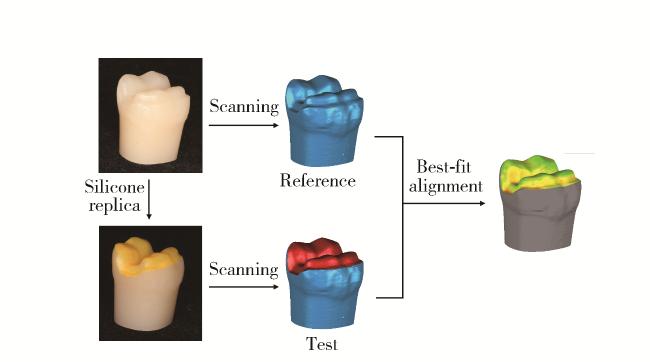
1.3 三维配准方法评价边缘适合性与内部适合性
1.4 统计学方法
2 结果
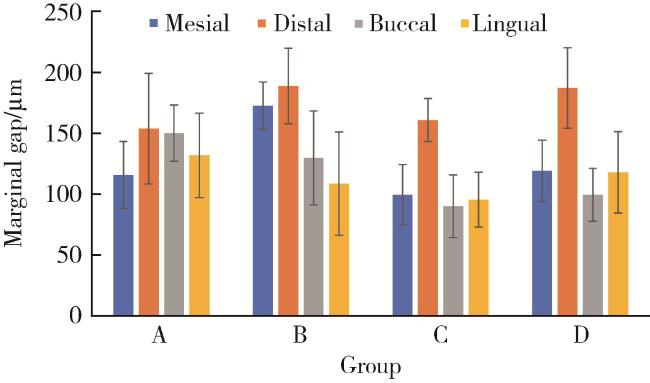
2.1 不同数字印模法制作的高嵌体内部适合性和边缘适合性
表1 各组高嵌体内部及边缘间隙值Table 1 Internal and marginal gap values for each group |
| Group | Method | Material | Internal gap values/μm | Marginal gap values/μm |
| A (n=12) | Direct | Zirconia | 135.54±14.69 | 144.30±20.44 |
| B (n=12) | Direct | Ceramic | 124.16±22.04 | 135.53±23.44 |
| C (n=12) | Indirect | Zirconia | 103.77±13.61 | 104.55±19.02 |
| D (n=12) | Indirect | Ceramic | 108.49±17.83 | 122.78±23.36 |
Data are expressed as $\bar x \pm s$. A,digital impression+zirconia;B,digital impression+ lithium disilicate glass-ceramic;C,conventional impression with model scanner+zirconia;D,conventional impression with model scanner+ lithium disilicate glass-ceramic. |
表2 内部间隙双因素方差分析统计结果Table 2 Two-way ANOVA analysis of internal gap |
| Source | Type Ⅲ sum of squares | df | Mean square | F | P |
| Corrected model | 5 251.241a | 2 | 2 625.621 | 8.717 | 0.001 |
| Intercept | 515 841.350 | 1 | 515 841.350 | 1 712.556 | < 0.001 |
| Method | 5 211.009 | 1 | 5 211.009 | 17.300 | < 0.001 |
| Material | 40.232 | 1 | 40.232 | 0.134 | 0.717 |
a, R2=0.332, adjusted R2=0.294. |
表3 边缘间隙多因素方差分析统计结果Table 3 Three-way ANOVA analysis of marginal gap |
| Source | Type Ⅲ sum of squares | df | Mean square | F | P |
| Corrected model | 150 406.021a | 15 | 10 027.068 | 9.374 | < 0.001 |
| Intercept | 2 532 324.909 | 1 | 2 532 324.909 | 2 367.339 | < 0.001 |
| Method | 13 937.982 | 1 | 13 937.982 | 13.030 | < 0.001 |
| Position | 84 163.215 | 3 | 28 054.405 | 26.227 | < 0.001 |
| Material | 3 819.499 | 1 | 3 819.499 | 3.571 | 0.061 |
| Method×Position | 12 588.477 | 3 | 4 196.159 | 3.923 | 0.010 |
| Method×Material | 3 140.300 | 1 | 3 140.300 | 2.936 | 0.089 |
| Position×Material | 14 902.929 | 3 | 4 967.643 | 4.644 | 0.004 |
| Method×Position×Material | 9 945.476 | 3 | 3 315.159 | 3.099 | 0.029 |
a, R2=0.508, adjusted R2=0.454. |