1 材料与方法
1.1 组织样本
1.2 实验动物
1.3 实验细胞
1.4 主要试剂
1.5 实验方法
1.5.1 细胞培养、分组与转染
1.5.2 免疫组化检测
1.5.3 Western blotting检测
1.5.4 MTS检测
1.5.5 克隆形成实验
1.5.6 划痕实验
1.5.7 Transwell实验
1.5.8 实时荧光定量PCR(real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR,qRT-PCR)检测
表1 引物序列Table 1 Primer sequence |
| Gene | Primer sequences (5′-3′) |
| HDAC2 | Forward:ATGGCGTACAGTCAAGGAGGC |
| Reverse:AAATCAGAACAGCTCAGCAAC | |
| GAPDH | Forward:ATGGGGAAGGTGAAGGTCGG |
| Reverse:TTACTCCTTGGAGGCCATGT |
HDAC, histone deacetylase; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphatedehydrogenase. |
1.5.9 HDAC2活性检测
1.5.10 染色质免疫共沉淀-高通量测序(chromatin immunoprecipitation high-throughput sequencing,ChIP-seq)
1.5.11 体内异种移植实验
1.6 统计学分析
2 结果
2.1 HDAC2、H3K27ac在肝癌中的表达情况与HDAC2表达和肝癌临床病理特征的关系
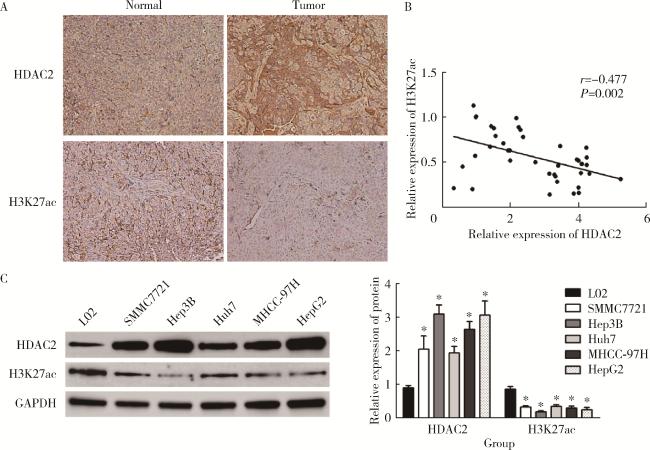
图1 HDAC2、H3K27ac在肝癌中的表达情况Figure 1 Expression of HDAC2 and H3K27ac in hepatocellular carcinoma A, immunohistochemical detection of HDAC2 and H3K27ac expression in hepatocellular carcinoma; B, correlation analysis of HDAC2 and H3K27ac expression in hepatocellular carcinoma; C, detection of HDAC2 and H3K27ac expression in hepatocellular carcinoma cell line by Western blotting. HDAC, histone deacetylase; H3K27ac, histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphatedehydrogenase. *P < 0.05, vs. L02 cell. |
表2 HDAC2表达水平与肝癌患者临床病理特征间的关系Table 2 Relationship between HDAC2 expression level and clinicopathological features of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma |
| Items | Total | HDAC2 expression | χ2 | P | |
| High (n=20) | Low (n=20) | ||||
| Age/years | |||||
| ≥59 | 25 (62.50) | 14 (35.00) | 11 (27.50) | 0.960 | 0.327 |
| <59 | 15 (37.50) | 6 (15.00) | 9 (22.50) | ||
| Gender | |||||
| Male | 21 (52.50) | 13 (32.50) | 8 (20.00) | 2.506 | 0.113 |
| Female | 19 (47.50) | 7 (17.50) | 12 (30.00) | ||
| Tumor size/cm | |||||
| ≥3 | 28 (70.00) | 17 (42.50) | 11 (27.50) | 4.286 | 0.038 |
| <3 | 12 (30.00) | 3 (7.50) | 9 (22.50) | ||
| HBV infection | |||||
| Positive | 30 (75.00) | 19 (47.50) | 11 (27.50) | 8.533 | 0.003 |
| Negative | 10 (25.00) | 1 (2.50) | 9 (22.50) | ||
| Alpha-fetoprotein/(μg/L) | |||||
| ≥400 | 27 (67.50) | 12 (30.00) | 15 (37.50) | 1.026 | 0.311 |
| <400 | 13 (32.50) | 8 (20.00) | 5 (12.50) | ||
| Histologic grade | |||||
| Well and moderate | 25 (62.50) | 10 (25.00) | 15 (37.50) | 2.667 | 0.102 |
| Low | 15 (37.50) | 10 (25.00) | 5 (12.50) | ||
| TNM stage | |||||
| Ⅰ to Ⅱ | 19 (47.50) | 6 (15.00) | 13 (32.50) | 4.912 | 0.027 |
| Ⅲ to Ⅳ | 21 (52.50) | 14 (35.00) | 7 (17.50) | ||
| Portal vein tumor thrombus | |||||
| Yes | 11 (27.50) | 9 (22.50) | 2 (5.00) | 6.144 | 0.013 |
| No | 29 (72.50) | 11 (27.50) | 18 (45.00) | ||
| Cirrhosis | |||||
| Yes | 15 (37.50) | 6 (15.00) | 9 (22.50) | 0.960 | 0.327 |
| No | 25 (62.50) | 14 (35.00) | 11 (27.50) | ||
Data are n(%). HDAC, histone deacetylase; HBV, hepatitis B virus. |
2.2 抑制HDAC2对肝癌细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭的影响
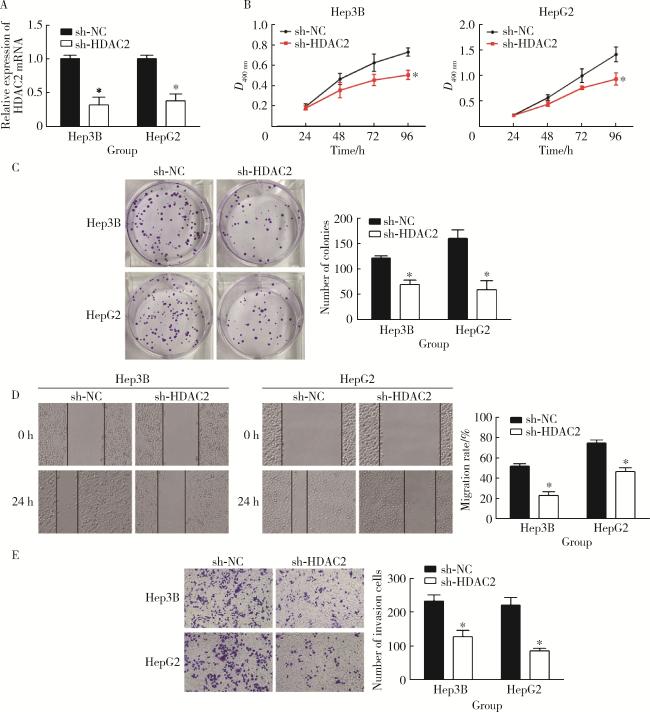
图2 抑制HDAC2对肝癌细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭的影响Figure 2 Effects of inhibition of HDAC2 on proliferation, migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells A, qRT-PCR assay results; B, MTS assay result; C, clone formation experiment results; D, wound scratch assay results; E, transwell assay results. HDAC, histone deacetylase; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphatedehydrogenase. *P < 0.05, vs. sh-NC group. |
2.3 HDAC2介导H3K27ac修饰
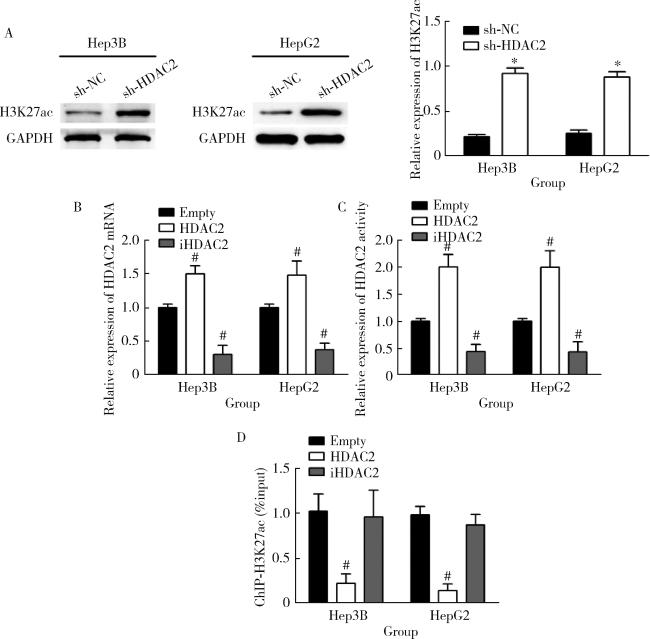
图3 HDAC2介导H3K27ac修饰Figure 3 Acetylation of H3K27 mediated by HDAC2 A, Western blotting assay result; B, qRT-PCR assay results; C, result of HDAC2 activity detection; D, ChIP-seq assay results. HDAC, histone deacetylase; H3K27ac, histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphatedehydrogenase. *P < 0.05, vs. sh-NC group. # P < 0.05, vs. empty group. |
2.4 HDAC2介导H3K27ac修饰启动PI3K/PTEN/AKT/mTOR信号通路促进肝癌细胞增殖、迁移、侵袭
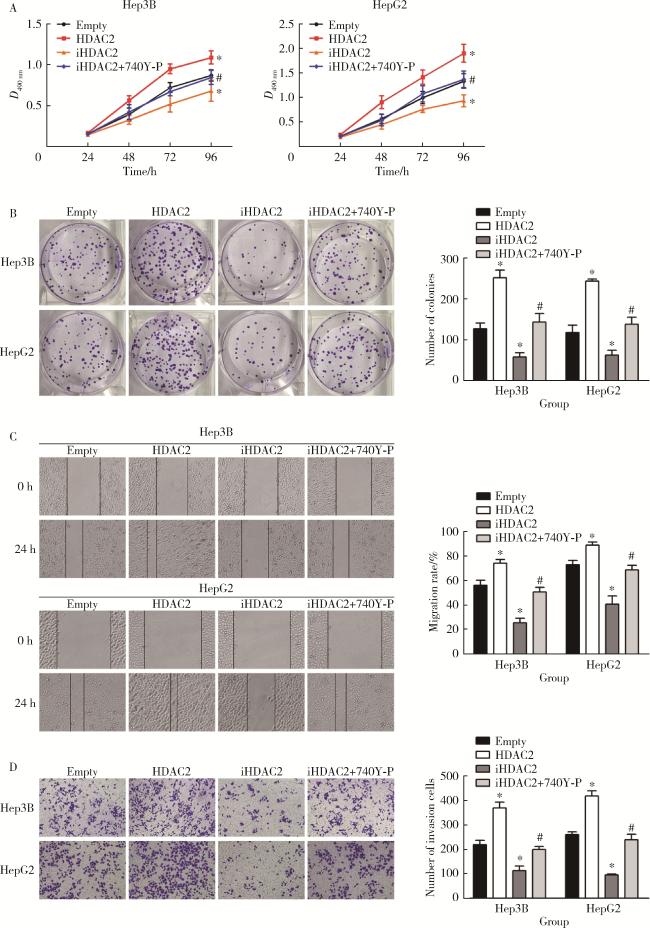
图4 体外细胞实验验证HDAC2介导H3K27ac修饰促进肝癌细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭Figure 4 In vitro cell experiments show that HDAC2-mediated H3K27 acetylation promotes the proliferation, migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells A, MTS assay result; B, clone formation experiment results; C, wound scratch assay results; D, transwell assay results. HDAC, histone deacetylase; H3K27ac, histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphatedehydrogenase. *P < 0.05, vs. empty group. #P < 0.05, vs. iHDAC2 group. |
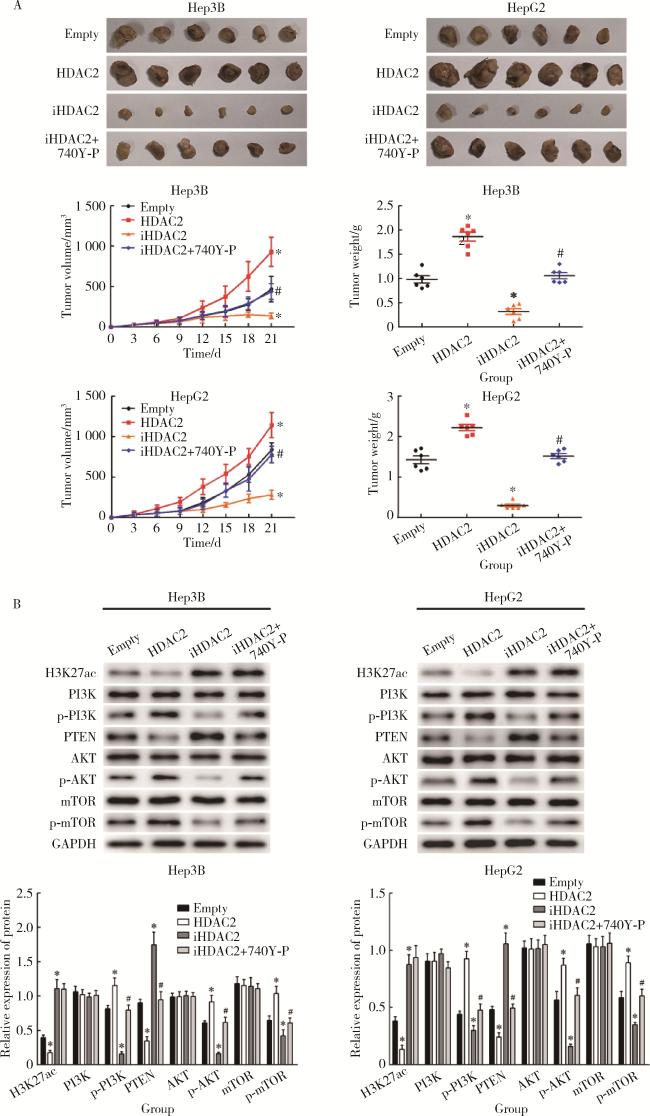
图5 体内细胞实验验证HDAC2介导H3K27ac修饰启动PI3K/PTEN/AKT/mTOR信号通路增强肝癌细胞成瘤能力Figure 5 In vivo cell experiments show that HDAC2-mediated H3K27 acetylation initiates PI3K/PTEN/AKT/mTOR signal pathway to enhance the tumorigenicity of hepatocellular carcinoma cells A, experimental results of xenotransplantation in vivo; B, Western blotting assay results of transplanted tumor. HDAC, histone deacetylase; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphatedehydrogenase. H3K27ac, histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation; PI3K/PTEN/AKT/mTOR, phosphoinositide 3-kinases/phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome ten/protein kinase B/mammalian target of rapamycin. *P < 0.05, vs. empty group. #P < 0.05, vs. iHDAC2 group. |
2.5 HDAC2介导H3K27ac修饰促进肝癌进展的作用机制
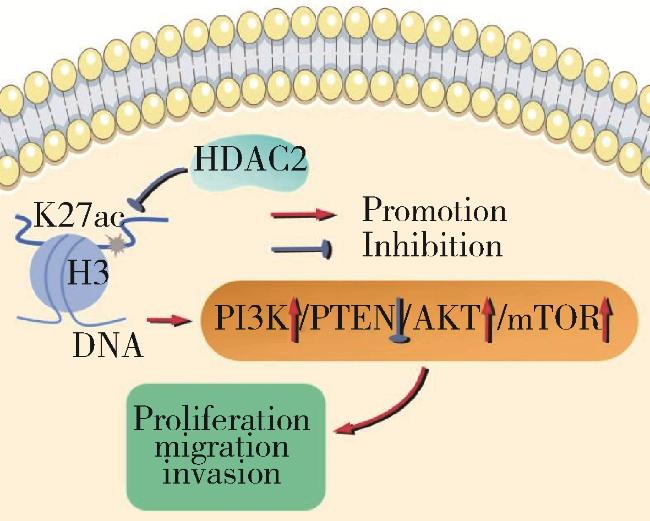
图6 HDAC2介导H3K27ac修饰促进肝癌进展的作用机制Figure 6 Specific mechanism of HDAC2-mediated H3K27 acetylation modification in promoting the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma HDAC, histone deacetylase; H3K27ac, histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation; PI3K/PTEN/AKT/mTOR, phosphoinositide 3-kinases/phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome ten/protein kinase B/mammalian target of rapamycin. |